Incarcerated persons, just like any other citizen, are bound by the legal obligations of the tax system. They are required to file taxes if they have any taxable income. This obligation doesn't disappear upon incarceration. In many ways, the tax responsibilities of an incarcerated individual mirror those of any other citizen. The sources of taxable income for incarcerated persons can vary. Common forms include wages earned in prison, usually for jobs that help in prison maintenance or manufacturing. However, other forms of income, such as interest from savings accounts, dividends from investments, or even income from ventures prior to incarceration, are also taxable. These incomes should be reported accurately to avoid any complications. Obtaining the necessary documentation for filing taxes can be a challenging task for someone in prison. Incarcerated individuals might need to coordinate with family members or prison officials to get their W-2s, 1099s, and other income-related documents. Some prisons may have protocols in place to assist inmates with this process, especially if they earned wages within the correctional facility. Based on the type and amount of income, incarcerated persons would need to select the appropriate tax form. For most, the 1040 form will suffice. However, in cases with more straightforward financial situations, simpler forms like 1040A or 1040EZ might be applicable. Tax laws can be intricate and challenging to navigate. For incarcerated individuals, understanding these nuances can be even more daunting. Fortunately, some prisons offer programs or workshops on tax filing. Additionally, an incarcerated individual can seek help from a tax professional or enlist a family member's assistance. It's crucial to ensure that the chosen method complies with prison rules and guidelines. Filling out a tax form demands attention to detail. Each section should be completed based on the instructions, ensuring that income is reported accurately and deductions are applied where necessary. For those who were primary caregivers before their incarceration, claiming dependents can bring about some tax benefits. However, it's crucial to understand the rules around this. Typically, to claim someone as a dependent, you need to have provided over half of their support. Being incarcerated can complicate this, but if the criteria are met, the benefits remain valid. There are specific tax breaks, credits, or deductions that individuals typically claim. However, incarceration might influence the eligibility for some of these. It's essential to research and determine which tax benefits are accessible and which might be forfeited due to one's incarcerated status. Sending tax returns from prison requires understanding and following the prison mail protocols. Often, incarcerated individuals will need to pass their filled forms to the prison officials for mailing. It's crucial to ensure everything is correctly addressed and sent well before the tax deadline to avoid late filing penalties. While many prefer e-filing due to its convenience, this method might present challenges for someone in prison. Access to computers or the internet is limited. However, with the assistance of a trusted family member or friend on the outside, e-filing can be a viable option. If taxes are owed, arrangements need to be made for payment. This could involve transferring money from a prison account or having a family member make the payment. Conversely, if a refund is due, the incarcerated individual needs to designate an account for the deposit or have a check mailed to a trusted address. With restricted internet access and limited resources, staying updated on tax laws can be tricky. However, through prison libraries or assistance from family members, one can gather the necessary information. Some prisons might even provide informational sessions or pamphlets on the topic. Having someone file on behalf of an incarcerated person can be immensely beneficial. This representative could be a professional tax preparer or a trusted family member. They can ensure accuracy and timely submission and act as a liaison between the taxpayer and the IRS if needed. Incarcerated individuals, like any other vulnerable group, can be targeted for scams. It's vital to be cautious, especially if someone offers tax filing services unsolicited. Ensuring transparency, using reputable services, and double-checking all information can prevent potential fraud. Ignoring tax obligations can lead to hefty penalties and accruing interest. Over time, these can compound, leading to significant debts that will need to be addressed upon release. Beyond the financial penalties, failing to file or inaccurately filing taxes can result in legal consequences and added complications upon release. Staying compliant not only avoids these issues but also helps in reintegration into society post-incarceration. Incarcerated individuals, like all citizens, have tax obligations that persist even during imprisonment. These responsibilities encompass reporting various income sources, from prison wages to external investments. Although acquiring necessary documentation and understanding intricate tax laws can pose challenges, it's imperative for the incarcerated to navigate this with diligence. Prisons may provide resources, or external assistance from family or tax professionals can be sought. Despite the hurdles, such as limited access to updated information or potential scams, fulfilling these duties is essential. Neglecting tax obligations can lead to severe financial and legal consequences, exacerbating difficulties upon reentry into society. On the flip side, timely and accurate tax filing can pave the way for a smoother transition post-incarceration, emphasizing the significance of being informed and proactive in this domain.Filing Taxes While Incarcerated Overview
Eligibility for Filing
Types of Taxable Income
Preparation for Filing Taxes While Incarcerated
Gather Documentation
Tax Forms
Seeking Assistance
Steps to File Taxes While Incarcerated
Filling Out the Form
Claiming Dependents
Special Considerations

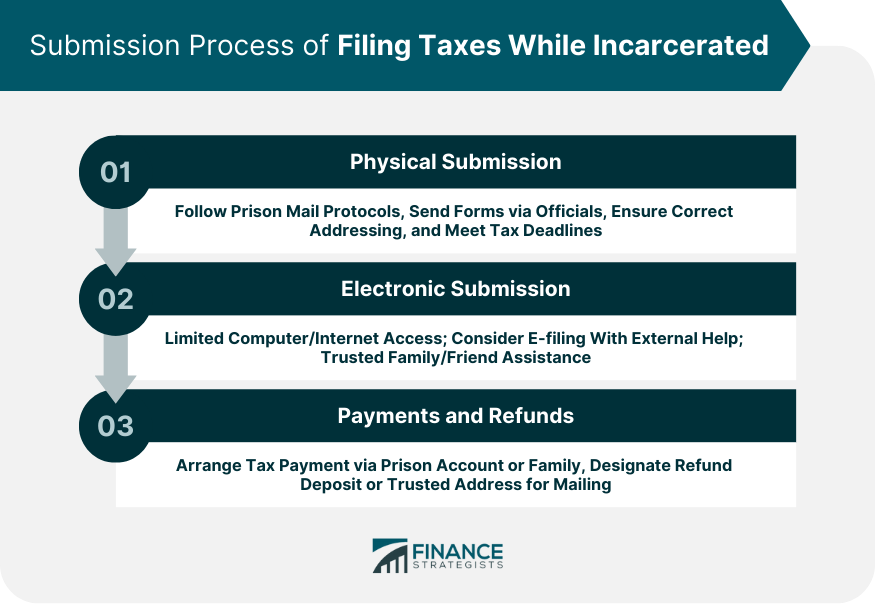
Submission Process of Filing Taxes While Incarcerated
Physical Submission
Electronic Submission
Payments and Refunds
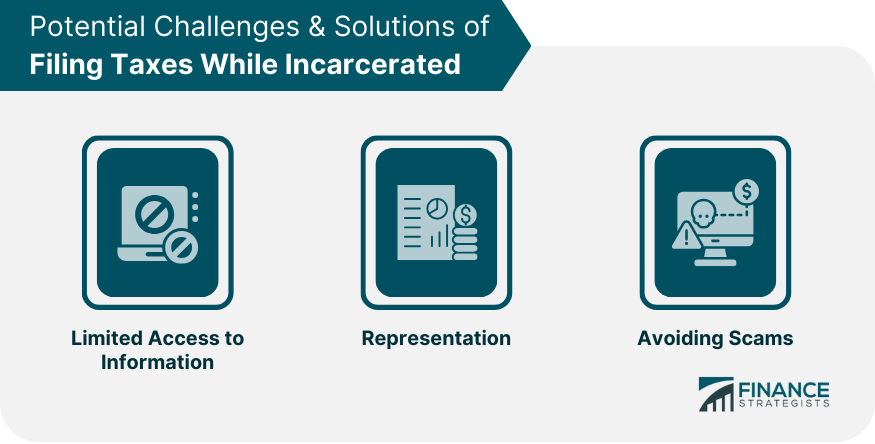
Potential Challenges & Solutions of Filing Taxes While Incarcerated
Limited Access to Information
Representation
Avoiding Scams
Consequences of Not Filing Taxes While Incarcerated
Penalties & Interest
Complications Upon Release
Conclusion
How Does an Incarcerated Person File Taxes? FAQs
Yes, incarcerated individuals can claim dependents if they were primary caregivers before incarceration and provided over half of their dependent's support. However, the specific circumstances and rules should be thoroughly reviewed to ensure eligibility.
They can coordinate with family members or prison officials to gather these documents. Some prisons may assist inmates in obtaining income documents, especially if the wages were earned within the facility.
Direct e-filing might be challenging due to limited access to computers and the internet in prison. However, with the help of a trusted family member or friend outside, e-filing can be facilitated on their behalf.
They may face financial penalties and accruing interest on owed taxes. Over time, this can lead to significant debts. Additionally, there could be legal repercussions and added complications upon their release.
While incarcerated individuals can claim many standard tax breaks or credits, there might be some influenced by their incarceration status. It's essential to research specific tax benefits to determine eligibility based on one's incarcerated status.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











