Asset Management Company (AMC) Overview
An Asset Management Company (AMC) is a firm that invests pooled funds from clients into a variety of securities and assets. AMCs manage these investments to achieve specific financial goals based on the client's needs, risk tolerance, and investment horizon.
These goals can range from capital appreciation, and preserving capital to providing regular income. The assets managed can be diverse, including stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and other investment vehicles like mutual funds.
AMCs charge a fee for their services, usually, a percentage of the total assets managed. They play a vital role in the financial sector, helping individuals, corporations, and governments efficiently manage their wealth and navigate complex financial markets.
Functions of an Asset Management Company
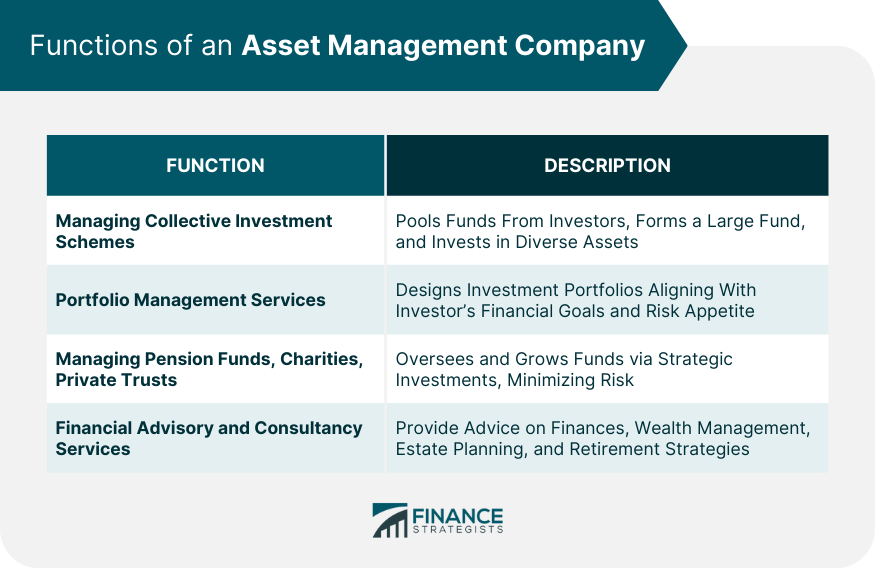
Managing Collective Investment Schemes
At the heart of an AMC's function is the management of collective investment schemes, such as mutual funds. AMCs pool together money from multiple investors to form a large fund, which is then invested across a variety of assets like stocks, bonds, and commodities.
This diversification mitigates risks and helps to ensure more stable returns.
Portfolio Management Services
Another function of AMCs is offering portfolio management services. These services involve understanding the financial goals and risk appetite of individual investors and tailoring an investment portfolio to match these needs.
Managing Pension Funds, Charities, and Private Trusts
AMCs also oversee pension funds, charities, and private trusts, aiming to grow these funds through strategic investments while minimizing risk.
Financial Advisory and Consultancy Services
Lastly, AMCs provide financial advisory and consultancy services. This entails advising clients on various aspects of their finances, from wealth management to estate planning and retirement strategies.
Types of Asset Management Companies
There are several types of AMCs that cater to different markets and clients.
Independent AMCs
These are standalone companies that focus solely on asset management. Independent AMCs are not tied to any banking or financial institution and therefore offer a wide range of investment opportunities.
Bank-Affiliated AMCs
As the name suggests, these are asset management companies that are part of larger banking institutions. They often manage the wealth of the bank's customers and offer a range of investment products.
Insurance AMCs
Insurance AMCs are tied to insurance companies and manage the investment portfolios that underpin insurance contracts.
Boutique AMCs
Smaller, specialized AMCs focus on specific sectors or investment strategies. They often appeal to investors who prefer a more personalized service.

How an Asset Management Company Operates
An AMC operates by understanding the financial needs and risk tolerance of its clients and then constructing a suitable investment portfolio to meet those needs.
Understanding the Client's Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
The AMC works closely with the client to understand their financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment time horizon.
Constructing a Suitable Investment Portfolio
Based on the client's preferences and risk tolerance, the AMC then constructs an investment portfolio. This portfolio is a carefully chosen mix of assets designed to achieve the client's financial goals.
Constant Monitoring and Rebalancing of Portfolio
Once the portfolio is created, the AMC continuously monitors the investments and rebalances the portfolio as needed to maintain the desired level of risk and return.
Services Offered by Asset Management Companies
AMCs offer a range of services to meet the diverse needs of their clients.
Mutual Fund Management
AMCs manage mutual funds, which pool together money from many investors to invest in a diverse array of assets.
Hedge Fund Management
AMCs also manage hedge funds, which are sophisticated investment vehicles designed to hedge against market volatility.
Private Equity and Venture Capital Management
In addition, AMCs manage private equity and venture capital funds. These funds are designed for high-net-worth individuals and institutions looking for higher returns and are willing to take on more risk.
Real Estate Asset Management
Finally, some AMCs specialize in managing real estate investments. This can involve purchasing and managing properties or investing in real estate investment trusts (REITs).

Benefits of Asset Management Companies
Professional Management
AMCs provide professional investment management services, leveraging expert knowledge and sophisticated tools to navigate financial markets effectively.
Diversification
AMCs spread investments across a wide range of assets, which can help to reduce risk and enhance potential returns.
Convenience and Time-Saving
With an AMC, investors can access a variety of investments without having to manage each one individually, saving time and effort.
Risks of Asset Management Companies
Market Risk
Like all investment vehicles, AMCs are exposed to market risks. Changes in market conditions can impact the performance of the investments managed by the AMC.
Management Risk
There is always a risk that the AMC's investment strategies may not perform as expected, potentially leading to losses.
Fees and Charges
AMCs charge fees for their services, which can erode returns if not managed correctly. It's essential for investors to understand the fee structure of their chosen AMC.

Regulatory Environment of an Asset Management Company
AMC operates in a highly regulated environment, designed to protect investors and maintain the integrity of the financial markets.
Regulatory Bodies Overseeing AMCs
Various regulatory bodies oversee the operation of AMCs. In the U.S., this includes the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Common Regulations and Compliances for AMCs
AMCs must comply with various regulations, including those regarding disclosure of information, fair practices, and risk management.
Role of Transparency and Disclosure
Transparency and disclosure plays a critical role in the regulatory environment of AMCs. This includes the disclosure of all relevant information to the investors, such as fees, risks, and performance.
Role of Technology in an Asset Management Company
Technology plays a significant role in modern AMCs, helping to improve efficiency and provide better services to clients.
Fintech and Robo-advisors
Fintech has revolutionized the asset management industry. Robo-advisors, for example, use algorithms to create and manage investment portfolios, often at a lower cost than traditional AMCs.
AI, Machine Learning, and Big Data in Asset Management
AI, machine learning, and big data are also increasingly used in asset management. These technologies can help to predict market trends, manage risks, and provide personalized investment advice.
Cybersecurity in Asset Management
As technology use increases, so too does the importance of cybersecurity. AMCs must ensure that their digital platforms are secure to protect sensitive client information and comply with data protection regulations.
Conclusion
Asset Management Companies (AMCs) play an instrumental role in the financial sector.
They oversee the allocation of pooled funds into a variety of assets to help clients reach their financial objectives, offering services like mutual fund management, hedge fund management, and financial advisory.
Different types of AMCs cater to various markets, including independent, bank-affiliated, insurance, and boutique firms.
The operation of an AMC involves understanding a client's financial goals and risk tolerance, building a suitable portfolio, and continuously monitoring and adjusting it.
While the benefits of AMCs include professional management, diversification, and convenience, they do come with risks like market volatility and management risk. In the highly regulated environment in which they operate, transparency and disclosure are paramount.
Lastly, AMCs are leveraging technology such as fintech, AI, and big data to enhance their services, underscoring the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
Asset Management Company (AMC) FAQs
The primary role of an AMC is to manage its clients' investments to achieve specific financial goals. They construct and manage investment portfolios, diversifying across various asset classes to minimize risk and maximize returns.
AMCs offer a wide range of services including mutual fund management, hedge fund management, private equity and venture capital management, real estate asset management, and financial advisory and consultancy services.
An AMC begins by understanding the financial goals and risk tolerance of its clients. Based on these insights, the AMC constructs a suitable investment portfolio. The AMC then continuously monitors the portfolio's performance, making necessary adjustments to keep it aligned with the client's goals.
AMCs face several challenges including market volatility and investment risk, changes in regulations and compliance risk, and operational and technological risks such as system failures and cybersecurity threats.
Technology plays a significant role in modern AMCs, helping to improve efficiency and provide better services. This includes the use of fintech and robo-advisors, AI and machine learning for data analysis and personalized advice, and increased focus on cybersecurity to protect client information.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











