Contingent Income Securities are financial instruments that pay interest or dividends to investors based on specific triggers or conditions. These securities typically include features such as conversion to equity or principal write-downs, which can occur if certain predefined events take place. This allows issuers to manage their capital structure more effectively, while also providing investors with a higher yield compared to traditional fixed income instruments. Contingent Income Securities offer a number of benefits for both issuers and investors. Issuers can use these instruments to raise capital while maintaining flexibility in their capital structure. Investors, on the other hand, can benefit from the potential for higher yields and the opportunity to diversify their investment portfolios. There are several types of Contingent Income Securities, each with its own unique features and characteristics. CoCos are a type of bond that can be converted into equity or have their principal written down under specific circumstances. CIES are securities that pay interest or dividends based on the performance of an underlying equity index or individual stocks. These instruments may also include features such as conversion to equity or principal write-downs, depending on the terms of the security. There are other types of Contingent Income Securities that may not fit neatly into the categories above. These can include instruments with unique features or structures, designed to meet the specific needs of issuers and investors. To better understand Contingent Income Securities, it is essential to be familiar with some key terms and concepts. Coupon payments refer to the interest paid by the issuer to the investor for holding the security. In the case of Contingent Income Securities, these payments may be contingent on certain events or conditions being met. Conversion triggers are specific events or conditions that, when met, can result in the security being converted into equity or having its principal written down. These triggers can vary depending on the terms of the security and may include factors such as the issuer's capital ratios, stock price, or other predefined events. The capital structure of a company refers to the mix of debt and equity used to finance its operations. Contingent Income Securities can play a role in managing a company's capital structure, as they can be used to raise capital while maintaining flexibility in terms of conversion or principal write-downs. Credit ratings are an assessment of the creditworthiness of a company or financial instrument. Contingent Income Securities may have different credit ratings than traditional fixed income instruments, as they often include features such as conversion or principal write-downs that can impact the issuer's credit profile. Investing in Contingent Income Securities comes with a set of risks that investors should be aware of before making an investment decision. Credit risk refers to the possibility that the issuer of a security may default on their obligations, such as interest or principal payments. Contingent Income Securities can be subject to credit risk, as the issuer's ability to meet their obligations may be affected by factors such as conversion triggers or principal write-downs. Market risk is the potential for changes in market conditions, such as interest rates, economic conditions, or credit spreads, to negatively impact the value of an investment. Contingent Income Securities can be exposed to market risk, as their value may be influenced by factors such as changes in the issuer's credit profile or overall market sentiment. Liquidity risk is the risk that an investor may not be able to buy or sell a security easily, resulting in potential losses or missed opportunities. Contingent Income Securities may have lower liquidity than traditional fixed income instruments due to their unique features and the complexity of their structures. Regulatory risk refers to the potential for changes in regulations or the regulatory environment to impact the value of an investment. Contingent Income Securities can be subject to regulatory risk, as changes in regulations or the approach taken by regulators could impact the terms or attractiveness of these instruments. Before investing in Contingent Income Securities, it is important for investors to consider their suitability, potential benefits, and tax implications. Contingent Income Securities may be more suitable for sophisticated investors with a higher risk tolerance, given the potential for higher yields and the complex nature of these instruments. Investors should carefully assess their risk tolerance and investment objectives before considering Contingent Income Securities. Investing in Contingent Income Securities can provide diversification benefits for investors, as these instruments can offer exposure to different sectors, industries, and asset classes. However, it is essential to maintain a balanced and diversified portfolio to manage the overall risk. The tax treatment of Contingent Income Securities can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific features of the instrument. Investors should consult with a tax professional to understand the potential tax implications of investing in Contingent Income Securities. The market for Contingent Income Securities includes issuers, investors, and secondary market trading. Contingent Income Securities are typically issued by companies, banks, and other financial institutions seeking to raise capital while maintaining flexibility in their capital structure. Contingent Income Securities can be bought and sold in the secondary market, providing investors with the opportunity to trade these instruments and potentially realize capital gains or losses. However, liquidity in the secondary market may be limited due to the complexity of these instruments. The market for Contingent Income Securities is continually evolving, with new instruments, structures, and trends emerging. Investors should stay informed about market developments and the potential impact on their investments. Contingent Income Securities are subject to regulation and supervision by various authorities. The regulatory framework for Contingent Income Securities can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific features of the instrument. Regulations may cover aspects such as issuance, disclosure, and trading of Contingent Income Securities. Regulatory authorities responsible for overseeing Contingent Income Securities may include central banks, securities regulators, and other financial supervisory bodies. These authorities are responsible for ensuring the stability and integrity of financial markets, as well as investor protection. As the market for Contingent Income Securities evolves, regulators may introduce new rules or amend existing regulations to address emerging risks and market developments. Investors should stay informed about regulatory changes that may impact their investments in Contingent Income Securities. Contingent Income Securities offer a unique investment opportunity, combining the features of debt and equity securities while providing potential benefits for both issuers and investors. However, these instruments also come with risks, including credit, market, liquidity, and regulatory risks. It is essential for investors to understand the potential rewards and risks associated with Contingent Income Securities and to consider their suitability before making an investment decision. By tapping on the services of an expert in wealth management and staying informed about market developments, regulatory changes, and emerging trends, investors can better navigate the evolving landscape of Contingent Income Securities.Definition and Basic Features of Contingent Income Securities
Purpose and Benefits of Investing in Contingent Income Securities
Types of Contingent Income Securities
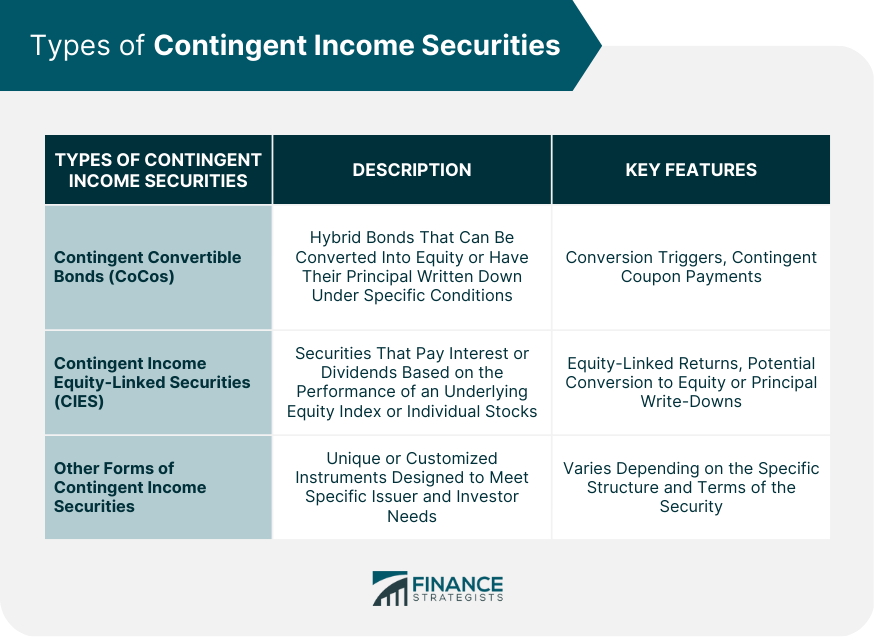
Contingent Convertible Bonds (CoCos)
These triggers can include the issuer's capital ratios falling below a predetermined level, or other predefined events. CoCos are often issued by banks as a way to meet regulatory capital requirements.Contingent Income Equity-linked Securities (CIES)
Other Forms of Contingent Income Securities
Contingent Income Securities: Key Terms and Concepts
Coupon Payments in Contingent Income Securities
Conversion Triggers in Contingent Income Securities
Capital Structure and Contingent Income Securities
Credit Ratings and Contingent Income Securities
Risks Associated With Contingent Income Securities
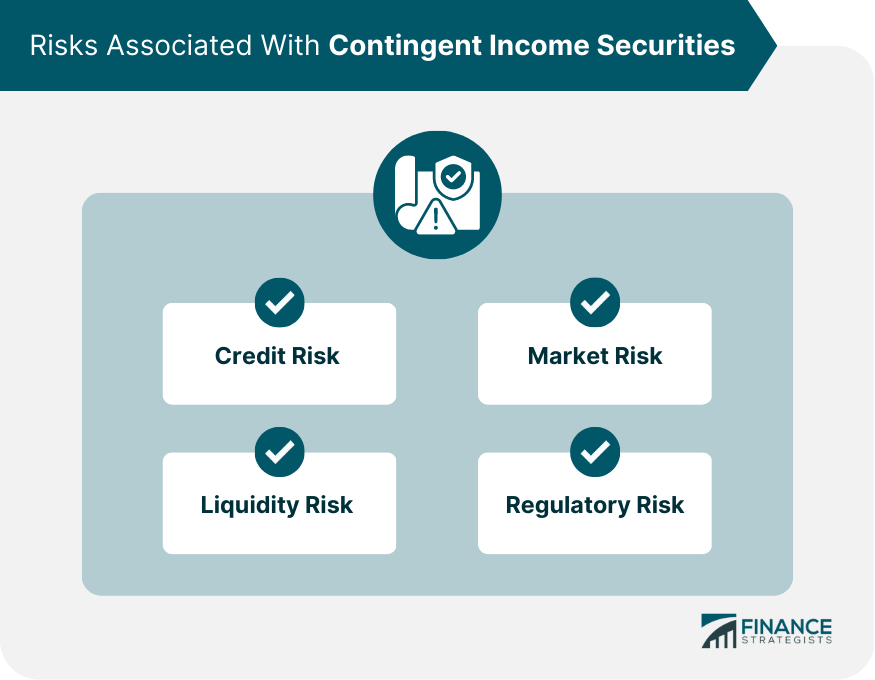
Credit Risk
Market Risk
Liquidity Risk
Regulatory Risk
Investing in Contingent Income Securities
Suitability of Contingent Income Securities for Different Investors
Portfolio Diversification With Contingent Income Securities
Tax Considerations for Contingent Income Securities
Contingent Income Securities Market
Issuers of Contingent Income Securities
Trading Contingent Income Securities in the Secondary Market
Market Trends and Developments in Contingent Income Securities
Regulation and Supervision of Contingent Income Securities
Regulatory Framework for Contingent Income Securities
Key Regulatory Authorities Overseeing Contingent Income Securities
Ongoing Regulatory Developments in Contingent Income Securities
Conclusion
Contingent Income Securities FAQs
Contingent Income Securities are hybrid financial instruments that combine features of debt and equity securities. They pay interest or dividends to investors based on specific triggers or conditions, and may include features such as conversion to equity or principal write-downs. These securities offer potential for higher returns and greater flexibility for issuers compared to traditional fixed income instruments.
There are several types of Contingent Income Securities, including Contingent Convertible Bonds (CoCos), Contingent Income Equity-linked Securities (CIES), and other forms with unique features or structures. Each type has its own characteristics and serves different purposes for issuers and investors.
Investing in Contingent Income Securities comes with several risks, including credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, and regulatory risk. Investors should carefully assess these risks and their overall risk tolerance before considering an investment in Contingent Income Securities.
Contingent Income Securities can provide diversification benefits for investors, as they offer exposure to different sectors, industries, and asset classes. By including Contingent Income Securities in a well-balanced portfolio, investors can potentially reduce overall portfolio risk and enhance returns.
Contingent Income Securities are subject to regulation and supervision by various authorities, such as central banks, securities regulators, and other financial supervisory bodies. The regulatory framework for Contingent Income Securities can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific features of the instrument. Investors should stay informed about regulatory changes that may impact their investments in Contingent Income Securities.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











