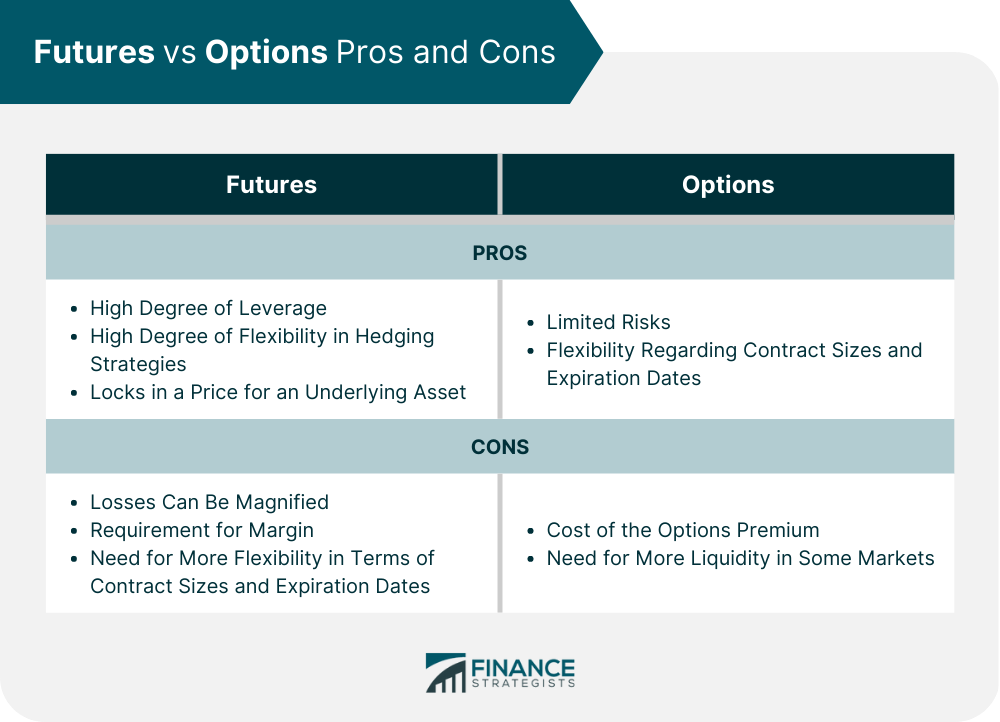
Futures and options are both financial derivatives used in trading, but they have distinct differences. Futures contracts let traders purchase or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specified date in the future. In contrast, options contracts provide traders the right to buy or sell an asset at a fixed price on a specific date, without any obligation. It is important to comprehend these variations to make informed investment decisions. Deciding between Futures and Options? Click here. Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a particular asset at a set price on a specific date in the future. These contracts are typically traded on organized exchanges and are standardized regarding contract size, delivery date, and underlying asset quality. The most common types of futures contracts are commodities futures, which allow investors to trade commodities like crude oil, gold, and wheat. One of the primary advantages of futures trading is that it offers a high degree of leverage. This means that investors can control a large amount of the underlying asset with a relatively small investment. However, this leverage also comes with significant risk, as losses can be magnified as quickly as gains. Another advantage of futures trading is that it allows for a high degree of flexibility in hedging strategies. Futures contracts can be used to lock in a price for an underlying asset, protecting investors from price volatility. For example, a farmer might use a futures contract to lock in the price of his crop before planting it, ensuring a guaranteed price at harvest time. However, there are also some disadvantages to futures trading. One of the biggest is the requirement for margin. Investors must post an initial margin payment to open a futures position. They may also be required to make additional margin payments if the price of the underlying asset moves against them. This can lead to significant losses if investors are not careful. Another disadvantage of futures trading is the need for more flexibility in terms of contract sizes and expiration dates. Futures contracts are standardized, meaning investors must trade the specified contract sizes and expiration dates. This can limit the ability to tailor hedging strategies to specific needs. Options contracts are similar to futures contracts, allowing investors to trade assets without actually owning them. However, options contracts give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price on a particular date. Unlike futures contracts, options are traded both on organized exchanges and in Over-the-Counter (OTC) markets. One of the primary advantages of options trading is the limited risk involved. Unlike futures trading, options trading allows investors to control the upside potential of an asset without exposing themselves to unlimited downside risk. This can be particularly useful for investors who want to protect themselves from unexpected price movements. Another advantage of options trading is the flexibility regarding contract sizes and expiration dates. In addition, options contracts can be tailored to specific needs, allowing investors to create hedging strategies that meet their unique requirements. For example, an investor may opt for a call or put option. A call option to protect against a price increase in a particular asset, while a put option could be used to protect against a price decrease. However, there are also some disadvantages to options trading. One of the biggest is the cost of the option premium. Options contracts require investors to pay a premium for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset. This premium can be significant, particularly for options with longer expiration dates. Another disadvantage of options trading is the need for more liquidity in some markets. Some options markets can be relatively illiquid, meaning that buying or selling options contracts at a fair price can be difficult. This can be a huge challenge for investors who need to quickly sell options contracts in order to control risk. While futures and options share some similarities, these two financial derivatives also have several key differences. One of the most significant differences between futures and options is the underlying assets that they can be used to trade. Futures contracts are typically used for trading commodities like oil, gold, and wheat, as well as financial assets like currencies, bonds, and stock indices. Options contracts can be used to trade a much wider range of assets, including stocks, bonds, currencies, and commodities. Another vital difference between futures and options is the obligations of buyers and sellers. In a futures contract, both the buyer and seller are obligated to fulfill the terms of the contract when it expires. The buyer of an option only has the right, not the responsibility, to buy or sell the underlying asset. Nonetheless, if the buyer decides to exercise their option, the seller is still obligated to uphold the terms of the agreement. Futures and options contracts are priced differently. Futures contracts are valued depending on the current market value of the underlying item as well as elements like supply and demand, storage expenses, and interest rates. Options contracts are priced based on a range of factors, including the current market price of the underlying asset, the time remaining until expiration, and the volatility of the underlying asset. The liquidity of futures and options markets can also differ significantly. Futures contracts are typically traded on organized exchanges, which tend to be highly liquid. Options contracts can be traded on exchanges or in OTC markets, and some options markets can be relatively illiquid. Futures and options also have different reward and risk profiles. Futures trading can be highly risky, as losses can be magnified by the use of leverage. However, futures trading also offers the potential for high rewards. Options trading is generally less risky than futures trading, but the potential rewards are also limited by the premium paid for the option. Finally, futures and options contracts also have different timeframes. Futures contracts typically have set expiration dates, and the price of the underlying asset is fixed at the time the contract is entered into. Options contracts can have a range of expiration dates, and the price of the underlying asset can fluctuate significantly over the life of the option. When deciding between futures and options, there are several factors that investors should consider. Some of these include: The underlying asset that they want to trade Their risk tolerance The time horizon of their investment The liquidity of the markets in which they want to trade The flexibility of the contracts they are considering The cost of trading In general, futures trading may be a better option for investors who are comfortable with high levels of risk and volatility and who have a shorter investment time horizon. Options trading may be a better choice for investors who are looking to limit their risk exposure and who have a longer investment time horizon. Two of the most often utilized financial derivatives in trading and investing are futures and options. While both offer a range of advantages and disadvantages, they also differ in significant ways. Understanding the key differences between futures and options is essential for anyone looking to invest in these financial instruments. By considering their investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon, investors can make informed decisions about whether futures or options are right for their needs. A wealth management professional can guide you in choosing your investments.Futures vs Options Overview
What Is Futures?
Futures Advantages and Disadvantages
What Is Options?
Options Advantages and Disadvantages
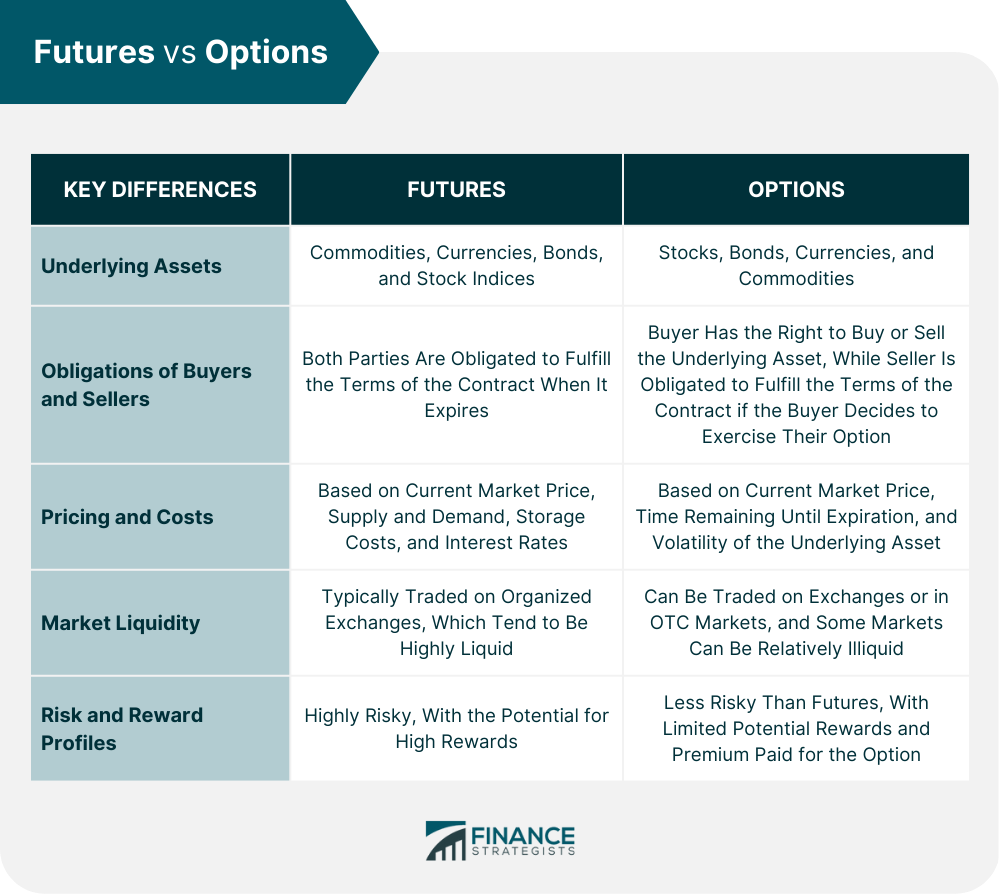
Key Differences Between Futures and Options
Underlying Assets
Obligations of Buyers and Sellers
Pricing and Costs
Market Liquidity
Risk and Reward Profiles
Timeframes
Choosing Between Futures and Options
The Bottom Line
Futures vs Options FAQs
Futures and options are two types of financial derivatives used in trading. Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an underlying asset at a set price on a specific date in the future, while options contracts give investors the right to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price on a specific date.
There are several key differences between futures and options, including the underlying assets that can be traded, the obligations of buyers and sellers, pricing and costs, market liquidity, risk and reward profiles, and timeframes.
Futures trading offers a high degree of leverage, flexibility in terms of hedging strategies, and the ability to trade a range of commodities and financial assets.
Options trading allows investors to control the upside potential of an asset while limiting downside risk and offers flexibility in terms of contract sizes and expiration dates.
Investors should consider factors like risk tolerance, investment goals, time horizon, market liquidity, the flexibility of contracts, and the cost of trading when choosing between futures and options. In general, futures trading may be better suited for investors with a shorter time horizon and higher risk tolerance, while options trading may be better suited for investors looking to limit their risk exposure and with a longer time horizon.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











