Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have emerged as a popular and versatile investment tool, offering a wide array of investment opportunities across various sectors, including energy. A Natural Gas ETF is one such fund that provides investors an opportunity to gain exposure to the performance of natural gas without owning the physical commodity or trading futures contracts. These ETFs primarily track the price of natural gas and reflect the returns potential investors would theoretically attain if they had invested directly in natural gas. They can be designed differently - some may invest in natural gas futures contracts, while others may invest in stocks of companies involved in the exploration and production of natural gas. Investors can select a Natural Gas ETF that aligns with their investment objective, risk tolerance, and expected returns. Natural Gas ETFs play a crucial role in the financial markets by allowing investors to gain exposure to the natural gas sector, a key segment of the energy industry. By doing so, these ETFs provide a means for portfolio diversification, as the natural gas sector often has different performance patterns compared to other sectors of the economy. Moreover, Natural Gas ETFs simplify the investment process by eliminating the need to directly trade natural gas futures or to analyze individual companies in the natural gas sector. This reduced complexity makes these ETFs an attractive option for both novice and experienced investors. Natural gas is a fossil fuel used as a source of energy for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. It's also a raw material in products such as plastics and chemicals. As a commodity, the price of natural gas can fluctuate due to supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical issues, weather patterns, and other factors. The global natural gas market is vast and interconnected, with major producers such as the United States, Russia, and Qatar supplying to regions with high energy demand, such as Europe and Asia. Developments in this market can significantly impact the performance of Natural Gas ETFs. For instance, during the winter of 2022, Europe faced a severe natural gas shortage, leading to skyrocketing prices. This had a direct impact on Natural Gas ETFs tracking European markets, leading to significant price movements. Several factors can influence natural gas prices, including: 1. Weather: Natural gas demand often rises during periods of extreme cold or heat, leading to higher prices. 2. Production Levels: If natural gas production levels decrease, prices may increase due to reduced supply. 3. Storage Levels: The amount of natural gas in storage can also impact prices. Low storage levels can lead to higher prices, especially during periods of high demand. 4. Economic Growth: Higher economic growth can lead to increased demand for natural gas and higher prices. Natural Gas ETFs work by either tracking the price of natural gas futures contracts or by investing in a portfolio of stocks from companies involved in the natural gas sector. Futures-based Natural Gas ETFs primarily hold natural gas futures contracts and aim to track the price of natural gas. These ETFs may face challenges in accurately tracking the natural gas price due to the futures roll process, which involves selling expiring contracts and buying contracts with later expiration dates. This can lead to tracking errors, especially in volatile markets. Equity-based Natural Gas ETFs, on the other hand, invest in stocks of companies involved in the exploration, production, and distribution of natural gas. The performance of these ETFs is influenced by the business performance of these companies and the overall stock market conditions, along with the price of natural gas. Natural Gas ETFs can play various roles in an investment portfolio. For investors seeking exposure to the energy sector, these ETFs provide a direct and straightforward way to gain such exposure. Investors seeking diversification can also benefit from these ETFs, as the natural gas sector can behave differently compared to other sectors. Moreover, given the potential for high volatility in natural gas prices, these ETFs can also serve as a hedge against inflation or as a tool for speculative trading. However, like all investments, Natural Gas ETFs come with their own set of risks, and these should be carefully considered before investing. These risks include commodity price volatility, risks associated with futures contracts (for futures-based ETFs), and company-specific risks (for equity-based ETFs). It's always recommended that investors carefully consider their investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon before investing in any ETF, including Natural Gas ETFs. Equity Natural Gas ETFs invest primarily in stocks of companies involved in the exploration, production, and distribution of natural gas. These ETFs aim to track the performance of these companies, making them indirectly influenced by natural gas prices. Futures-Based Natural Gas ETFs aim to track the price of natural gas directly. They invest primarily in natural gas futures contracts. These ETFs might face challenges due to the futures roll process, leading to potential tracking errors. Leveraged Natural Gas ETFs aim to deliver multiple times the daily performance of the underlying index they track. Conversely, Inverse Natural Gas ETFs aim to deliver the opposite of the daily performance of their underlying index. These types of ETFs are more suitable for sophisticated investors who understand the risks associated with leverage and short-selling. When evaluating Natural Gas ETFs, investors should consider factors such as the ETF’s tracking error, expense ratio, trading volume, and performance history. Additionally, understanding the underlying assets, whether they are futures contracts or equity stocks, is also important. Investing in Natural Gas ETFs can provide significant rewards, including sector exposure and potential returns during periods of high natural gas prices. However, these ETFs also carry risks, such as commodity price volatility and the complexities of futures contracts trading. Investors should carefully weigh these risks and rewards before investing. Before investing in Natural Gas ETFs, it is essential to identify one's investment goals and risk tolerance. Investment goals may vary from short-term to long-term, and they can be focused on capital appreciation, income generation, or portfolio diversification. A clear understanding of these goals will help an investor choose the most suitable Natural Gas ETF for their portfolio. Additionally, investors should assess their risk tolerance. Natural Gas ETFs, like any investment, come with inherent risks. These risks may include fluctuations in natural gas prices, changes in supply and demand dynamics, and geopolitical factors. By understanding their risk tolerance, investors can make informed decisions about which Natural Gas ETFs are most appropriate for them. Once investment goals and risk tolerance have been established, investors should research various Natural Gas ETFs to find the one that best aligns with their objectives. Key factors to consider when evaluating Natural Gas ETFs include the ETF's strategy, underlying assets, expense ratio, and performance history. Natural Gas ETFs may follow different strategies to achieve their investment goals. Some may track the performance of natural gas futures contracts, while others may invest in a basket of stocks involved in the natural gas industry. Understanding the ETF's strategy will help investors determine if it aligns with their investment goals. Investors should also examine the ETF's underlying assets, which may include natural gas futures, stocks of natural gas companies, or other related investments. This information can provide insight into the ETF's exposure to natural gas and the specific risks associated with its investments. The expense ratio is a key consideration for investors, as it represents the annual costs associated with managing the ETF. A lower expense ratio generally indicates a more cost-effective investment. However, investors should also weigh the expense ratio against other factors, such as the ETF's strategy and performance history, to determine if the costs are justified. An ETF's historical performance can help investors gauge its potential for future returns. While past performance is not a guarantee of future results, examining the track record of an ETF can provide insights into how it has navigated various market conditions and how it may perform in the future. Once investors have identified the Natural Gas ETF that best aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance, they can purchase shares through a brokerage account. Investors should be aware of any fees associated with trading ETF shares, as these can impact overall investment returns. Additionally, it's important to monitor the performance of the ETF and make adjustments as needed, in order to keep the investment aligned with one's goals and risk tolerance. When considering investing in Natural Gas ETFs, it's crucial to clarify your investment objectives. These objectives can range from capital appreciation and income generation to portfolio diversification. Knowing your specific goals will help you select a suitable Natural Gas ETF that aligns with your expectations and desired outcomes. Understanding your risk tolerance is vital before investing in Natural Gas ETFs. These investments carry inherent risks, such as price volatility, geopolitical factors, and changes in supply and demand dynamics. Assessing your risk tolerance will help you make informed decisions about which Natural Gas ETFs are most appropriate for your investment portfolio. Your investment horizon, or the length of time you plan to hold the investment, is another essential factor to consider before investing in Natural Gas ETFs. A longer investment horizon may allow you to weather short-term market fluctuations and potentially benefit from long-term trends. On the other hand, a shorter investment horizon may expose you to increased risks and limit your ability to recover from potential losses. Investing in Natural Gas ETFs also exposes investors to unique risks specific to the natural gas market. These risks include: Natural gas prices can be highly volatile, influenced by factors such as weather, storage levels, and global economic conditions. This volatility can impact the value of Natural Gas ETFs, resulting in potential losses for investors. Many Natural Gas ETFs invest in natural gas futures contracts, which can be complex and difficult to understand for some investors. Trading futures contracts involves risks, such as contango or backwardation, which can negatively impact the performance of the ETF. Investors should have a thorough understanding of futures contracts and their associated risks before investing in Natural Gas ETFs that utilize this strategy. While both types of ETFs provide exposure to the energy sector, they are influenced by different factors. Oil ETFs are more influenced by geopolitical events and global production levels, while Natural Gas ETFs are more impacted by weather patterns and storage levels. Natural Gas ETFs and Renewable Energy ETFs represent different ends of the energy spectrum. While Natural Gas ETFs are tied to fossil fuel, Renewable Energy ETFs are tied to sources like wind and solar. Investing in either or both can depend on an investor's outlook on energy trends, regulatory changes, and environmental impact. A Natural Gas ETF is a type of investment fund and exchange-traded product, which aims to track the price of natural gas. It offers exposure to the energy sector, diversification potential, and an alternative to direct investment in natural gas futures or stocks of individual natural gas companies. The key types of Natural Gas ETFs are equity-based, futures-based, and leveraged or inverse ETFs. Before investing, it's crucial to evaluate the performance indicators of Natural Gas ETFs and understand the inherent risks and rewards. Comparisons between Natural Gas ETFs, Oil ETFs, and Renewable Energy ETFs can help investors make more informed decisions based on their investment goals, risk tolerance, and perspectives on energy trends. Investing in Natural Gas ETFs requires research and advice. Consult a financial advisor to align investments with goals and risk tolerance.What Is Natural Gas ETF?
Importance of Natural Gas ETF in the Financial Market
Understanding Natural Gas
Basics of Natural Gas as a Commodity
Global Natural Gas Market and Its Impact on Natural Gas ETF
Factors Influencing Natural Gas Prices
Function of Natural Gas ETF
How Natural Gas ETFs Work
Role of Natural Gas ETFs in Investment Portfolios
Key Types of Natural Gas ETFs
Equity
Futures-Based
Leveraged and Inverse
Evaluating Natural Gas ETFs
Key Performance Indicators for Natural Gas ETFs
Risks and Rewards of Investing in Natural Gas ETFs
Steps to Invest in Natural Gas ETFs
Step 1: Identify Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance
Step 2: Research Natural Gas ETFs
ETF Strategy
Underlying Assets
Expense Ratio
Performance History
Step 3: Buy Shares of Natural Gas ETFs
Factors to Consider Before Investing in Natural Gas ETFs
Investment Objectives
Risk Tolerance
Investment Horizon
Unique Risks Associated with Natural Gas Market
Price Volatility
Complexities of Futures Contracts Trading
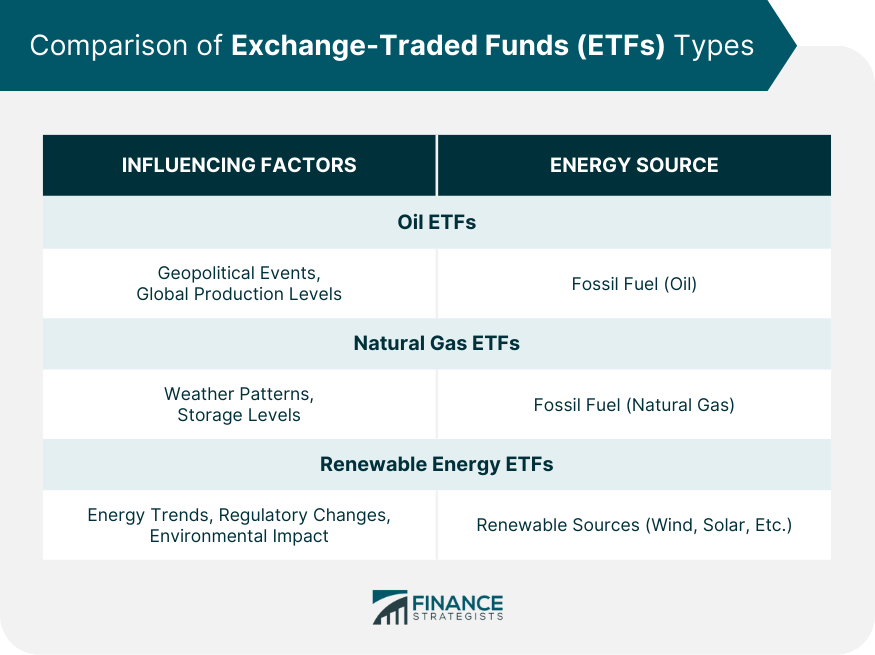
Natural Gas ETFs vs Other Energy ETFs
Comparison Between Natural Gas ETFs and Oil ETFs
Comparison Between Natural Gas ETFs and Renewable Energy ETFs
Final Thoughts
Natural Gas ETF FAQs
A Natural Gas ETF is an exchange-traded fund designed to track the price of natural gas. It allows investors to gain exposure to natural gas without owning the physical commodity or trading futures contracts.
Natural Gas ETFs work by investing in natural gas futures contracts or stocks of companies involved in natural gas exploration and production. These investments aim to replicate the price performance of natural gas.
The key types of Natural Gas ETFs include Equity Natural Gas ETFs, Futures-Based Natural Gas ETFs, and Leveraged and Inverse Natural Gas ETFs.
The rewards of investing in a Natural Gas ETF include sector exposure and potential returns during periods of high natural gas prices. However, these ETFs also carry risks such as commodity price volatility, risks associated with futures contracts trading, and company-specific risks.
You can invest in a Natural Gas ETF by buying shares of the ETF through a brokerage account. Before investing, it's crucial to research different Natural Gas ETFs and understand their strategies, underlying assets, expense ratios, and performance histories.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











