The New York Board of Trade (NYBOT) is a leading commodity futures exchange where a variety of physical commodities, such as coffee, cocoa, sugar, cotton, and orange juice, as well as financial derivatives, are traded. It's a marketplace where buyers and sellers connect to negotiate contracts specifying the purchase and sale of commodities at a future date. Trading on NYBOT is conducted through both open outcry—a method where traders use verbal and hand signal communication—and electronic trading systems. The NYBOT plays a pivotal role in the global financial markets. It is one of the key exchanges where commodities futures contracts are bought and sold, making it a central hub for commodities trading worldwide. As a result, it plays a crucial role in the determination of global prices for the commodities traded on its platform. Additionally, it also contributes to the risk management strategies of various businesses through its futures and options contracts, allowing companies to hedge against potential price changes in key commodities. The NYBOT has a rich history starting from 1870 with the New York Cotton Exchange. Mergers led to its formation in 1998. In 2004, it merged with the Coffee, Sugar & Cocoa Exchange for broader commodity offerings. The Intercontinental Exchange acquired NYBOT in 2007, transitioning it to ICE Futures U.S. Electronic trading became prominent. Key milestones include the 2004 merger and the 2007 acquisition, as well as the shift to electronic trading, enhancing trade speed and efficiency. Careful consideration and advice are crucial for investing in Natural Gas ETFs, aligning with financial goals and risk tolerance. NYBOT's governance structure is designed to ensure the smooth operation of the exchange and to uphold its integrity. The Board of Directors, which includes representatives from various sectors of the trading community, oversees the exchange's operations. The Board is responsible for setting the strategic direction of the exchange and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. The NYBOT has several key departments, each with its own set of responsibilities. The Market Regulation Department is responsible for enforcing trading rules and regulations, while the Market Operations Department oversees the daily trading activities. The Business Development Department is tasked with attracting new business and developing new trading products. The members of the Board of Directors have a variety of responsibilities. They are tasked with setting the strategic direction of the exchange, ensuring compliance with all applicable laws and regulations, and overseeing the exchange's daily operations. Additionally, they play a vital role in the development of new trading products and services. Trading on NYBOT begins with the opening of the trading session, during which traders start placing their orders. These orders are either market orders, which are executed at the best available price, or limit orders, which are executed at a specific price or better. The trades are then matched and executed, either through the open outcry method or via the electronic trading platform. One of the primary financial instruments traded on NYBOT is commodity futures and options contracts. These contracts enable traders to buy or sell a specific commodity at a predetermined price on a future date. Commodity futures contracts involve an agreement to purchase or sell a standardized quantity of a commodity, such as agricultural products (wheat, corn, soybeans), energy resources (crude oil, natural gas), or metals (gold, silver). Options contracts, on the other hand, provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying commodity. NYBOT also facilitates the trading of currency futures. Currency futures contracts involve the exchange of one currency for another at a specified price on a future date. These contracts enable market participants to speculate on or hedge against fluctuations in exchange rates. Traders can take positions on various currency pairs, such as USD/EUR (U.S. Dollar/Euro), USD/JPY (U.S. Dollar/Japanese Yen), or GBP/USD (British Pound/U.S. Dollar). Interest rate futures are another type of financial instrument traded on NYBOT. These futures contracts allow market participants to speculate on or hedge against changes in interest rates. They are based on an underlying debt instrument, such as government bonds or Treasury bills. By trading interest rate futures, investors can manage the risk associated with interest rate fluctuations and potentially benefit from movements in interest rates. NYBOT is a leading commodity futures exchange facilitating global commodities and futures trading. It enables traders to negotiate and execute futures and options contracts, contributing to price discovery. These contracts help businesses manage commodity price risk, playing a vital role in global risk management. The NYBOT plays an integral role in the U.S. financial sector. It is a key platform for the trading of commodity futures and options, providing liquidity and facilitating price discovery in these markets. By doing so, it supports the functioning of various industries that depend on these commodities and indirectly contributes to economic growth. Commodity prices are largely determined by supply and demand dynamics on exchanges like NYBOT. These prices influence the cost of goods and services throughout the economy, thereby impacting the rate of inflation. In addition, information derived from futures prices can help policymakers anticipate future inflation trends. NYBOT plays a significant role in promoting market stability and risk management. By offering futures and options contracts, it allows businesses to hedge against volatile commodity prices. This risk mitigation function contributes to overall market stability by reducing the potential for significant financial losses. NYBOT faces several challenges, including competition from other exchanges, regulatory pressures, and the need to continually innovate and adapt to changing market conditions. Maintaining the integrity and reliability of its trading platform is also a key challenge. Like many financial institutions, NYBOT has faced its share of controversies and criticisms. These have often been related to issues such as market manipulation, the role of speculative trading in commodity price volatility, and the impact of high-frequency trading on market stability. NYBOT has a robust system in place to handle regulatory issues and disputes. This includes a comprehensive set of trading rules, a dedicated market regulation department, and procedures for investigating and resolving disputes. The New York Board of Trade plays a crucial role in the global financial markets as a hub for the trading of commodity futures and options, including physical commodities and financial derivatives. Its historical evolution, governance structure, and trading processes demonstrate a complex yet efficient financial institution. The commodities traded here have a significant impact on the U.S. economy and global markets, influencing price discovery, risk management, and market stability. Amidst challenges and controversies, NYBOT continues to uphold its trading integrity, ensure regulatory compliance, and innovate in response to market conditions. Its influence extends beyond U.S. borders, shaping international trade and finance, and fostering relationships with other global exchanges. Given the complexity and potential impacts of trading on NYBOT, seeking the guidance of professional financial advisors is highly recommended to navigate this intricate world of commodity futures and options trading.What Is the New York Board of Trade (NYBOT)?
Significance of NYBOT in the Global Financial Market
History of the NYBOT
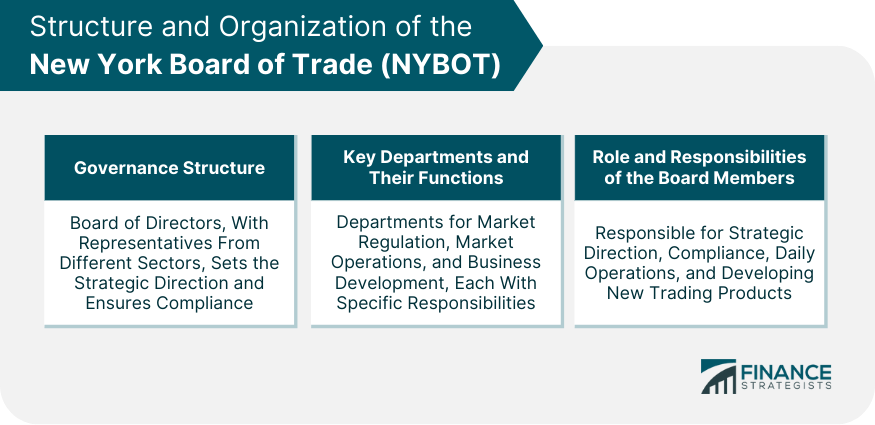
Structure and Organization of the NYBOT
Governance Structure of NYBOT
Key Departments and Their Functions
Role and Responsibilities of the Board Members
Trading on the NYBOT
Understanding the Trading Process
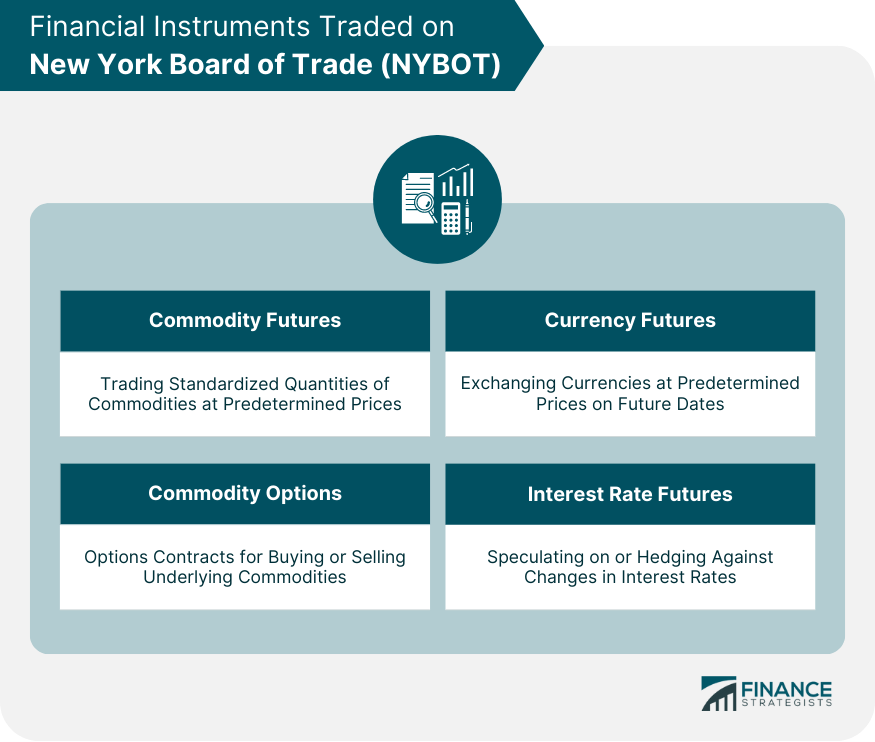
Different Types of Financial Instruments Traded
Commodity Futures and Options Contracts
Currency Futures
Interest Rate Futures
Role of NYBOT in Commodities and Futures Trading
Impact of the NYBOT on the U.S. Economy
Contribution to the U.S. Financial Sector
Influence on Commodity Prices and Inflation
Role in Risk Management and Market Stability
Challenges and Controversies Associated With the NYBOT
Major Challenges Faced
Controversies and Criticisms
Handling Regulatory Issues and Disputes
Final Thoughts
New York Board of Trade (NYBOT) FAQs
The New York Board of Trade (NYBOT) is a leading commodity futures exchange where various commodities and financial derivatives are traded.
Trading on NYBOT occurs through both open outcry and electronic trading systems, with the latter becoming more dominant in recent years.
NYBOT plays a significant role in the global financial markets by providing a platform for trading commodity futures and options, contributing to price discovery, and offering risk management tools.
Some of the challenges faced by NYBOT include competition from other exchanges, regulatory pressures, and the need to continually innovate in response to changing market conditions.
NYBOT has evolved through various mergers and acquisitions and has transitioned from open outcry trading to a predominantly electronic trading platform.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











