The Electronic Federal Tax Payment System is a free system provided by the U.S. Department of the Treasury to facilitate the electronic payment of all federal taxes. It was first introduced in 1996 as part of an initiative to modernize tax payments, a digital shift that has proved crucial in the contemporary digital economy. In this modern age, where nearly everything is going digital, the ability to pay taxes online has become not just a luxury but a necessity. The EFTPS plays a critical role in ensuring a seamless digital tax payment process, enabling taxpayers to fulfill their obligations without the traditional inconveniences associated with the process. The first step to using the EFTPS is to enroll in the system. Registration is a simple process that can be completed online at the EFTPS website. Once enrolled, taxpayers receive a Personal Identification Number (PIN) through the mail, which they use in conjunction with their Employer Identification Number (EIN) or Social Security Number (SSN). The EFTPS website is user-friendly and intuitive. It is designed to make the tax payment process as straightforward as possible. Once logged in, taxpayers can access a range of services, including making a tax payment, scheduling future tax payments, and reviewing payment history. Making a payment through EFTPS is a straightforward process. After logging in with your EIN/SSN and PIN, you select the tax form, tax period, and payment type. The system then prompts you to enter the amount you wish to pay and the date you want the funds to be debited from your account. EFTPS also allows users to review and print payment history for up to 16 months. This feature enables taxpayers to keep track of their payment records effectively, providing a valuable resource during tax audits or for personal record keeping. Users can make tax payments from the comfort of their homes or offices any time of the day or night. Additionally, scheduling payments in advance allows taxpayers to plan their financial obligations effectively. The EFTPS system employs robust security measures to protect users' information. These include Secure Socket Layer (SSL) technology, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. It also uses a two-factor authentication process – EIN/SSN and PIN – to ensure that only authorized users can access the system. EFTPS helps streamline the tax payment process, eliminating the need for paper checks and reducing the risk of lost or delayed payments. It also provides an efficient method for record-keeping, as users can access their payment history at any time. Individual taxpayers can use EFTPS to pay their federal income taxes, estimated taxes, and even property and gift taxes. For businesses, EFTPS is a valuable tool that simplifies the payment of employment, corporate income, and other business-related taxes. The system allows businesses to schedule payments up to 365 days in advance, which can be particularly helpful for planning purposes. Federal agencies also use EFTPS to manage and track tax payments. This system allows for efficient management of public funds and ensures timely payment of federal obligations. Tax professionals, such as Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) and Enrolled Agents (EAs), often use EFTPS on behalf of their clients. The system allows these professionals to manage multiple accounts efficiently, making it easier to handle large client bases. EFTPS is commonly used for making federal income tax payments. This includes payments for annual tax returns and estimated tax payments for the upcoming tax year. Businesses use EFTPS to pay employment taxes, including federal income tax withholding, Social Security and Medicare taxes, and federal unemployment tax. Companies that deal with goods and services subject to excise tax, such as gasoline, alcohol, and tobacco, can use EFTPS to pay these taxes. Both individual taxpayers and businesses can use EFTPS to make estimated tax payments. This is particularly useful for self-employed individuals and businesses needing to pay quarterly estimated taxes. Like any online system, users may encounter issues with EFTPS. These can range from login problems to difficulties in scheduling payments. Most common issues can be resolved by following the troubleshooting tips provided on the EFTPS website. For instance, if you forget your PIN, you can request a new one through the website. If you cannot resolve an issue alone, EFTPS provides customer support through a toll-free number. Customer service representatives can assist with various issues, including enrollment problems, lost or forgotten PINs, and payment difficulties. It is a simple and secure way to make a tax payment directly from your checking or savings account at no additional cost. This service offers the advantage of convenience since you can pay from the comfort of your home or office. Additionally, it's designed to provide instant payment confirmation for record-keeping purposes. However, it only supports payments from individual taxpayers and not businesses. Therefore, while IRS Direct Pay is a good option for individuals, businesses may need to look at other alternatives. Paying your tax bill with a credit or debit card offers the convenience of being able to pay anytime and anywhere. Plus, if you have a rewards credit card, you could potentially earn points, miles, or cash back. However, this method comes with processing fees, which can be quite substantial for large tax bills. Also, if you use a credit card and carry a balance, you could end up paying significant interest charges. This traditional method of payment involves writing a check or buying a money order, then mailing it to the IRS. While this method can be slower than electronic payments and there's the potential risk of your payment getting lost in the mail, it still serves as a reliable and straightforward option, especially for those who prefer to avoid electronic transactions. This payment method can be used at participating retail partners. While it might be convenient for those who primarily deal with cash, this method does come with some limitations. For example, there's usually a limit to how much you can pay at once, and there's a small fee involved. Additionally, it typically takes about 5 to 7 business days for the payment to be processed and posted to your account. Wire transfers provide an option for same-day payment, making them useful for last-minute tax payments to avoid late penalties. This method involves initiating a same-day wire from your financial institution. It's important to remember that this option typically involves a fee from your bank, and you'll need to complete a Same Day Payment Worksheet, which you can find on the IRS website. If you find yourself unable to pay your tax bill in one lump sum, you can consider applying for an installment agreement with the IRS. This option allows you to make smaller, more manageable monthly payments. However, remember that interest and possibly a late payment penalty will continue to accrue on any unpaid balances. This method allows for direct deduction of your tax payments from your wages. For those who are employed and can make arrangements with their employers, this is an excellent way to ensure that payments are made consistently and on time. It's an automated process, which reduces the risk of forgetting a payment. There are a plethora of tax preparation and filing software available that offer integrated tax payment solutions. These software packages are designed to streamline the entire process of preparing and paying your taxes. Some of these include popular options like TurboTax and H&R Block. While these services can offer added convenience, they usually come with a fee, so it's crucial to consider the cost-benefit before choosing this method. The Electronic Federal Tax Payment System has transformed the process of paying taxes by providing a convenient and secure electronic platform. Introduced in 1996, the system modernized tax payments to align with the digital era and the evolving needs of the economy. EFTPS offers numerous advantages, including a user-friendly website and intuitive interface that enables taxpayers to make payments at any time and from anywhere. Robust security measures, such as SSL technology and two-factor authentication, ensure the protection of sensitive information. The system also enhances efficiency by eliminating paper checks and reducing the risk of payment delays or losses. Users can access their payment history for record-keeping purposes or tax audits. While EFTPS is highly beneficial, alternative payment methods like IRS Direct Pay, credit/debit card payments, traditional checks, wire transfers, payroll deduction, and third-party software solutions offer additional options for taxpayers. EFTPS plays a vital role in modernizing tax payments, offering convenience, security, and efficiency to ensure the timely fulfillment of tax obligations.What Is the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)?
Understanding the EFTPS Process
Registration and Enrollment
EFTPS Website and User Interface
Making Payments
Checking Payment History and Status
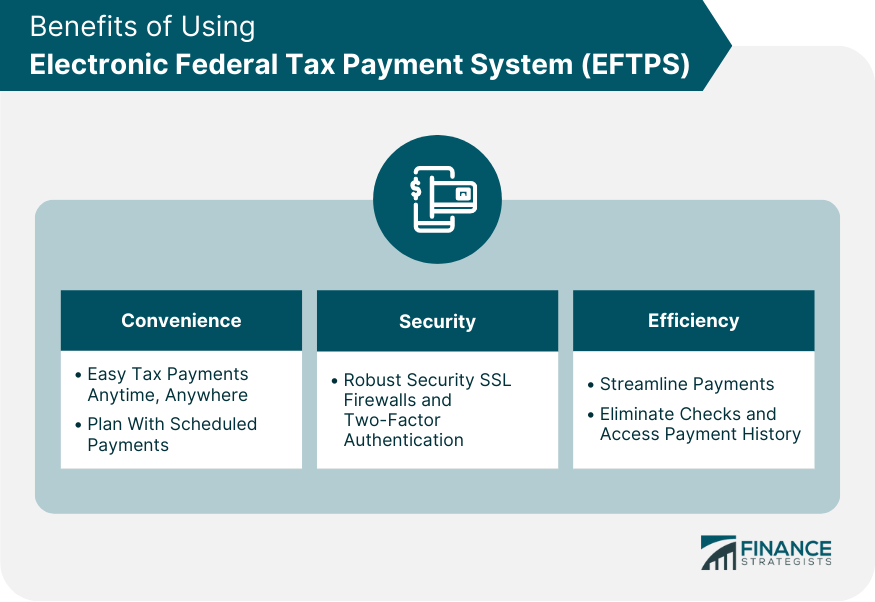
Benefits of Using EFTPS
Convenience
Security
Efficiency
Who Can Use EFTPS?
Individual Taxpayers
Business Taxpayers
Federal Agencies
Tax Professionals
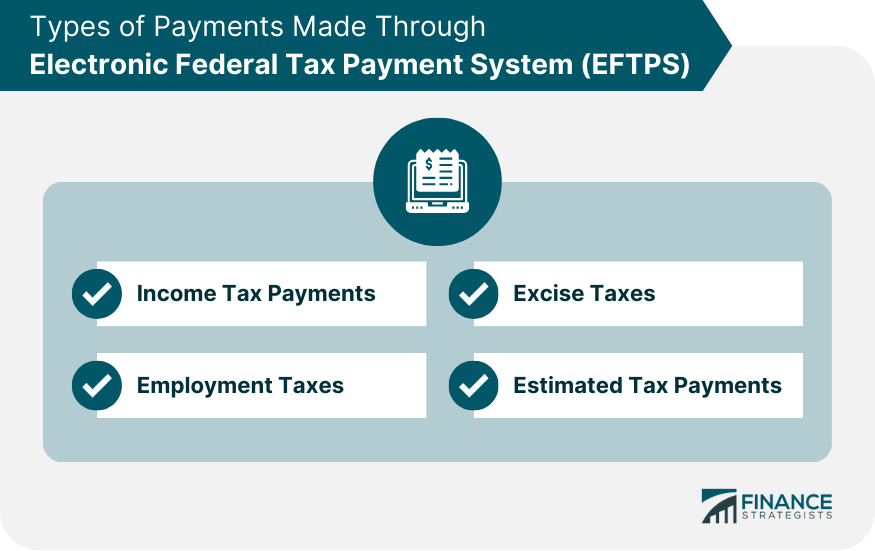
Types of Payments Made Through EFTPS
Income Tax Payments
Employment Taxes
Excise Taxes
Estimated Tax Payments
Troubleshooting and Customer Support in EFTPS
Common Issues
Reaching Out to EFTPS Customer Support
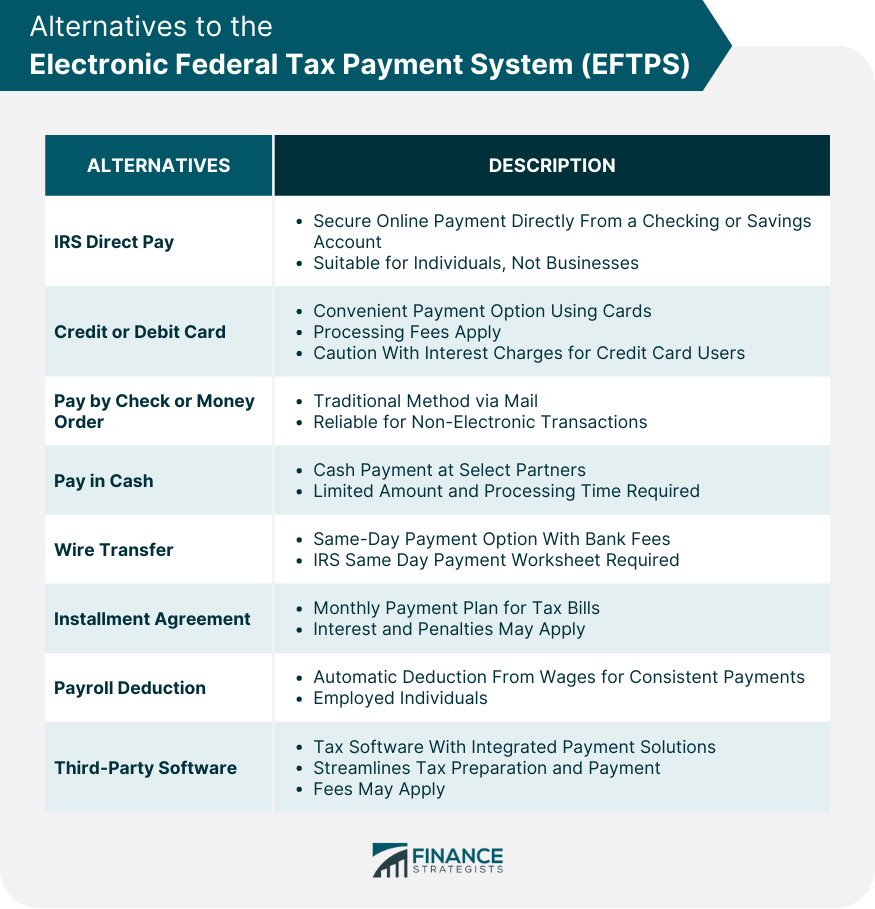
Alternatives to the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System
IRS Direct Pay
Credit or Debit Card
Pay by Check or Money Order
Pay in Cash
Wire Transfer
Installment Agreement
Payroll Deduction
Third-Party Software
Final Thoughts
Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS) FAQs
The Electronic Federal Tax Payment System is a secure online service the U.S. Department of the Treasury provides for making federal tax payments electronically.
To enroll in EFTPS, visit the official EFTPS website and follow the enrollment process, which includes verifying your information and selecting a personal identification number (PIN) for secure access.
EFTPS allows for the electronic payment of various federal taxes, including income taxes, estimated taxes, employment taxes (e.g., payroll taxes), and excise taxes.
No, there are no fees to enroll in or use EFTPS. It is a free service provided by the U.S. Department of the Treasury to facilitate electronic tax payments.
The use of EFTPS is mandatory for certain taxpayers, particularly businesses with a federal tax deposit requirement. However, individuals and businesses not mandated to use EFTPS can still choose to utilize it as a convenient and secure method for making federal tax payments.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











