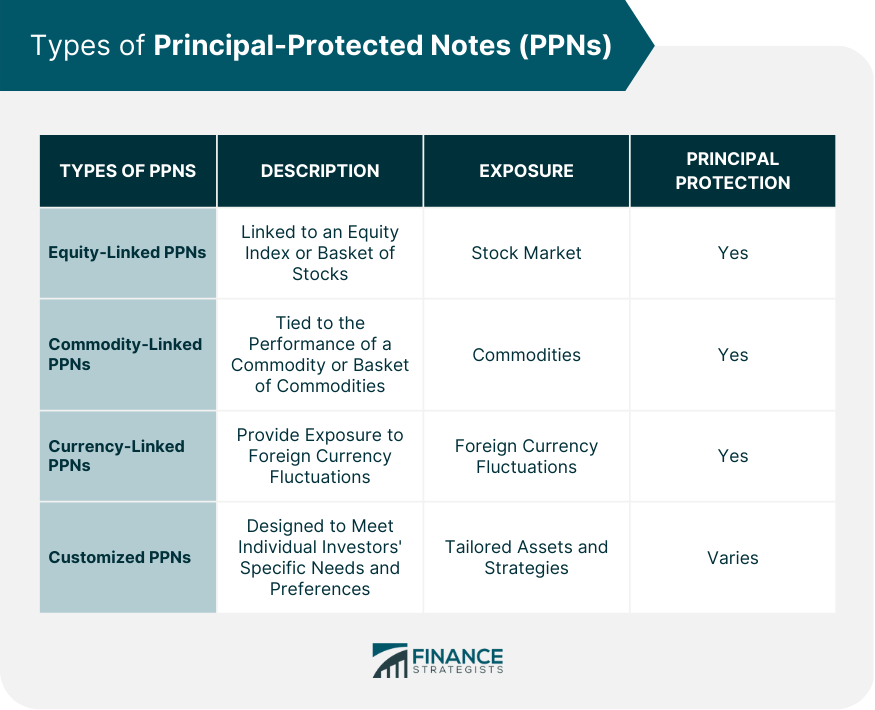
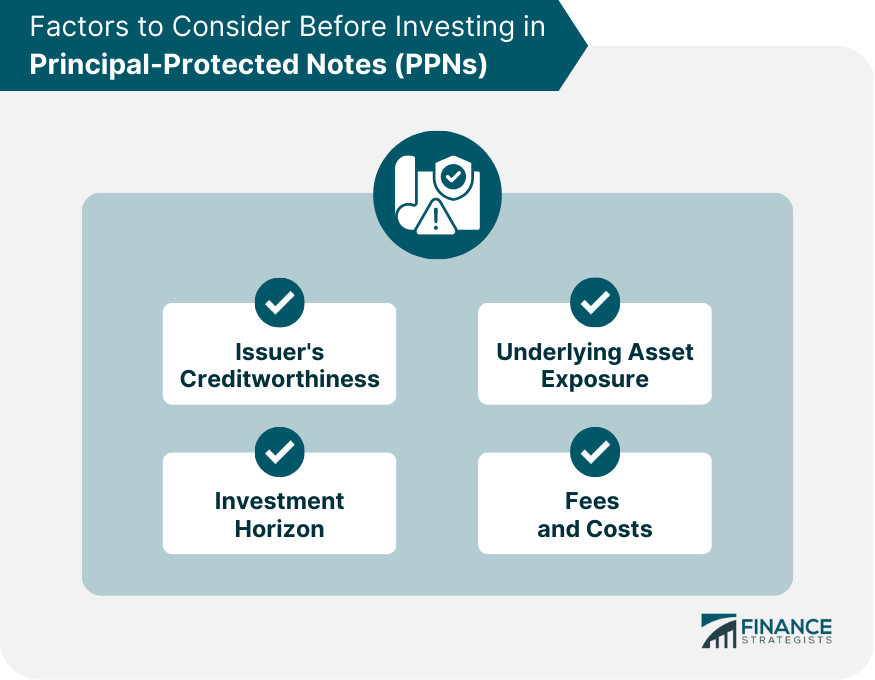
Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs) are a type of fixed-income security that allows investors to participate in the potential growth of an underlying asset while preserving their initial investment. PPNs are structured financial products that combine the features of both traditional bonds and derivative instruments. The primary purpose of PPNs is to provide investors with a balance of risk and reward, ensuring the safety of their principal investment while offering the potential for higher returns. PPNs are characterized by several key features, including principal protection, the potential for higher returns, and diversification. These features make PPNs an attractive investment option for conservative investors seeking to balance risk and reward in their portfolios. The structure of a PPN consists of two main components: a bond and a derivative. The bond portion of the PPN is typically a zero-coupon bond, which guarantees the return of the principal amount at maturity. The derivative component, often in the form of an option or a basket of options, provides exposure to the underlying asset, such as stocks, indices, or commodities. The combination of these components allows investors to benefit from the potential growth of the underlying asset without risking their initial investment. There are several types of PPNs, which vary based on the structure and underlying assets. Some common types include: Equity-Linked PPNs: These PPNs are linked to an equity index or a basket of stocks, allowing investors to gain exposure to the stock market while protecting their principal investment. Commodity-Linked PPNs: These PPNs are tied to the performance of a commodity or a basket of commodities, offering investors the opportunity to invest in commodities without risking their initial investment. Currency-Linked PPNs: These PPNs provide exposure to foreign currency fluctuations while preserving the principal investment. Customized PPNs: Some PPNs are designed to meet individual investors' specific needs and preferences, offering tailored exposure to various assets and strategies. PPNs are particularly suited for conservative investors seeking a balance between risk and reward in their investment portfolios. This includes risk-averse individuals, such as retirees or those nearing retirement, who wish to preserve their capital while still participating in the potential growth of various asset classes. Before investing in PPNs, investors should consider the following factors: Issuer's Creditworthiness: Assessing the credit rating and financial stability of the PPN issuer is crucial to ensure the safety of the principal invested. Underlying Asset Exposure: Investors should evaluate the underlying asset or index to which the PPN is linked, considering their investment objectives and risk tolerance. Investment Horizon: PPNs are typically long-term investments, so investors should ensure that their investment horizon aligns with the maturity of the PPN. Fees and Costs: PPNs may involve various fees and costs, such as management fees or sales charges, which can affect the overall return on investment. Investors should consider their overall investment strategy, risk tolerance, and investment objectives when incorporating PPNs into their portfolios. PPNs can complement other fixed-income securities, such as bonds and bond funds, and serve as a diversification tool by providing exposure to various asset classes and strategies. The tax treatment of PPNs may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific structure of the note. Generally, interest income, capital gains, and losses from PPNs are subject to taxation. Investors should consult a tax advisor to understand the tax implications of investing in PPNs and to ensure compliance with applicable tax laws. PPNs are subject to various regulatory requirements and oversight, depending on the jurisdiction in which they are issued. Regulatory bodies, such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), govern the issuance, marketing, and trading of PPNs to protect investors and maintain market integrity. One of the main benefits of investing in PPNs is the safety of the initial investment. The bond component of the PPN guarantees the return of the principal amount at maturity, ensuring that investors do not lose their initial investment, regardless of the underlying asset's performance. PPNs offer higher returns than traditional bonds, as the derivative component provides exposure to the underlying asset's growth. This allows investors to participate in the potential gains of the underlying asset without directly investing in it and risking their principal. PPNs can serve as an effective diversification tool in a balanced investment portfolio. By offering exposure to various asset classes and strategies, PPNs can help reduce a portfolio's overall risk and improve its risk-adjusted returns. While PPNs offer principal protection, they are not entirely risk-free. The guarantee of principal repayment is contingent on the creditworthiness of the PPN issuer. If the issuer defaults or becomes insolvent, the principal protection may be compromised, and investors may suffer losses. PPNs may be less liquid than other types of fixed-income securities, as they are often issued in smaller quantities and may not be widely traded. This can make it difficult for investors to sell their PPNs before maturity, potentially limiting their ability to access their invested capital in case of emergencies or changing market conditions. Investing in PPNs may involve an opportunity cost, as the potential returns may be lower compared to other investment options, such as directly investing in stocks, commodities, or currencies. Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance and investment objectives before opting for PPNs over other investment alternatives. The market for PPNs is influenced by various factors, including interest rates, economic conditions, and investor sentiment. Changes in these factors can affect the demand for PPNs and their pricing and structure. Investors should stay informed about market trends and developments to make informed investment decisions in PPNs. As financial markets evolve and investor preferences change, the PPN landscape may undergo transformations, with new types of PPN structures and underlying assets emerging. Innovations in financial technology and the increasing adoption of digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies, may also influence the development of PPNs. Investors should watch the PPN market's evolution closely to capitalize on potential opportunities and adapt their investment strategies accordingly. Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs) present a compelling investment option for conservative investors who wish to balance risk and reward in their portfolios. These unique financial instruments combine the safety of traditional bonds with the potential for higher returns through exposure to various underlying assets. However, it is crucial for investors to consider the risks, limitations, and factors associated with PPNs to make informed investment decisions. As the market for PPNs evolves, staying informed about emerging trends and developments is essential for capitalizing on potential opportunities. To ensure that PPNs align with your investment goals and risk tolerance, seek professional wealth management services to help you navigate the complexities of these financial instruments and create a tailored investment strategy for your unique needs.What Are Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs)?
Structure of Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs)
Types of Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs)
Principal-Protected Notes’ (PPNs) Investment Strategies and Considerations
Suitable Investors for Principal-Protected Notes
Factors to Consider Before Investing in PPNs
Incorporating PPNs into an Investment Portfolio
Tax Implications and Regulatory Aspects of Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs)
Tax Treatment of PPNs
Regulatory Framework
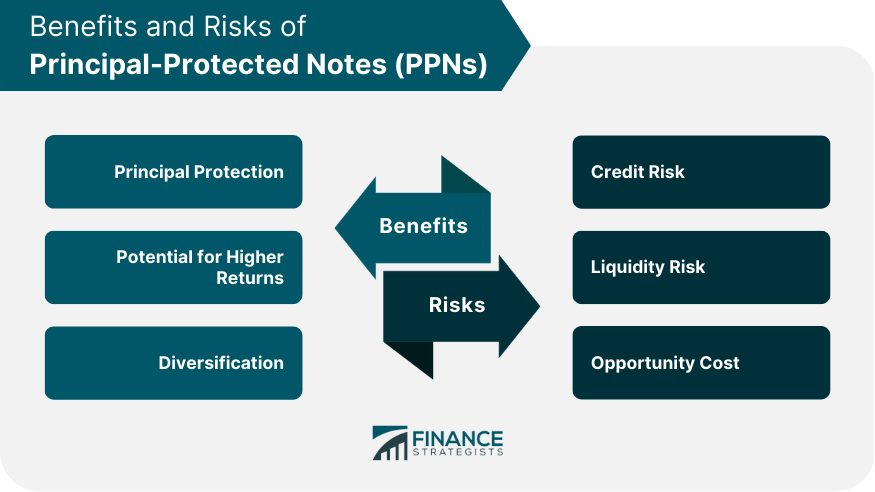
Benefits of Investing in Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs)
Principal Protection: Safety of Initial Investment
Potential for Higher Returns: PPNs vs Traditional Bonds
Diversification: PPNs in a Balanced Portfolio
Risks and Limitations of Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs)
Credit Risk: Dependence on Issuer's Creditworthiness
Liquidity Risk: Challenges in Trading PPNs
Opportunity Cost: PPNs vs Other Investment Options
Future Prospects and Developments in the Principal-Protected Notes Market
Market Trends and Influences on PPNs
Potential Innovations and Changes in the PPN Landscape
Final Thoughts
Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs) FAQs
Principal-Protected Notes (PPNs) are a type of fixed-income security that offers investors the opportunity to participate in the potential growth of an underlying asset, such as stocks or commodities while preserving their initial investment. PPNs combine the features of both traditional bonds and derivative instruments, providing principal protection and the potential for higher returns.
PPNs consist of two main components: a bond and a derivative. The bond portion, typically a zero-coupon bond, guarantees the return of the principal amount at maturity. The derivative component, often in the form of an option or a basket of options, provides exposure to the underlying asset. This structure allows investors to benefit from the potential growth of the underlying asset without risking their initial investment.
The primary benefits of investing in PPNs include principal protection, the potential for higher returns compared to traditional bonds, and diversification. Principal protection ensures the safety of the initial investment, while the derivative component offers the potential for higher returns through exposure to various underlying assets.
While PPNs offer principal protection, they are not entirely risk-free. The main risks associated with PPNs include credit risk (dependence on the issuer's creditworthiness), liquidity risk (challenges in trading PPNs), and opportunity cost (potential lower returns compared to other investment options).
PPNs are particularly suited for conservative investors seeking a balance between risk and reward in their investment portfolios. This includes risk-averse individuals, such as retirees or those nearing retirement, who wish to preserve their capital while still participating in the potential growth of various asset classes.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











