A 1031 exchange, named after Section 1031 of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code, allows real estate investors to defer capital gains tax by reinvesting the proceeds from the sale of a business or investment property into another 'like-kind' property. When it comes to foreign properties, the same principle applies. However, a critical point to remember is that properties must be within the same country to qualify as 'like-kind.' In other words, U.S. properties can only be exchanged for other U.S. properties, and foreign properties for other foreign properties. Investors must adhere to specific timelines: identifying the replacement property within 45 days of the sale and acquiring it within 180 days. Although the process can be complex, it allows for significant tax advantages and potential portfolio diversification. The process of conducting a 1031 exchange with foreign properties generally follows the same timeline and rules as a domestic 1031 exchange. However, added complexities due to international real estate laws and foreign taxation may come into play. Once the original property is sold, the exchanger has 45 days to identify potential replacement properties. This is known as the "Identification Period". The potential replacement properties must be clearly described in a written document and signed by the exchanger, then delivered to a person involved in the exchange like the seller of the replacement property or the qualified intermediary. The "Exchange Period" is the period within which the person selling the relinquished property must receive the replacement property. It ends at the earlier of 180 days after the date on which the person transfers the property relinquished or the due date for the person's tax return for the taxable year in which the transfer of the relinquished property occurs. 1031 exchange provides a significant opportunity to defer capital gains taxes. An integral part of this process is the Qualified Intermediary (QI), whose role is essential for a successful transaction. A Qualified Intermediary, also known as an Exchange Facilitator or Accommodator, is an independent third party who facilitates tax-deferred exchanges according to Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code. Their primary role is to ensure the exchange transaction adheres to the necessary regulations, providing a legal and seamless process for the investor. The QI has a multitude of duties. They start by preparing the necessary legal documents required for the exchange agreement. This includes the Exchange Agreement itself, assignment agreements, and notices to all parties involved. Once the relinquished property is sold, the QI holds the sales proceeds to avoid "constructive receipt" by the investor, a situation that would disqualify the exchange under IRS rules. The QI's role as the custodian of the funds is a critical element in preserving the integrity of the 1031 exchange process. After the investor identifies the replacement property within the required 45-day period, the QI transfers the funds to the seller of the replacement property or their agent. The QI effectively "purchases" the property on behalf of the investor and transfers it to the investor to complete the exchange. The QI should possess robust knowledge of the 1031 exchange process and related tax laws. They should have substantial experience in managing exchanges and dealing with potential issues that could arise. Inquire about their track record and seek out references from past clients. The financial stability of the QI is paramount, as they will be holding and managing your funds during the transaction. Look for a QI that uses a federally or state-chartered bank and ask if the funds will be held in a segregated, insured account. A reputable QI should maintain high ethical and professional standards. Check to see if the QI is a member of industry organizations like the Federation of Exchange Accommodators, which requires members to adhere to a strict code of ethics. Be sure to understand the QI's fee structure upfront. Fees can vary widely, so it's important to know what services are included and if any additional fees may be incurred. While QIs do not give tax or legal advice, having access to this expertise can be valuable. Some QIs have attorneys and tax experts on staff or on call, which can be beneficial in complex transactions. While the process can be complex, conducting a 1031 exchange with foreign properties also brings several benefits. The most apparent benefit of a 1031 exchange is the ability to defer capital gains tax. By reinvesting the proceeds from the sale of a property into a like-kind property, investors can avoid a significant tax burden. This frees up more capital for investment into the replacement property. When conducted with foreign properties, a 1031 exchange also allows investors to diversify their real estate portfolio internationally. This can provide exposure to new markets and economic dynamics, spreading risk, and potentially increasing returns. Despite the benefits, investors must also navigate a series of challenges when considering a 1031 exchange with foreign properties. While a 1031 exchange can defer taxes in the U.S., the tax laws of the foreign country where the replacement property is located will also apply. These laws vary greatly and may impose different types of taxes on real estate transactions, potentially diminishing the benefits of the exchange. Investing in foreign real estate requires a deep understanding of the local market. Factors such as property values, rental demand, and economic stability can all impact the success of your investment. Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can also affect the value of your investment. If the U.S. dollar weakens against the foreign currency, your property may lose value, and vice versa. A 1031 exchange with foreign properties offers significant benefits, including tax deferral and diversification of an investment portfolio. It allows investors to swap 'like-kind' properties while deferring capital gains tax, albeit with the constraint that properties must be within the same country. A key component of a successful exchange is the role of a Qualified Intermediary (QI), who facilitates the process by holding the proceeds from the property sale, purchasing the replacement property, and ensuring adherence to legal regulations. While considering a QI, factors such as their experience, financial stability, ethical standards, fee structure, and access to legal and tax counsel should guide your decision. However, challenges exist in 1031 exchanges with foreign properties, such as understanding the foreign market, tax implications in the foreign country, and exchange rate risks, all of which require thorough consideration and planning.1031 Exchange With Foreign Properties: Overview
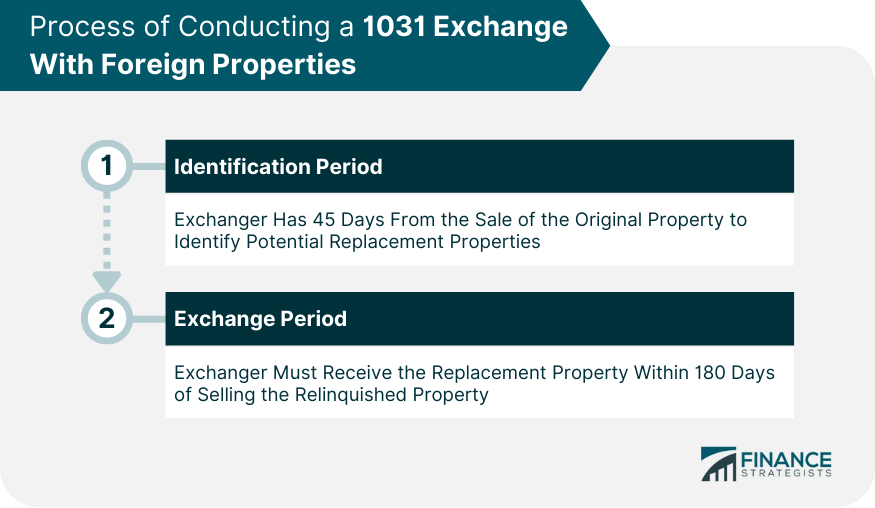
Process of Conducting a 1031 Exchange With Foreign Properties
Identification Period
Exchange Period
Role of a Qualified Intermediary
Responsibilities of a Qualified Intermediary
Criteria for Choosing a Qualified Intermediary
Experience and Knowledge
Financial Stability and Security
Professional Ethics and Standards
Fee Structure
Access to Legal and Tax Counsel
Benefits of a 1031 Exchange With Foreign Properties
Tax Deferral Benefits
Diversification of Investment Portfolio
Potential Challenges in a 1031 Exchange With Foreign Properties
Tax Implications in Foreign Countries
Understanding Foreign Real Estate Markets
Possible Exchange Rate Risks

Conclusion
1031 Exchange With Foreign Properties FAQs
A 1031 Exchange with foreign properties involves selling a foreign investment property and replacing it with another foreign property of 'like-kind,' allowing the investor to defer capital gains tax.
U.S. investors who own business or investment properties overseas can benefit from a 1031 exchange. It helps in deferring capital gains tax and provides an opportunity to diversify the investment portfolio internationally.
There are two critical timeline requirements in a 1031 exchange. Firstly, the investor has 45 days from the date of selling the relinquished property to identify potential replacement properties. Secondly, the purchase of the replacement property must be completed within 180 days of the sale of the relinquished property.
No, according to IRS rules, a U.S. property cannot be exchanged for a foreign property and vice versa in a 1031 exchange. Both the relinquished property and the replacement property must be located in the same country.
Challenges may include understanding the foreign real estate market, dealing with tax implications in foreign countries, and handling potential exchange rate risks. It's crucial to seek advice from experts familiar with the property laws and taxes in the country of investment.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











