Convertible securities are hybrid financial instruments that combine features of both debt and equity securities. They allow the holder the option to convert the security into a predetermined number of common shares at a specified conversion price. Convertible securities are popular among investors because they offer the potential for capital appreciation and income generation while providing downside protection. Companies issue convertible securities as a way to raise capital at a lower cost than issuing common stock or non-convertible debt. Investors are attracted to convertible securities because they offer a combination of income, capital appreciation, and downside protection. The conversion ratio is the number of common shares an investor receives upon converting their convertible security. It is determined by dividing the face value of the security by the conversion price. The conversion price is the predetermined price at which the convertible security can be exchanged for common shares. It is usually set at a premium to the market price of the underlying stock at the time of issuance. The conversion premium is the difference between the market price of the underlying stock and the conversion price. It represents the additional cost an investor must pay to acquire the common shares by converting the security. The maturity date is the date when the convertible security must be redeemed or converted. At maturity, the issuer will either pay the face value of the security or convert it into common shares, depending on the investor's preference. Call provisions allow the issuer to redeem the convertible security before its maturity date, typically at a premium. This feature is advantageous for issuers when interest rates decline or the underlying stock price appreciates significantly. Anti-dilution provisions protect investors from potential dilution of their equity stake if the issuer issues additional shares at a lower price or carries out a stock split. These provisions adjust the conversion ratio to maintain the investor's proportional ownership in the company. Discussed below are the common classifications of convertible securities: Convertible bonds are debt securities that can be converted into a predetermined number of common shares. They pay regular interest to bondholders and have a fixed maturity date. The interest rate is typically lower than that of non-convertible bonds due to the conversion feature. The advantages of convertible bonds include income generation, capital appreciation potential, and downside protection. However, they may have lower interest rates compared to non-convertible bonds, and their market value may be affected by fluctuations in interest rates and the underlying stock price. Convertible preferred stock is a type of equity security that pays regular dividends and can be converted into a predetermined number of common shares. Preferred stockholders have priority over common stockholders in receiving dividends and assets in the event of liquidation. The advantages of convertible preferred stock include higher dividend yield, potential capital appreciation, and downside protection. Disadvantages include the possibility of forgone dividends if the issuer suspends dividend payments and the impact of interest rates and stock prices on the security's market value. Convertible notes are short-term debt instruments issued by companies that can be converted into common shares at a predetermined conversion price. They are often used as a financing tool during the early stages of a company's growth, as they provide investors with the option to convert their debt into equity. The advantages of convertible notes include lower interest rates compared to traditional debt, potential capital appreciation, and the ability to participate in the company's growth through equity ownership. Disadvantages include the risk of default, potential dilution of equity, and sensitivity to interest rates and stock price fluctuations. The intrinsic value of a convertible security is the difference between the market value of the underlying common shares and the conversion price, multiplied by the conversion ratio. It represents the minimum value of the convertible security if it were to be converted immediately. The time value of a convertible security represents the potential for additional capital appreciation or income generation before the security's maturity date or conversion deadline. This value depends on factors such as interest rates, stock price volatility, and credit quality. Stock Price An increase in the underlying stock price will increase the value of the convertible security, as the conversion feature becomes more attractive. Rising interest rates can negatively affect the value of convertible securities, as their fixed-income component becomes less attractive compared to other fixed-income investments. Higher stock price volatility can increase the value of convertible securities, as it creates a higher probability of capital appreciation. Credit Quality The value of convertible securities is also influenced by the credit quality of the issuer. A downgrade in credit rating may decrease the value of the security, as the risk of default increases. Listed below are the common valuation models for convertible securities: The binomial model is a widely used method for valuing convertible securities. It divides the security's life into discrete periods and estimates the value of the security in each period based on various factors, including stock price, interest rates, and credit quality. The Black-Scholes model is another popular method for valuing convertible securities. It uses a continuous-time approach to estimate the value of the security based on stock price, volatility, interest rates, and time to maturity or conversion. Capital Appreciation Convertible securities offer the potential for capital appreciation if the underlying stock price increases. Income Generation Convertible securities provide income through interest payments (convertible bonds and notes) or dividends (convertible preferred stock). Convertible securities can provide portfolio diversification due to their hybrid nature, combining elements of both debt and equity investments. Downside Protection Convertible securities offer downside protection, as their value is supported by their fixed-income component in the event of a decline in the underlying stock price. Interest Rate Risk Convertible securities are sensitive to changes in interest rates, which can affect their market value. Credit Risk Investors in convertible securities are exposed to credit risk, as the issuer may default on interest or principal payments. Conversion Risk If the underlying stock price declines, the conversion feature of convertible securities may become less attractive, reducing their value. Market Risk Convertible securities are subject to market risk, as their value can be affected by fluctuations in the broader financial markets. A long-term investment approach where investors purchase convertible securities and hold them until maturity or conversion, aiming to benefit from capital appreciation and income generation. This strategy involves simultaneously buying a convertible security and short-selling the underlying stock. The goal is to profit from discrepancies in the pricing of the two securities while reducing overall market risk. Investors can use various hedging techniques to manage the risks associated with convertible securities, such as using options or futures to hedge against interest rate risk or credit risk. Lower Interest Rates Issuers can benefit from lower interest rates on convertible securities compared to traditional debt, as investors accept a lower yield in exchange for the conversion feature. Attract Investors Convertible securities can attract a broader range of investors, as they appeal to both fixed-income and equity-focused investors. Minimize Dilution Issuers can minimize potential dilution of existing shareholders by setting the conversion price at a premium to the market price of the underlying stock. Timing Issuers must consider market conditions and investor appetite for convertible securities before deciding to issue them. Pricing Issuers need to determine the appropriate conversion price and conversion ratio to make the convertible security attractive to investors while minimizing potential dilution. Terms and Conditions Issuers should carefully consider the terms and conditions of the convertible security, such as call provisions and anti-dilution provisions, to balance the needs of the company and the interests of investors. Convertible securities are hybrid financial instruments that offer a unique combination of income, capital appreciation, and downside protection. They come in various forms, including convertible bonds, convertible preferred stock, and convertible notes. Valuation of convertible securities depends on factors such as the underlying stock price, interest rates, volatility, and credit quality. Convertible securities play a significant role in the financial market, providing companies with a flexible financing option and offering investors an attractive mix of risk and return. Understanding the features, valuation, and investment strategies associated with convertible securities is essential for investors and issuers alike. Consult a professional in wealth management for further guidance on convertible securities.What Are Convertible Securities?
Features of Convertible Securities
Conversion Ratio
Conversion Price
Conversion Premium
Maturity Date
Call Provisions
Anti-Dilution Provisions
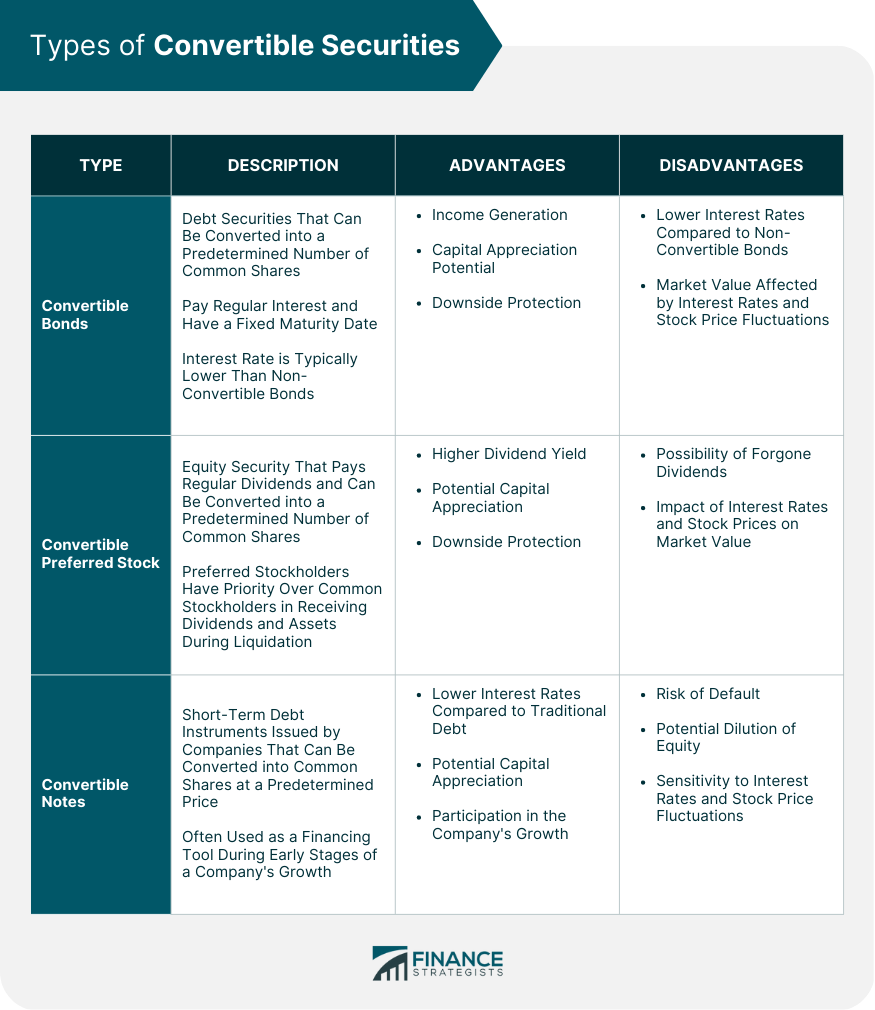
Types of Convertible Securities
Convertible Bonds
Convertible Preferred Stock
Convertible Notes
Valuation of Convertible Securities
Intrinsic Value
Time Value
Factors Affecting Valuation of Convertible Securities
Valuation Models for Convertible Securities
Binomial Model
Black-Scholes Model
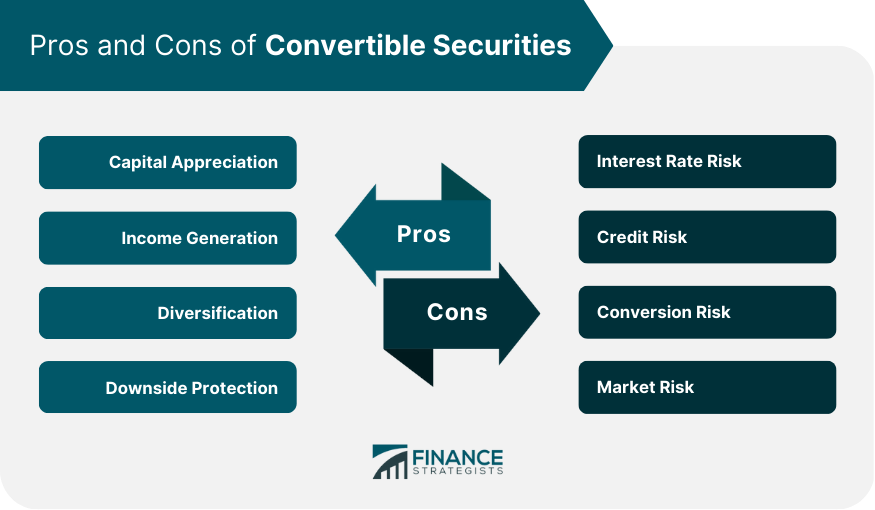
Advantages of Investing in Convertible Securities
Disadvantages of Investing in Convertible Securities
Investment Strategies for Convertible Securities

Buy-and-Hold
Convertible Arbitrage
Hedge Strategies
Reasons for Issuing Convertible Securities
Considerations for Issuers of Convertible Securities
Final Thoughts
Convertible Securities FAQs
Convertible securities are hybrid financial instruments that combine features of both debt and equity securities. They allow the holder the option to convert the security into a predetermined number of common shares at a specified conversion price.
There are three main types of convertible securities: convertible bonds, convertible preferred stock, and convertible notes. Each type has unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
The valuation of convertible securities is based on their intrinsic value and time value. Factors affecting their valuation include the underlying stock price, interest rates, volatility, and credit quality. Valuation models such as the binomial model and Black-Scholes model can be used to estimate the value of convertible securities.
Benefits of investing in convertible securities include capital appreciation, income generation, diversification, and downside protection. Risks include interest rate risk, credit risk, conversion risk, and market risk.
Companies issue convertible securities to raise capital at a lower cost than issuing common stock or non-convertible debt. Convertible securities can attract a broader range of investors and help minimize potential dilution of existing shareholders by setting the conversion price at a premium to the market price of the underlying stock.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











