Life Cycle Asset Management Overview
Life Cycle Asset Management (LCAM) is a strategic approach employed by organizations to optimize the value and performance of their assets throughout their life cycle.
This comprehensive process starts from asset acquisition, through its use and maintenance, and up to its disposal. LCAM enables informed decision-making by providing insights into an asset's total cost of ownership and expected life span.
It also plays a critical role in financial planning, facilitating accurate budgeting and investment decisions. Moreover, LCAM incorporates the use of technology, such as AI and machine learning, for predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of assets.
With evolving trends like sustainability, circular economy, and integration of ESG principles, LCAM is set to play an increasingly crucial role in strategic asset management.
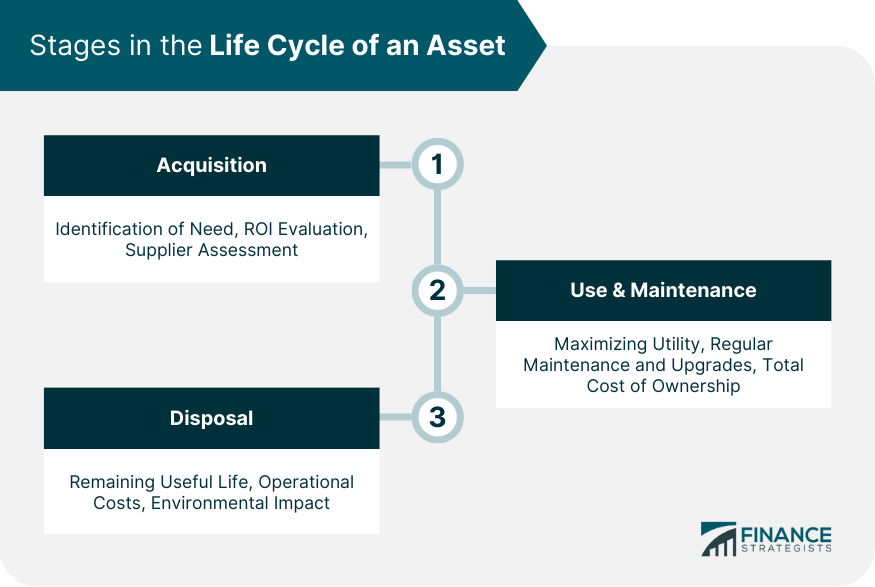
Stages in the Life Cycle of an Asset
Acquisition Stage
The acquisition phase represents the inception of an asset's life cycle. During this stage, organizations identify the need for an asset, evaluate available options, and procure the most appropriate one.
This process requires a deep understanding of the asset's role in the organization's operations and the anticipated return on investment. It also involves a thorough assessment of potential suppliers and negotiation of the terms of the acquisition.
Use and Maintenance Stage
Once acquired, an asset enters the use and maintenance stage. Here, organizations focus on maximizing the asset's utility and extending its life span through regular maintenance and upgrades.
Proper maintenance not only ensures efficient operation of the asset but also prevents premature breakdowns and costly repairs. In this stage, an organization's asset management strategy can influence the total cost of ownership and the overall value derived from the asset.
Disposal Stage
The final stage in an asset's life cycle is disposal.
This could involve selling the asset, recycling its components, or decommissioning it. Disposal decisions should be guided by considerations such as the remaining useful life of the asset, the costs associated with continued operation, and environmental impact.
Even in this final stage, effective LCAM can yield significant cost savings and mitigate potential risks.
Strategies for Life Cycle Asset Management
Asset Management Policy
An asset management policy sets the overall direction for managing an organization's assets. It establishes the principles and expectations for asset management and provides a framework for decision-making.
A robust asset management policy should align with the organization's strategic objectives and comply with relevant regulatory requirements.
Asset Management Strategy
The asset management strategy outlines how an organization will achieve its asset management objectives. It includes strategic initiatives, performance targets, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
The strategy should be dynamic, reflecting changes in the organization's operating environment and evolving business needs.
Asset Management Plan
An asset management plan provides a detailed roadmap for managing an asset over its life cycle. It specifies the actions, resources, and timelines required to maintain and improve the asset's performance.
The plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness.

Technology in Life Cycle Asset Management
Role of Technology in Life Cycle Asset Management
Technology plays a pivotal role in LCAM. It facilitates data collection, analysis, and visualization, enabling organizations to make evidence-based decisions.
Technology also automates routine tasks, improving efficiency and accuracy. Moreover, it supports real-time monitoring of assets, allowing organizations to proactively manage asset performance and mitigate potential risks.
Use of AI and Machine Learning in Life Cycle Asset Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming LCAM. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, wherein algorithms analyze asset data to predict potential failures before they occur.
This approach reduces downtime and extends the life span of assets. AI and ML also support decision-making by providing insights into patterns and trends that might not be readily apparent.
Digital Twin and IoT in Life Cycle Asset Management
The digital twin and the Internet of Things (IoT) are other technological advancements shaping LCAM. A digital twin is a virtual model of a physical asset that simulates its performance under various conditions.
This tool helps in testing and optimizing asset performance without disrupting operations. On the other hand, IoT devices facilitate real-time data collection from assets, enhancing monitoring and control capabilities.
Impact of Blockchain on Life Cycle Asset Management
Blockchain technology offers significant potential for LCAM. It provides a transparent and immutable record of asset transactions, improving traceability and accountability.
Blockchain can also facilitate automated contractual agreements through smart contracts, streamlining procurement and disposal processes. Furthermore, it enhances security by protecting data from unauthorized access and manipulation.
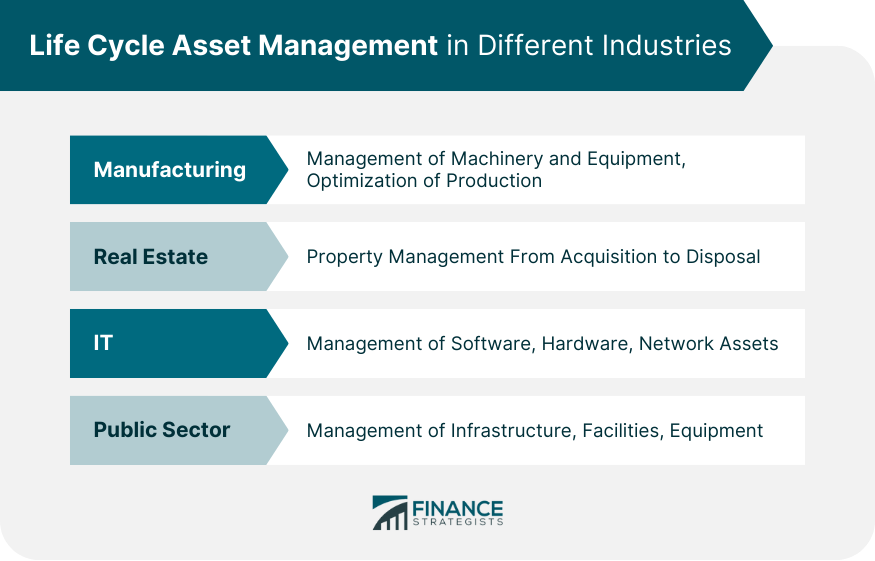
Life Cycle Asset Management in Different Industries
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, LCAM is critical for optimizing production and minimizing costs. It involves managing a wide range of assets, from machinery and equipment to IT systems.
Effective LCAM ensures these assets function optimally, reducing downtime, improving product quality, and enhancing operational efficiency.
Real Estate
In real estate, LCAM encompasses the management of properties from acquisition to disposal. It includes activities such as property valuation, maintenance, renovation, leasing, and sale.
Through effective LCAM, real estate firms can enhance property values, improve tenant satisfaction, and maximize returns on investment.
IT
In the IT sector, LCAM focuses on managing software, hardware, and network assets. It involves tasks such as software licensing, hardware maintenance, network management, and data security.
Effective LCAM in IT not only enhances system performance and reliability but also ensures regulatory compliance and mitigates cyber risks.
Public Sector
In the public sector, LCAM is used to manage assets like infrastructure, facilities, and equipment. Public sector entities utilize LCAM to optimize public service delivery, ensure asset longevity, comply with regulations, and safeguard public investments.
Conclusion
Life Cycle Asset Management (LCAM) is an essential strategic tool that enhances an organization's ability to optimize the value and performance of assets across their life cycle. This holistic approach includes acquisition, utilization, maintenance, and disposal stages.
Underpinned by robust policies, strategies, and plans, LCAM ensures alignment with organizational goals and compliance with regulations.
The use of advanced technologies, including AI, machine learning, digital twins, IoT, and blockchain, bolsters the effectiveness of LCAM, providing predictive maintenance capabilities, real-time monitoring, and improved decision-making.
Applied across various sectors, from manufacturing and real estate to IT and the public sector, LCAM enhances operational efficiency, financial planning, risk management, and service delivery.
As trends like sustainability, circular economy, and ESG principles continue to evolve, LCAM's importance is set to increase, making it central to strategic asset management.
Life Cycle Asset Management FAQs
Technology plays a pivotal role in Life Cycle Asset Management (LCAM). It facilitates the collection, analysis, and visualization of data, enabling informed decision-making. Innovations such as AI and machine learning, IoT, digital twins, and blockchain are particularly influential, aiding in predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and enhancing security and traceability.
LCAM is integral to financial planning as it provides a comprehensive view of an asset's costs and value over its life cycle. This information enables accurate budgeting, informed investment decisions, and overall financial performance improvement. It also guides strategic planning and resource allocation in alignment with organizational objectives.
Risk management is a crucial component of LCAM. It involves identifying, assessing, and managing potential risks associated with an asset throughout its life cycle. Effective risk management not only prevents financial losses but also enhances the reliability and performance of assets.
Future trends in LCAM include predictive maintenance, sustainability, circular economy, and integration of ESG principles. Predictive maintenance uses AI and machine learning to anticipate and prevent potential asset failures. Sustainability and circular economy principles promote environmentally friendly asset management. Integration of ESG principles enhances risk management and stakeholder engagement.
In the manufacturing industry, for instance, LCAM involves managing a range of assets such as machinery, equipment, and IT systems. Effective LCAM ensures these assets function optimally, reducing downtime, improving product quality, and enhancing operational efficiency.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











