A Quantity-Adjusting Option, or Quanto Option, is a derivative instrument that offers exposure to a foreign asset while eliminating foreign exchange risk. It's a cross-derivative security, deriving its value from an asset in one country while being denominated in the currency of another. There are three main types: Quanto Call Options, Quanto Put Options, and Exotic Quanto Options, each offering different rights to the option holder. Quanto Options offer several benefits, including hedging against exchange rate risk, potential for high returns, and lower transaction costs. However, they also present certain risks, such as market risk due to poor asset performance, counterparty risk if the issuing institution defaults, potential for lower returns in cases of early exercise, and the possibility of significant losses due to incorrect pricing. As such, they represent a complex but potentially profitable instrument for sophisticated investors. Quanto Options are structured like traditional options, with a strike price and expiration date. However, they have an additional feature: the payout is converted from the asset's currency into the option holder's currency at a predetermined exchange rate, known as the Quanto Factor. This exchange rate is fixed and does not fluctuate with market exchange rates. The pricing of Quanto Options is more complex than traditional options due to the added layer of exchange rate risk. Quanto Option pricing uses the Black-Scholes model with an adjustment for the foreign exchange risk. This adjustment is the expected return on the foreign currency relative to the domestic currency. The underlying asset in a Quanto Option could be a stock, commodity, or index, while the currency in which it is denominated is typically a stable, widely traded currency like the US Dollar or Euro. For instance, a US investor could buy a Quanto Option on a European stock, where the payoff is in dollars, thereby eliminating the need to worry about Euro-Dollar exchange rate fluctuations. Quanto Options offer the unique advantage of hedging against exchange rate risk. By locking in the exchange rate at the outset, investors can focus on the performance of the underlying asset without worrying about adverse currency movements. A Quanto Call Option gives the holder the right to purchase the underlying asset at a specific price before the option expires. The payoff is converted from the asset's currency into the holder's currency at the pre-determined Quanto Factor. For example, an American investor buys a Quanto Call Option on a European stock priced in euros. The strike price is $100, and at expiration, the stock trades at €120. If the exchange rate is $1.2/€, the intrinsic value should be €201.2 = $24. However, in a Quanto Option, the payoff is unaffected by exchange rates. If the contract specifies $1/€, the payoff would be €201 = $20, protecting the investor from exchange rate fluctuations. A Quanto Put Option, on the other hand, gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at a specific price before the option expires. As with the Quanto Call Option, the payoff is converted into the holder's currency using the Quanto Factor. For example, let's say you're an investor based in the U.S. You purchase a Quanto Put Option on a European stock currently priced at €100. The strike price of the option is also €100, and the payoff is in USD with a fixed exchange rate of 1.2 (1€ = $1.2). If the European stock drops to €90 at expiry, your Quanto Put Option would give you the right to sell the stock at the strike price (€100), even though the market price is only €90. The payoff would be the difference between the strike price and the market price (€10), converted into dollars at the fixed rate, which equals $12 ($1.2 * 10€). The payoff is received in USD, irrespective of the current exchange rate. There are also variations of Quanto Options, often referred to as exotic options, such as Quanto Barrier Options and Quanto Binary Options. These exotic options have additional features that offer more flexibility or complexity. An Exotic Quanto Option could have additional features. For instance, a Knock-In Quanto Put Option only becomes active if the underlying asset's price drops to a certain level (the knock-in level). So, if the knock-in level was €95, and the stock's price never drops to that level, the option would expire worthless, even if it would've been profitable under regular Quanto Option terms. One of the primary benefits of Quanto Options is their ability to hedge against exchange rate risk. For international investors, exchange rate risk can significantly impact returns. Quanto Options eliminate this risk, making them an attractive instrument for investors. Quanto Options can provide high returns if the underlying asset performs well, and the investor's home currency strengthens against the asset's currency. Quanto Options also lower transaction costs because there is no need for separate foreign exchange transactions. The payout is already in the investor's home currency. Like any investment, Quanto Options carry market risk. If the underlying asset performs poorly, the investor stands to lose their investment. Counterparty risk is the likelihood that the other party in a financial contract will default or fail to meet their obligations. This risk can occur in various transactions, such as swaps, forward contracts, and loans. It becomes particularly prominent during periods of financial instability. In certain scenarios, there may be a risk of early exercise. If the underlying asset performs exceptionally well before the option expires, the holder might choose to exercise the option prematurely. However, this could potentially result in lower-than-expected returns if the asset's price continues to rise. Finally, given the complexity of Quanto Options pricing, there's a risk associated with incorrect pricing. If the option is not correctly priced at the outset, it could lead to significant losses. Investors use Quanto Options to gain exposure to foreign assets without taking on foreign exchange risk. For instance, an American investor might buy a Quanto Option on a Japanese stock to benefit from its potential rise while avoiding fluctuations in the USD/JPY exchange rate. Companies and financial institutions also use Quanto Options as a risk management tool. For instance, a European company might purchase a Quanto Option on a commodity like oil, which is priced in dollars, to hedge against both oil price risk and Euro-Dollar exchange rate risk. In international trade, Quanto Options can be used to hedge against currency and commodity price risks. For instance, an exporter who gets paid in a foreign currency and whose costs are linked to a commodity price could use a Quanto Option to manage both these risks. Quanto Options can be used to diversify a portfolio. By offering exposure to foreign assets without foreign exchange risk, they allow investors to broaden their investment universe and reduce portfolio risk. Quanto Options are also a valuable risk management tool. By hedging against foreign exchange risk, they reduce the portfolio's volatility and protect against adverse market movements. If used correctly, Quanto Options can enhance portfolio performance. By allowing investors to invest in high-performing foreign assets without worrying about currency risk, they can potentially boost returns. Like all financial instruments, Quanto Options are subject to regulatory oversight. In the US, for instance, they come under the jurisdiction of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). Quanto Options trading involves certain legal aspects, such as contract law and securities law. It's crucial for investors to understand these legal aspects to ensure compliance and protect their interests. Ethical considerations also play a role in Quanto Options trading. Market manipulation, insider trading, and front-running are some of the unethical practices that traders need to be aware of and avoid. Quantity-Adjusting Options, or Quanto Options, are a type of exotic option that derive their value from an asset in one country but are denominated in the currency of another, removing exchange rate risk. There are three primary types: Quanto Call Options, Quanto Put Options, and Exotic Quanto Options, each offering unique trading possibilities. The benefits of these options include hedging against exchange rate risk, the potential for high returns, and reduced transaction costs. However, investors must be mindful of the risks, including market risk, counterparty risk, the potential for early exercise, and the risk of incorrect pricing. In essence, Quanto Options present an innovative financial instrument that allows investors to engage with international markets while mitigating currency volatility, but careful consideration of the inherent risks is crucial to successful investment.Definition of Quantity-Adjusting Options (Quanto Options)
Mechanics of Quanto Options
Understanding the Structure of Quanto Options
How Quanto Options Are Priced
Underlying Assets and Currencies in Quanto Options
Role of Exchange Rate Risk in Quanto Options
Types of Quanto Options
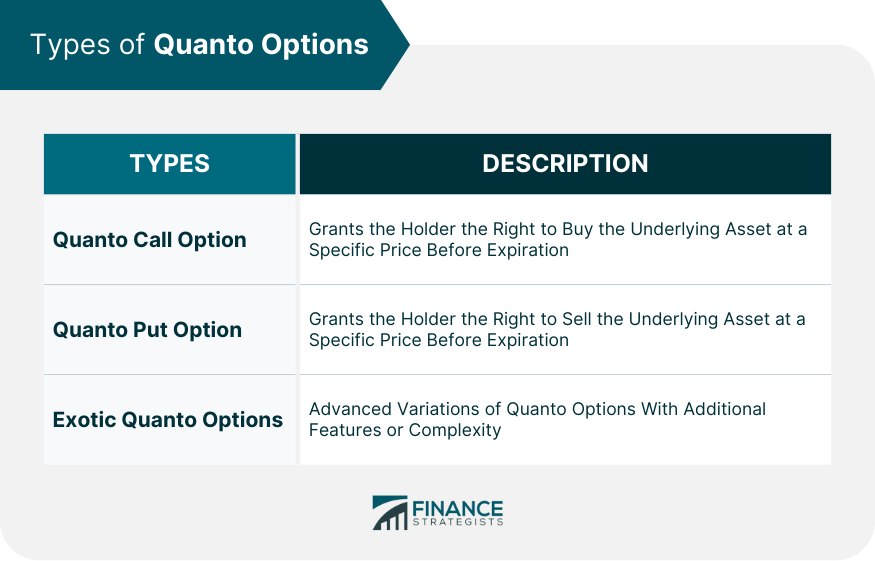
Quanto Call Option
Quanto Put Option
Exotic Quanto Options
The Benefits of Quanto Options

Hedging Against Exchange Rate Risk
Potential for High Returns
Lower Transaction Costs
Risks Associated With Quanto Options
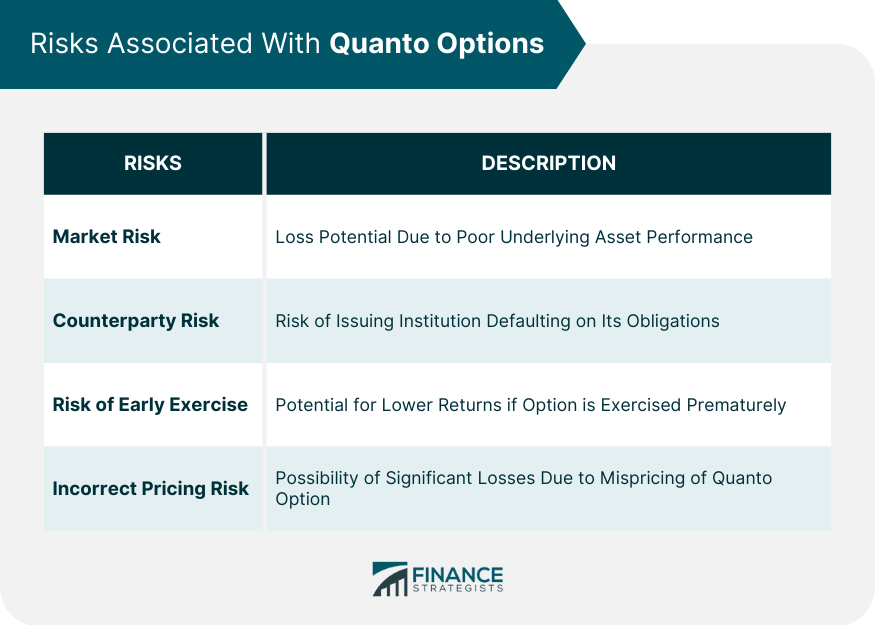
Market Risk
Counterparty Risk
Risk of Early Exercise
Risks Associated With Incorrect Pricing
Practical Uses of Quanto Options
Usage by Investors
Usage by Companies and Financial Institutions
Application in International Trade
The Role of Quanto Options in Portfolio Management
Diversification Benefits
Risk Management Strategies
Impact on Portfolio Performance
Regulatory and Legal Aspects of Quanto Options
Regulatory Bodies Overseeing Quanto Options
Legal Aspects of Quanto Options Trading
Ethical Considerations in Quanto Options Trading
Conclusion
Quantity-Adjusting Option (Quanto Option) FAQs
A Quanto Option is a derivative instrument that derives its value from an asset in one country while being denominated in the currency of another. This mechanism allows investors to gain exposure to foreign assets while eliminating foreign exchange risk.
There are three main types of Quanto Options: Quanto Call Options, Quanto Put Options, and Exotic Quanto Options. Each type offers different rights to the option holder regarding buying or selling the underlying asset.
Quanto Options offer several benefits, including the ability to hedge against exchange rate risk, the potential for high returns if the foreign asset performs well, and lower transaction costs as separate foreign exchange transactions are not required.
The risks associated with Quanto Options include market risk, counterparty risk, the risk of early exercise, and incorrect pricing risk. These risks could potentially lead to significant losses for the investor.
The pricing of Quanto Options is more complex than traditional options due to the added layer of exchange rate risk. Quanto Option pricing uses the Black-Scholes model with an adjustment for the foreign exchange risk, which is the expected return on the foreign currency relative to the domestic currency.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











