Tax planning is an essential aspect of running a successful small business. It involves understanding and managing tax obligations while maximizing deductions and credits to minimize the tax burden. This article provides an overview of tax planning strategies for small businesses, including selecting the right business structure, maximizing deductions and credits, working with tax professionals, and staying informed about tax law changes. Small businesses are subject to federal income tax based on their net income. The tax rates and filing requirements depend on the business structure, such as sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation. Small business owners, including sole proprietors and partners, are typically subject to self-employment tax, which covers Social Security and Medicare contributions. Businesses with employees must withhold payroll taxes, such as Social Security, Medicare, and federal income tax, from their employees' wages and remit them to the government. Small businesses engaged in selling goods or services may be required to collect and remit state and local sales taxes. Businesses that own real estate or personal property may be subject to property taxes assessed by local governments. Some states impose franchise and excise taxes on businesses for the privilege of operating within their jurisdiction. Certain industries, such as alcohol, tobacco, and fuel, may be subject to federal and state excise taxes. Businesses involved in activities that impact the environment, such as oil production or hazardous waste disposal, may be subject to environmental taxes. Some industries may have additional tax obligations specific to their line of business. A sole proprietorship is the simplest business structure, where the owner and the business are considered one entity for tax purposes. A partnership is a business structure where two or more individuals share ownership and profits. Partnerships are subject to pass-through taxation, where profits are distributed to partners and taxed at their individual income tax rates. An LLC is a flexible business structure that combines the benefits of a corporation and a partnership. It offers limited liability protection and can choose to be taxed as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation. A corporation is a separate legal entity from its owners and can be taxed as either an S-Corporation or a C-Corporation. S-Corporations are subject to pass-through taxation, while C-Corporations are taxed separately from their owners. Small businesses can claim various tax deductions, such as business expenses, vehicle use, home office, and depreciation. Tax credits, such as the Work Opportunity Tax Credit and the Research and Experimentation Tax Credit, can help reduce a small business's tax liability. Maintaining accurate records of business expenses is crucial for maximizing tax deductions and minimizing the risk of an audit. Accounting software and expense tracking apps can help small business owners keep track of their expenses and simplify tax preparation. Establishing retirement plans, such as SEP IRAs or 401(k)s, can provide tax benefits for small business owners and their employees. There are several retirement plan options available to small business owners, including SIMPLE IRAs, SEP IRAs, Solo 401(k)s, and traditional 401(k) plans. Each plan has its own eligibility requirements, contribution limits, and tax advantages. Offering employee benefits, such as health insurance and educational assistance, can provide tax deductions for the business and help attract and retain talent. Small business owners and self-employed individuals are typically required to make estimated tax payments throughout the year to avoid penalties. Conducting regular financial reviews and updating tax planning strategies can help small businesses stay on track and optimize their tax savings. Implementing tax-loss harvesting strategies, such as selling underperforming assets to offset capital gains, can help minimize tax liabilities. Hiring a tax professional can help small business owners navigate complex tax laws, ensure compliance, and maximize tax savings. When selecting a tax professional, consider factors such as experience, industry knowledge, and communication style to find the best fit for your business. Maintaining an ongoing relationship with a tax professional can help small business owners stay proactive in their tax planning and adapt to changes in tax laws. Tax laws are constantly changing, and staying informed about these changes is essential for effective tax planning. Small business owners can stay informed about tax law changes through resources such as the IRS website, professional associations, and tax newsletters. As tax laws change, small business owners should adjust their tax planning strategies to ensure compliance and optimize tax savings. Tax planning is essential for the success of small businesses as it involves managing tax obligations and maximizing deductions and credits to minimize the tax burden. Small businesses have federal tax obligations that depend on their business structure, self-employment tax obligations for owners, and payroll tax obligations for employees. Sales tax, property tax, and industry-specific taxes such as excise taxes and environmental taxes are other types of state and local tax obligations for small businesses. Selecting the right business structure, maximizing deductions and credits, tracking expenses accurately, establishing retirement and benefit plans, and working with tax professionals are some of the tax planning strategies for small businesses. Small business owners should stay updated with tax law changes and adjust their tax planning strategies accordingly. Regular financial reviews and ongoing collaboration with tax professionals can help optimize tax savings for small businesses.What Is Tax Planning for Small Businesses?
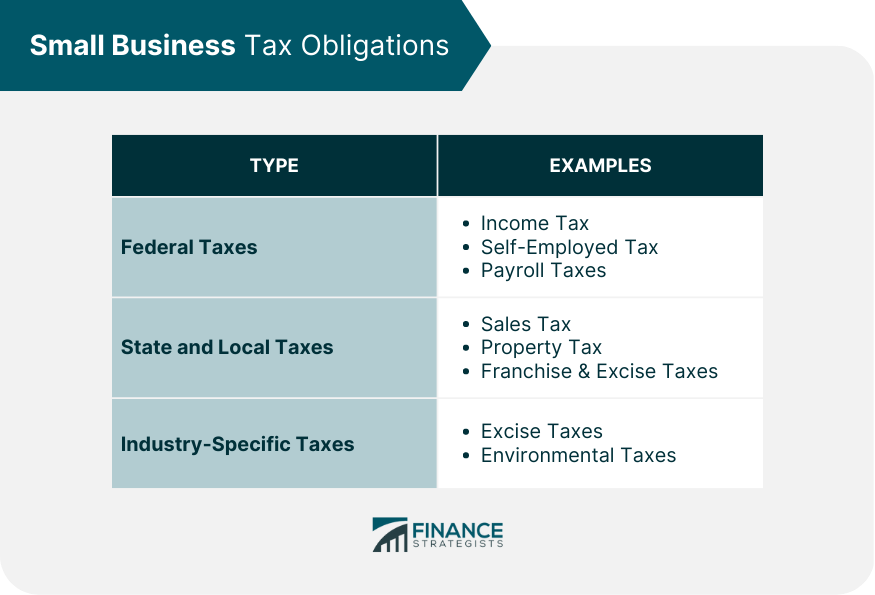
Understanding Small Business Tax Obligations
Federal Taxes
Income Tax
Self-Employment Tax
Payroll Taxes
State and Local Taxes
Sales Tax
Property Tax
Franchise and Excise Taxes
Industry-Specific Taxes
Excise Taxes
Environmental Taxes
Other Industry-Specific Taxes
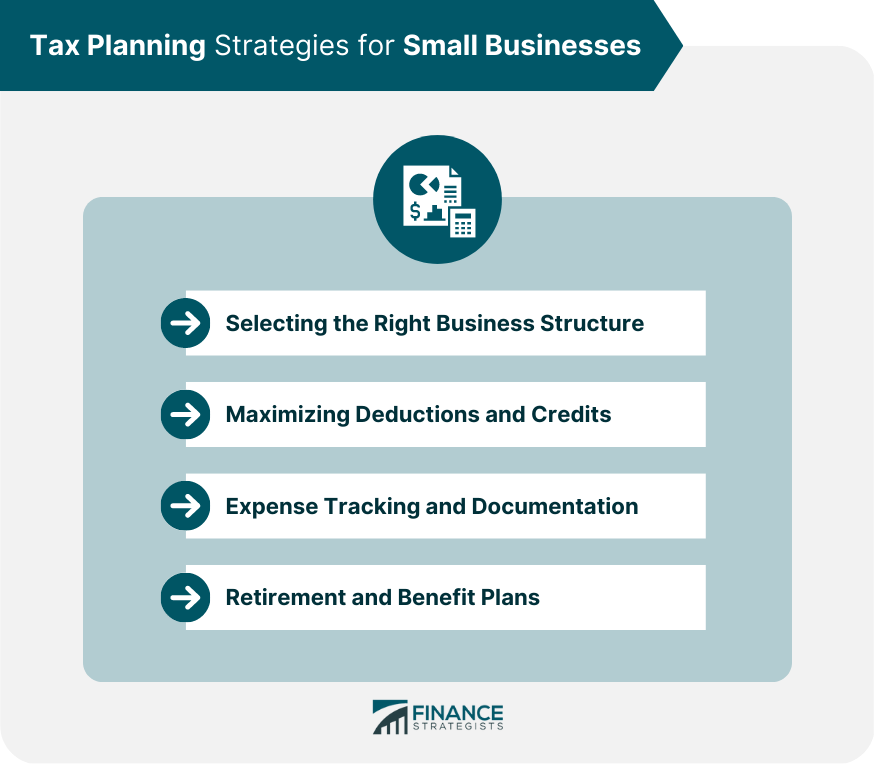
Tax Planning Strategies
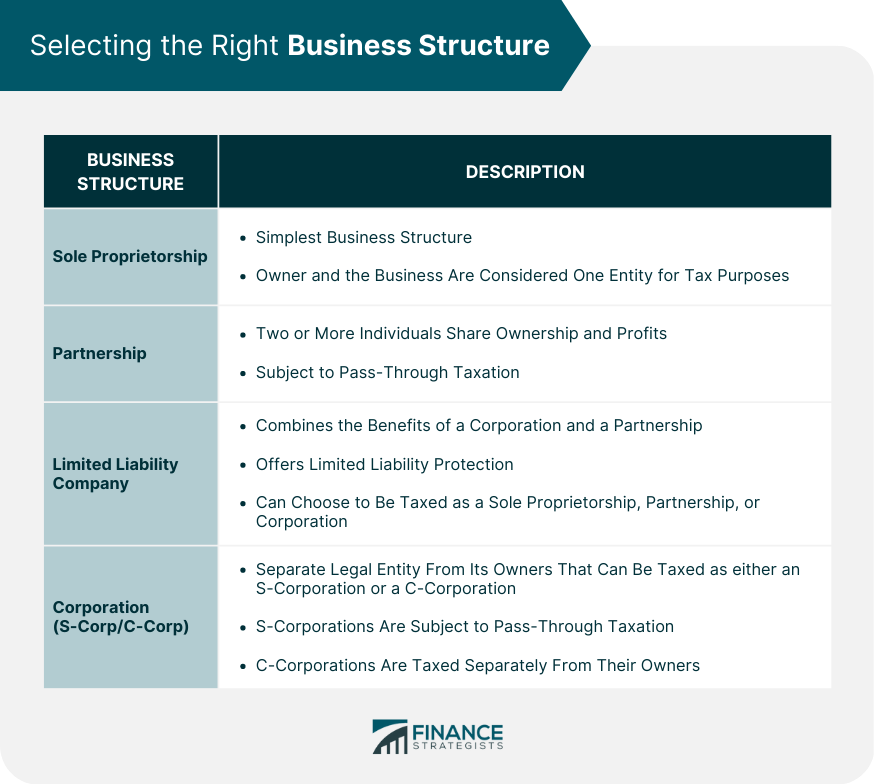
Selecting the Right Business Structure
Sole Proprietorship
Partnership
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
Corporation (S-Corp and C-Corp)
Maximizing Deductions and Credits
Common Small Business Tax Deductions
Tax Credits Available to Small Businesses
Expense Tracking and Documentation
Importance of Accurate Record-Keeping
Tools and Software for Expense Tracking
Retirement and Benefit Plans
Tax Advantages of Retirement Plans
Types of Retirement Plans for Small Business Owners
Employee Benefit Plans and Tax Implications
Tax Planning Throughout the Year
Quarterly Estimated Tax Payments
Regular Financial Review and Planning
Tax-Loss Harvesting Strategies
Working With Tax Professionals
Benefits of Hiring a Tax Advisor or Accountant
Finding the Right Tax Professional for Your Business
Collaborating With Tax Professionals for Ongoing Planning
Staying Updated With Tax Law Changes
Importance of Staying Informed
Resources for Tax Law Updates
Adjusting Tax Planning Strategies as Needed
Final Thoughts
Tax Planning for Small Businesses FAQs
Tax planning for small businesses is the process of managing and arranging the business's financial affairs in a way that reduces the amount of tax liability. It involves developing strategies to minimize taxes owed while maintaining compliance with all relevant tax laws and regulations.
Tax planning is crucial for small businesses because it helps to optimize financial performance by minimizing tax obligations. By planning ahead and taking advantage of tax-saving opportunities, small businesses can increase profitability and reinvest in their growth.
Small businesses can use a variety of tax-saving strategies, including maximizing deductions, deferring income, contributing to retirement accounts, taking advantage of tax credits, and investing in qualified business property. It is essential to consult with a tax professional to identify the strategies that are most appropriate for your business.
Small businesses should start tax planning as early as possible. It is crucial to have a plan in place well before the tax deadline to take advantage of all available opportunities. Ideally, tax planning should be a year-round process that involves monitoring income and expenses and making adjustments as necessary to minimize tax liability.
Small businesses can do tax planning on their own, but it is advisable to seek professional help from a tax advisor or accountant. Tax laws and regulations are complex and constantly changing, so it's essential to have a qualified expert who can provide guidance and help identify tax-saving opportunities that may not be apparent to the business owner.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











