Ad valorem tax is a type of tax that is based on the assessed value of an item, such as real estate or personal property. The Latin term "ad valorem" translates to "according to value," reflecting how the tax is applied. This tax type is typically expressed as a percentage of the item's value. The concept of ad valorem tax dates back to ancient civilizations, where taxes were levied based on the value of goods or property. It was a way for governments to generate revenue for public services. As societies evolved, so did the application and calculation of ad valorem tax, yet its core principle remains. Ad valorem taxes serve a significant purpose in maintaining public infrastructure and services. They fund schools, roads, police departments, and various other community services, contributing to the overall economic health of a region. The ad valorem principle is simple: the tax paid is proportional to the value of the item. It ensures that those with more valuable property pay more in taxes, establishing a sense of equity in tax contribution. Ad valorem tax is typically assessed based on the current market value of the item. Therefore, as market conditions fluctuate, so can the amount of ad valorem tax paid. Unlike ad valorem tax, specific tax is a fixed amount, regardless of the item's value. Ad valorem tax, on the other hand, varies with the item's value, thus providing a more flexible and equitable approach to taxation. This is the most common type of ad valorem tax. It is levied on the value of real property, including land and buildings. The rates and methods of assessment vary by jurisdiction. Ad valorem taxes can be applied to personal property, such as vehicles, boats, and aircraft. The tax amount is typically calculated based on the current market value of these items. Vehicle ad valorem tax is an annual tax based on the vehicle's value. It is usually included in the registration fee and varies from state to state. Ad valorem tax is often applied to imported and exported goods, contributing to a country's revenue. This tax type helps to regulate trade and protect domestic industries. Taxable value is the assessed value of the property or item upon which the ad valorem tax is based. It's determined through an appraisal process and may not necessarily be the same as the market value. Calculating ad valorem tax involves determining the taxable value of the item, applying the appropriate tax rate, and then calculating the tax amount. Local or state tax authorities usually provide the tax rate. Appraisals are vital in determining the taxable value for ad valorem tax. An appraiser assesses the property to estimate its market value, which is then used as the basis for taxation. Ad valorem taxes are calculated based on the value of a property, ensuring those who own more valuable properties pay more tax. This embodies the principle of vertical equity in taxation, where taxpayers with a higher ability to pay (in this case, those owning more valuable assets) contribute more to public funds. By proportionately linking tax liability to property value, ad valorem taxes foster a sense of fairness in the tax system. Ad valorem taxes, particularly those on real estate, provide a stable revenue stream for local governments. Unlike income or consumption, property values tend to be less volatile and not as directly affected by short-term economic fluctuations. As a result, the income from ad valorem taxes is predictable and steady, making it easier for local governments to plan their budgets and manage public resources effectively. Property taxes, a form of ad valorem tax, are typically used to fund local public services such as education, public safety, infrastructure maintenance, and local government operations. This means taxpayers can see a direct correlation between the taxes they pay and the services they receive, fostering a sense of community investment and involvement. This visibility could potentially improve taxpayers' willingness to contribute and their satisfaction with local governance. Since ad valorem taxes are usually assessed and collected by local authorities, they provide a level of financial autonomy for local governments. This autonomy allows them to tailor policies and spending to local needs and preferences without relying too heavily on state or federal funding, leading to more responsive and effective local governance. In some instances, ad valorem taxes can serve as a tool to stimulate economic development. Local governments might offer reduced property tax rates or tax abatements to attract businesses or incentivize development in specific areas. These initiatives can stimulate job creation, enhance local services, and spur economic growth. Depending on the financial needs of the community, local governments can adjust the tax rate or change the method of property assessment. For example, in times of economic hardship or when additional revenue is needed for specific projects, local governments might opt to raise property tax rates temporarily. This flexibility can be a valuable tool for managing local finances and addressing community needs. In some instances, ad valorem taxes can be regressive, particularly when applied to personal property or consumer goods. For example, if two people own cars of the same value, the person with a lower income will be contributing a higher proportion of their income toward the ad valorem tax than the person with a higher income. This regressive nature can disproportionately impact lower-income individuals, perpetuating income inequality. Property values are subject to fluctuations based on a range of factors, including market conditions, local policies, and broader economic trends. Sudden changes in property values can lead to unexpected increases or decreases in ad valorem tax liability. This unpredictability can make it challenging for property owners to plan financially and can cause strain if taxes increase substantially. Assessing the value of property can be a complex and time-consuming process that requires a fair degree of expertise. Property owners and tax assessors may not always agree on the value, leading to potential disputes and administrative challenges. Furthermore, the cost of regularly updating property assessments can be high, adding to the administrative burden of the tax system. Since ad valorem taxes are based on the value of owned property, they could incentivize individuals to take on debt rather than investing in appreciable assets, which would increase their tax liability. This dynamic could encourage over-leveraging and potentially contribute to debt-related issues. If making improvements to a property results in an increased valuation and, subsequently, higher taxes, property owners might be disincentivized to upgrade their properties. This could lead to under-investment in property maintenance and improvement, potentially affecting housing quality and neighborhood aesthetics over time. Ad valorem taxes, like all tax types, can be vulnerable to evasion or avoidance. Some individuals or businesses might undervalue their property or fail to declare certain assets in order to reduce their tax bill. This behavior can undermine the effectiveness of the tax system and lead to fairness issues. When property values in an area increase rapidly, existing residents may find it increasingly difficult to afford their property taxes. If these residents are forced to sell and move, it can lead to gentrification, which can disrupt communities and lead to a loss of cultural and socioeconomic diversity. Ad valorem taxes play a crucial role in funding public infrastructure and services, contributing to the economic health of a region. The principle of ad valorem taxation ensures a sense of equity by proportionally linking tax liability to property value. Furthermore, these taxes provide stability of revenue for local governments, allowing them to plan budgets and manage public resources effectively. Ad valorem taxes also promote local funding for local services, fostering community investment and autonomy for local governments. Moreover, they offer flexibility in adjusting tax rates and property assessments to meet the financial needs of the community and stimulate economic development. However, there are drawbacks to consider, such as the regressive nature of ad valorem taxes on personal property, the impact of market fluctuations, and the complexity and cost of property assessment. Ad valorem tax may also lead to the potential encouragement of debt, the disincentive to improve properties, the risk of tax evasion, and the potential for gentrification. These challenges highlight the need for careful implementation and continuous evaluation of ad valorem tax systems to ensure fairness and effectiveness in generating revenue for public services.What Is Ad Valorem Tax?
Principles of Ad Valorem Tax
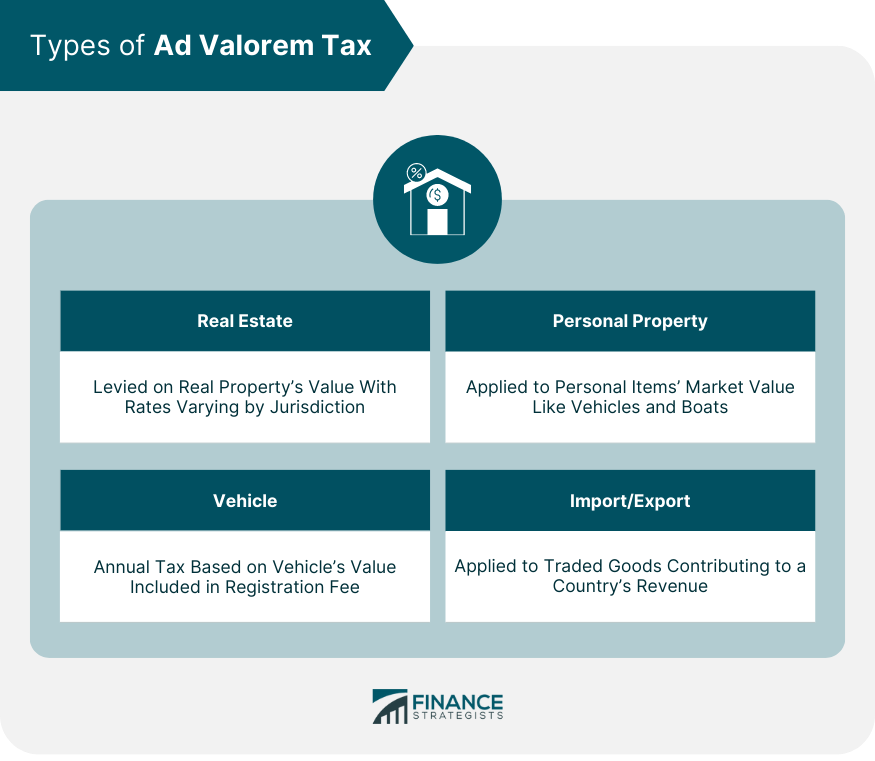
Types of Ad Valorem Tax
Real Estate
Personal Property
Vehicle
Import/Export
Calculation of Ad Valorem Tax
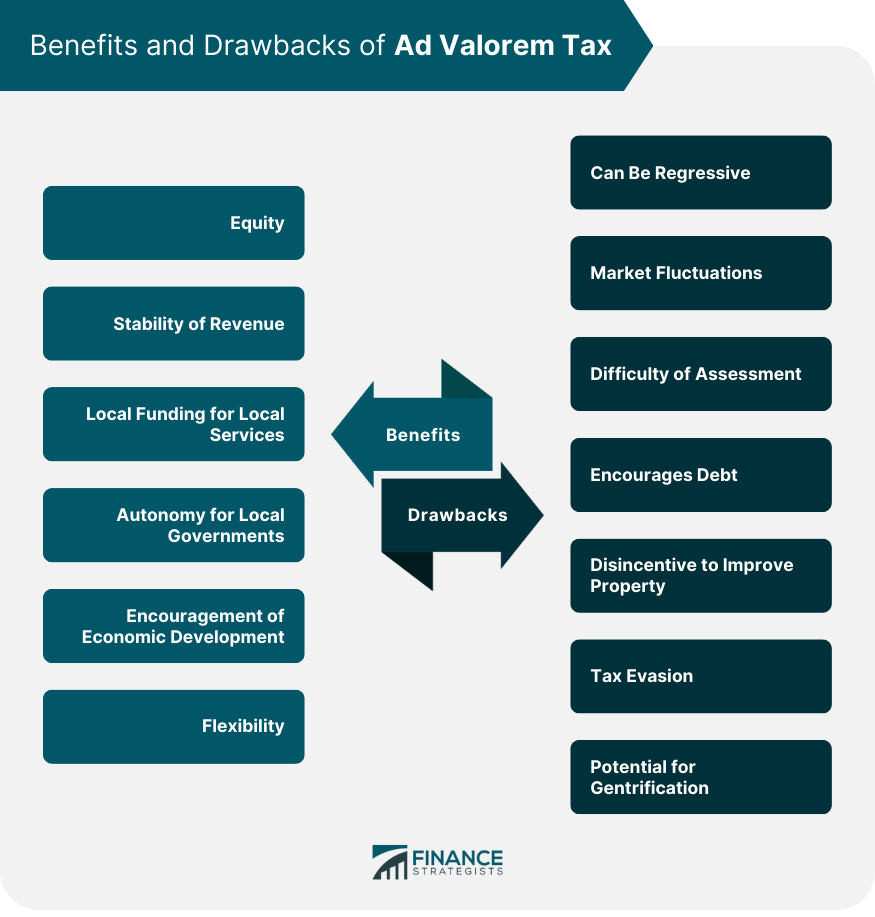
Benefits of Ad Valorem Tax
Equity
Stability of Revenue
Local Funding for Local Services
Autonomy for Local Governments
Encouragement of Economic Development
Flexibility
Drawbacks of Ad Valorem Tax
Can Be Regressive
Market Fluctuations
Difficulty of Assessment
Encourages Debt
Disincentive to Improve Property
Tax Evasion
Potential for Gentrification
Conclusion
Ad Valorem Tax FAQs
An ad valorem tax is based on an item's assessed value, such as real estate or personal property. The term "ad valorem" is Latin for "according to value," reflecting the way the tax is applied.
Ad valorem tax is calculated by multiplying the taxable value of an item by the tax rate. The taxable value is determined through an appraisal, which estimates the item's current market value.
The main difference between ad valorem tax and specific tax lies in how they're calculated. Ad valorem tax is based on the value of an item, while a specific tax is a fixed amount, regardless of the item's value.
Ad valorem tax is important because it provides a significant source of revenue for local and state governments, funding crucial public services and infrastructure. Its structure also ensures tax fairness, as those with more valuable properties pay more.
Many types of items can be subject to ad valorem tax, including real estate, personal property like vehicles and boats, and imported or exported goods. The specific application of ad valorem tax varies by jurisdiction and tax law.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











