Every job comes with its own set of responsibilities, and babysitting is no exception. Beyond the primary role of caring for children, babysitters must also navigate the intricate realm of taxation. With income coming in, it's essential to understand where babysitting fits within the broader tax landscape. Often, babysitters might overlook their position as earners, especially if it's a part-time gig or a temporary job during summer. However, the IRS sees any income as taxable, making it imperative for babysitters to know their tax obligations, irrespective of the amount they earn or the duration they work. Knowledge is key in navigating taxes. Timely and accurate filing prevents issues like penalties or audits. For babysitters, understanding tax duties signifies professionalism. Grasping the essentials lets babysitters manage taxes efficiently, building trust with employing families. At the heart of tax considerations lies the distinction between being an independent contractor or an employee. Most babysitters fall under the independent contractor category, meaning they're responsible for managing and paying their own taxes without withholdings by the parents. However, in some instances, a babysitter might be considered an employee, especially if a family dictates strict work hours, provides regular wages, or offers benefits. This distinction is crucial as it directly impacts how a babysitter will file and pay taxes. For independent contractors, the flexibility and freedom come with the added responsibility of managing tax obligations. This includes paying self-employment tax and possibly making quarterly tax payments. This structure contrasts with employees, whose taxes are often withheld from their pay, simplifying their tax filing process. On the flip side, being an employee means babysitters might have access to benefits such as health insurance or paid leave. The trade-off between autonomy and added benefits, along with varied tax structures, makes it essential for babysitters to clearly understand their employment status. Hourly Rates: It's an agreed-upon rate for every hour of service provided. It's essential for babysitters to clearly communicate and document their hourly rate with parents or guardians to avoid discrepancies. Bonuses: Often given during holidays or special occasions, bonuses are additional payments on top of the regular fees. They might be given as a token of appreciation or reward for consistent service throughout the year. Tips: Not always common, but tips are extra payments parents or guardians might give for outstanding service or on special occasions. It's crucial for babysitters to note any tips received, as they also count towards taxable income. Regardless of the income type, maintaining meticulous records is crucial. Whether it's an electronic transfer, check, or cash, every payment needs documentation for accurate tax reporting. For tax purposes, it's not just about how much you earn, but what constitutes taxable income. While the money received for services is undoubtedly taxable, certain gifts or reimbursements might not be. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate tax filings. For instance, if parents reimburse babysitters for buying craft supplies for the kids, this isn't income but a reimbursement. However, if they give a lump sum without specifying its purpose, then it typically counts as taxable income. Hence, clarity in financial transactions and maintaining clear records become paramount. In the age of technology, tracking earnings has never been easier. From specialized apps to basic spreadsheets, babysitters have a plethora of tools at their disposal to keep tabs on their income. Such documentation not only aids during tax season but also helps in budgeting and financial planning. While digital tools offer convenience, traditional methods like ledger books or simple diary entries still hold value. The key is consistency. By recording every payment, no matter how trivial it might seem, babysitters ensure they have a complete record of their earnings. Babysitting, like any profession, comes with its set of expenses. Some of these, if solely for work purposes, can be tax-deductible. For instance, toys or games bought specifically for the children being cared for can be considered a business expense. Similarly, if a babysitter travels to different locations for work, transportation costs might be deductible. However, it's essential to keep personal and professional expenses separate. Retaining all receipts and making notes on their specific purposes can prove invaluable when identifying valid deductions. The saying "the devil is in the details" holds especially true for taxes. While claiming deductions can reduce taxable income, these claims need validation. This is where receipts come into play. They serve as proof of expenditure, ensuring babysitters have the necessary evidence if questions arise. Though it might seem cumbersome, the practice of retaining receipts is a small effort compared to the potential challenges of not having them. Digital scans or physical copies, whichever method chosen, the goal is to have a comprehensive and accessible record of all transactions related to babysitting. Often referred to as the "U.S. Individual Income Tax Return", Form 1040 is used by all taxpayers. For independent contractor babysitters, it serves as the main form where they report their earnings, as well as any deductions they're eligible for. Familiarizing oneself with Form 1040 is essential, as it's the foundational form for individual tax filing. Attached to Form 1040, Schedule C is specifically for those earning income as a sole proprietor or independent contractor. On this form, babysitters detail their income and deductible expenses. Accurately completing Schedule C is key, as it can significantly impact the total tax owed or refund due. Not explicitly mentioned but important, Form SE is for those earning above a certain amount as an independent contractor. It's used to calculate and report self-employment taxes, which cover Medicare and Social Security. Babysitters should be aware of this form, especially if their earnings are substantial, to ensure compliance with self-employment tax obligations. Reporting income accurately to the IRS is paramount. For those classified as independent contractors, income and deductible expenses are typically detailed on Schedule C, which is attached to Form 1040. If a babysitter is an employee, they should receive a W-2 from their employer, and their wages are reported as regular income. Reporting may seem straightforward, but it's always wise to double-check all entries for accuracy. This not only ensures compliance with tax laws but also helps in securing any refunds that might be due. For many independent contractor babysitters, the self-employment tax is an additional consideration. Covering Medicare and Social Security, this tax becomes relevant when net earnings exceed a certain threshold. Filing Schedule SE with Form 1040 becomes necessary in such cases. Understanding the nuances of the self-employment tax can be tricky. However, with proper research or consultation, babysitters can navigate this aspect of taxation efficiently, ensuring they meet all obligations and avail of any potential deductions. While babysitters themselves can't claim the Child and Dependent Care Credit, the families employing them can. Being aware of this credit can be a valuable service to families, as it allows them to deduct a portion of their babysitting expenses. By being well-informed about such tax credits, babysitters can not only assist the families they work for but also solidify their professional relationships with them. It showcases their commitment to the job and their consideration for the family's financial well-being. The Earned Income Tax Credit is a potential boon for working individuals with low to moderate income. Part-time babysitters or those just starting might find themselves eligible for this credit. If applicable, the EITC can significantly reduce owed taxes and might even lead to a refund. However, there are specific criteria to meet for the EITC. Babysitters should familiarize themselves with these requirements, ensuring they claim the credit if they qualify, and avoid it if they don't. Deductions can play a pivotal role in reducing a babysitter's tax liability. For instance, if a babysitter has a dedicated space in their home for work-related activities, they might qualify for a home office deduction. Similarly, courses or certifications taken to enhance babysitting skills, like first aid or child psychology classes, can also be deductible. Being proactive in identifying potential deductions ensures babysitters make the most of tax-saving opportunities. Whether it's setting aside a workspace at home or investing in professional development, such expenses can bear fruit come tax season. Tax laws are intricate, often making them a challenge to navigate. In scenarios where a babysitter's income is substantial, or they have multiple sources of income, or they're unsure about eligible deductions, consulting a tax professional can be a wise decision. Such professionals provide guidance tailored to individual situations, ensuring compliance with tax laws while also maximizing potential savings. Their expertise can help babysitters avoid pitfalls and provide peace of mind. In today's digital era, several tax preparation software options cater specifically to the needs of self-employed individuals, including babysitters. These tools simplify the tax filing process, provide prompts for potential deductions, and ensure adherence to the latest tax laws. While there's a cost associated with most premium tax software, the potential benefits often outweigh the expense. The streamlined process, guided inputs, and the assurance of accuracy make them a valuable tool for babysitters venturing into the world of taxation. Navigating taxation as a babysitter requires a holistic understanding of one's employment status, income sources, and potential deductions. While babysitting may seem straightforward, its financial implications, particularly in the context of taxes, are multifaceted. From distinguishing between an independent contractor and an employee to the meticulous documentation of earnings and expenses, every detail matters. Utilizing available deductions and credits, like the EITC, can significantly ease tax burdens. However, the labyrinthine nature of tax codes often necessitates expert guidance. Fortunately, the digital age offers babysitters tax preparation software tailored to their needs. But in complex scenarios, professional consultation remains invaluable. In essence, to embrace the babysitting profession fully, one must not only care for children but also diligently attend to tax responsibilities. This fosters trust with employers and ensures compliance with the IRS.Role of a Babysitter in the Tax Landscape
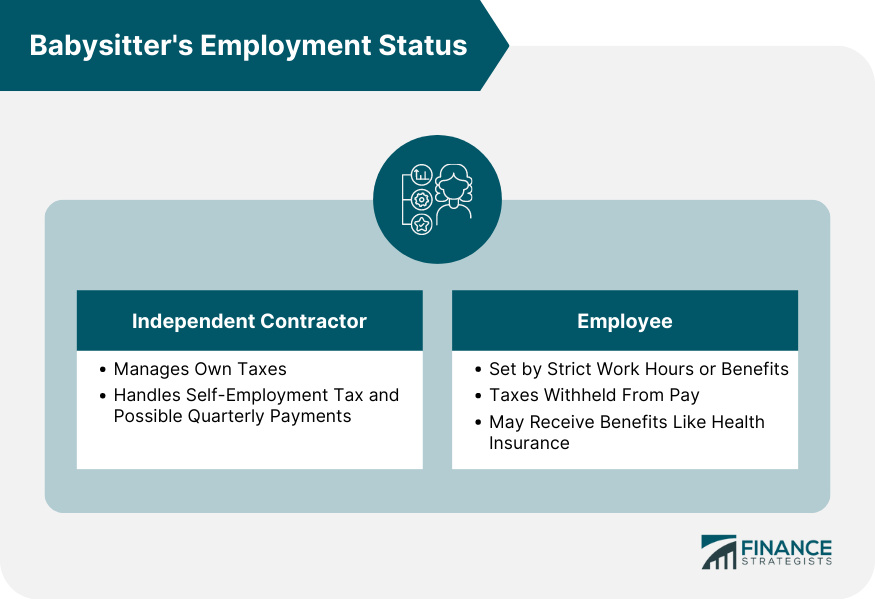
Babysitter's Employment Status
Babysitter as an Independent Contractor vs Employee
How a Babysitter's Employment Status Influences Tax Obligations
Babysitter's Taxable Income
Income Sources for a Babysitter
Determining What Counts as Taxable Income
Documenting Income and Expenses as a Babysitter
Tools and Methods for Babysitters to Track Earnings
Deductible Expenses Specific to Babysitting
Importance of Keeping Receipts and Records
Tax Filing Procedures for Babysitters
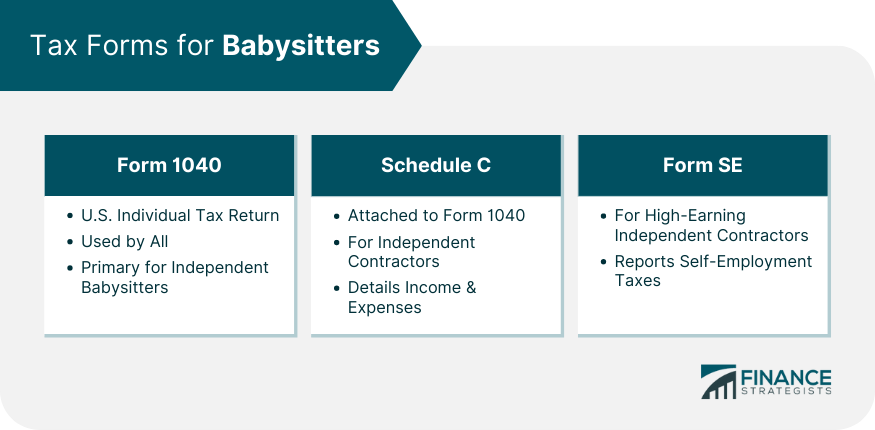
Tax Forms for Babysitters
Form 1040
Schedule C
Form SE (Self-Employment Tax)
How Babysitters Should Report Their Income
Navigating Self-Employment Tax for Babysitters Using Form SE
Tax Credits and Deductions for Babysitters
Utilizing Child and Dependent Care Credit as a Babysitter
Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) Considerations for Babysitters
Other Potential Deductions
Seeking Professional Tax Advice as a Babysitter
Situations Where Babysitters Should Consult Tax Professionals
Benefits of Tax Preparation Software Tailored for Babysitters
Bottom Line
How to File Taxes as a Babysitter FAQs
Most babysitters are independent contractors, but if a family sets strict hours or provides benefits, you might be an employee.
All earnings, including hourly rates, bonuses, and tips, are considered taxable income for babysitters.
Babysitters can use digital apps, spreadsheets, or traditional ledger books to consistently record earnings and work-related expenses.
Independent contractor babysitters typically use Form 1040 and Schedule C, while employee babysitters will receive a W-2.
Yes, babysitters can deduct expenses like toys, games, transportation, home office use, and costs for continued learning and certifications.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











