Natural resources investments involve buying and holding assets from nature, such as minerals, timber, water, and oil, to generate returns through price appreciation, dividends, or royalties Natural resources are essential materials that are derived from the Earth, which are required for various human needs and applications. As the global economy continues to expand, natural resource investments have become an increasingly popular means for investors to diversify their portfolios and tap into a variety of industries. Natural resources can be broadly classified into two categories: renewable and non-renewable resources. Water: Water is a vital natural resource for human survival and is used extensively in agriculture and industry. Solar Energy: Solar energy is harnessed through photovoltaic panels and solar thermal power plants. Wind Energy: Wind energy is generated through wind turbines, which convert wind's kinetic energy into electricity. Biomass: Biomass refers to organic material from plants and animals that can be converted into energy, such as biofuels and biogas. Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy is produced by tapping into the Earth's internal heat, which can be used for electricity generation and heating purposes. Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels include oil, natural gas, and coal, which are finite resources formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals. Metals and Minerals: Metals and minerals are essential for various industries, including construction, technology, and manufacturing. Investing in natural resources can be done through direct and indirect investments. Physical Assets: Investors can purchase physical assets, such as gold bars, oil fields, or timberland. Production Projects: Investments can be made in projects that involve the production of natural resources, such as mines or oil wells. Exploration Projects: Investors can fund projects that search for new natural resource deposits, such as mineral exploration or drilling for oil and gas. Stocks: Investors can buy shares of resource-based companies or invest in resource-focused exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mutual funds. Bonds: Investors can buy corporate bonds of natural resources companies or green bonds, which finance environmentally friendly projects. Commodity Futures and Options: Investors can trade commodity futures and options contracts, which allow them to speculate on the price movements of natural resources. Master Limited Partnerships (MLPs): MLPs are publicly traded partnerships that primarily invest in energy infrastructure, such as pipelines, storage facilities, and processing plants. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): REITs that focus on natural resources invest in properties and infrastructure related to resource extraction, production, and distribution. When investing in natural resources, several factors should be taken into account. Global Demand and Supply: The balance between global demand and supply can significantly impact natural resource prices. Inflation: Natural resources investments can act as a hedge against inflation, as their prices often rise with increasing inflation rates. Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can influence the profitability of natural resource investments. Geopolitical Risks: Political instability and conflicts in resource-rich regions can affect the supply and prices of natural resources. Environmental Impact: The extraction and production of natural resources can have significant environmental consequences, such as pollution and deforestation. Social Responsibility: Companies involved in natural resources should prioritize community engagement, fair labor practices, and human rights. Corporate Governance: Strong corporate governance can contribute to a company's long-term success and minimize investment risks. Sector Exposure: Diversifying across different resource sectors can help mitigate risks associated with specific industries. Geographic Exposure: Investing in natural resources across various geographic regions can reduce the impact of regional risks and political instability. Asset Class Exposure: Diversifying across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities, can provide a more balanced investment portfolio. Investors should consider their investment horizon and risk tolerance when selecting natural resources investments, as some investments may require a longer time horizon or carry higher risks. Portfolio Diversification: Investing in natural resources can help diversify an investment portfolio, reducing overall risk. Inflation Protection: Natural resources investments can act as a hedge against inflation, as their prices often rise with increasing inflation rates. Exposure to Global Economic Growth: Natural resources investments can provide exposure to global economic growth, as demand for resources increases with economic expansion. Potential for High Returns: Natural resources investments can offer high returns due to their inherent volatility and potential for significant price appreciation. Volatility: Natural resources investments can be subject to significant price fluctuations, driven by factors such as global demand and geopolitical risks. Geopolitical Risks: Political instability and conflicts in resource-rich regions can affect the supply and prices of natural resources. Regulatory Risks: Changes in government regulations and policies can impact natural resource companies and their profitability. Environmental Risks: The extraction and production of natural resources can have significant environmental consequences, which can lead to regulatory penalties and reputational damage. Market Liquidity: Some natural resources investments may have limited liquidity, making it difficult to buy or sell assets quickly without affecting their price. Long-term Buy and Hold Strategy: Investors with a long-term investment horizon can benefit from holding natural resources investments, as they can potentially generate substantial returns over time. Active Trading Strategies: Investors who are knowledgeable about the natural resources sector and comfortable with higher risk may opt for active trading strategies, such as trading commodity futures or options. Understanding natural resources investments is crucial for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on the global economy's expansion opportunities. By considering the various factors that can impact natural resources investments, such as economic factors, ESG factors, and diversification, investors can make informed decisions and balance the risks and rewards associated with this asset class. A well-diversified investment portfolio that includes exposure to natural resources can help investors achieve their long-term financial goals while mitigating potential risks.What Are Natural Resources Investments?
Types of Natural Resources
Renewable Resources
Non-Renewable Resources
Investment Vehicles
Direct Investments
Indirect Investments
Factors to Consider When Investing in Natural Resources
Economic Factors
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Factors
Diversification
Investment Horizon and Risk Tolerance

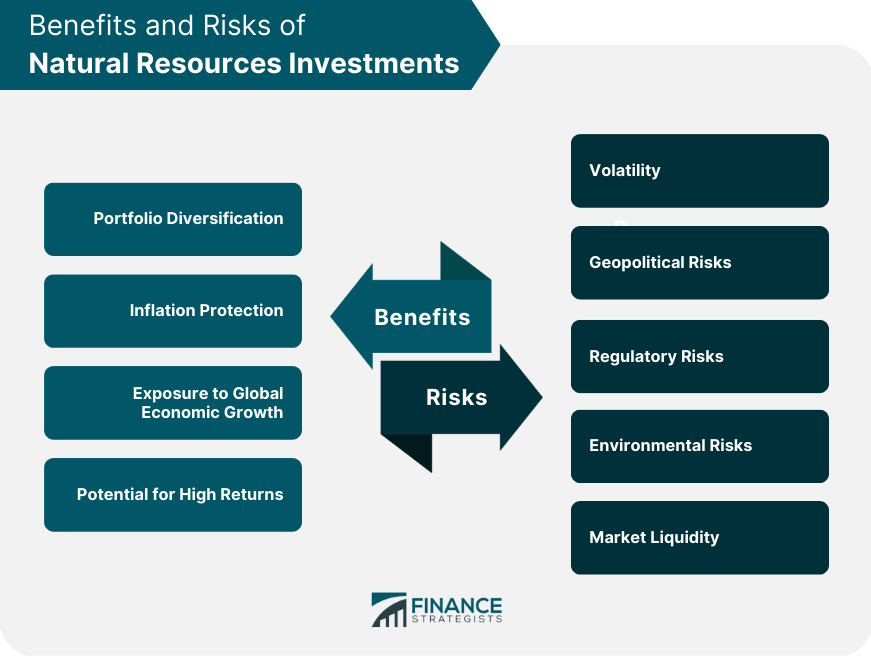
Benefits of Natural Resources Investments
Risks Associated With Natural Resources Investments
Strategies for Investing in Natural Resources
Conclusion
Natural Resources Investments FAQs
Natural resources investments refer to investments made in assets that come from nature, such as minerals, timber, water, and oil. These investments involve buying and holding these assets, with the goal of generating returns through price appreciation, dividends, or royalties.
Investing in natural resources can provide diversification benefits to a portfolio, as they tend to have a low correlation with other asset classes. Additionally, natural resources can serve as a hedge against inflation, as their prices tend to rise along with inflation.
Natural resources investments can be risky due to their dependence on factors outside of an investor's control, such as weather conditions, political instability, and changes in demand. Additionally, natural resources investments can be subject to price volatility, which can result in significant losses.
There are several ways to invest in natural resources, including buying stocks of companies involved in producing or distributing natural resources, investing in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track natural resources, or purchasing physical assets such as gold or silver.
Natural resources investments can be sustainable if they are managed responsibly and with consideration for the environment and local communities. Some companies in the natural resources sector are committed to sustainable practices and may be more attractive investments for socially conscious investors.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











