A Blockchain Address is a digital identifier unique to each user on the blockchain. Similar to how an email address allows you to send and receive emails, a blockchain address enables users to send and receive digital assets within the blockchain network. Each blockchain address is associated with a pair of cryptographic keys – a public key that is open to everyone on the network and a private key that remains confidential to the user. The primary purpose of a blockchain address is to facilitate transactions on a blockchain network. It serves as the destination or source of digital assets during a transaction. They are central to the functionality of blockchain technology and are a fundamental concept in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain addresses are created using complex cryptographic algorithms. When a user creates a digital wallet, a private key is randomly generated. From this private key, a corresponding public key is derived. The blockchain address is then created from a hash of this public key. Public and private keys serve as digital signatures for a blockchain address. The private key is confidential and used to sign transactions and access funds. The public key, derived from the private key, is shared with others in the network. It is used to verify the digital signature and confirm the authenticity of a transaction. When a transaction is initiated, it is signed with the sender's private key and then broadcasted to the network. The network participants can use the sender's public key to verify the transaction's authenticity. If the verification is successful, the transaction is added to the blockchain, and the digital assets are transferred from the sender's to the recipient's address. Blockchain addresses play a crucial role in the management of digital assets. In cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain addresses are used for sending and receiving digital currency. They're also pivotal in the operation of digital wallets and exchanges. In addition to handling transactions, blockchain addresses can be used for identity verification and authentication. Users can prove ownership of a digital asset or their identity through their private keys without disclosing sensitive personal information. Blockchain addresses are digital identifiers unique to each user on the blockchain, facilitating secure transactions and digital asset management. Through complex cryptographic algorithms, addresses are created from public and private keys. Practical applications include digital asset management and identity verification. Precautions involve secure storage of private keys, regular security updates, and awareness of scams. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, understanding and utilizing blockchain addresses remain essential for users to navigate this transformative landscape safely and effectively. Blockchain addresses offer robust security. The cryptographic keys used are nearly impossible to crack, making unauthorized access highly unlikely. Additionally, while transactions are transparent and traceable, the identity of the owner of a blockchain address remains anonymous, offering a degree of privacy. Blockchain addresses give users complete control over their digital assets. Unlike traditional bank accounts, users do not need approval from any third party to initiate transactions. This power enhances the autonomy of users and their control over their financial affairs. Blockchain addresses allow peer-to-peer transactions without the need for an intermediary, such as a bank or government. This decentralization makes transactions faster, cheaper, and accessible to people without access to traditional banking systems. The complexity of blockchain technology and the abstract nature of blockchain addresses can be overwhelming for the average user. Understanding the process of creating and managing blockchain addresses and their keys requires a certain level of technical knowledge. Once a transaction is verified and added to the blockchain, it cannot be reversed. If a user accidentally sends assets to an incorrect address, those assets are lost forever. This irreversibility can be a significant drawback for many users. While the use of blockchain addresses provides a level of anonymity, privacy can be compromised if addresses are reused for multiple transactions. Sophisticated analysis techniques can link addresses to individuals, potentially exposing their transaction history. Given that private keys grant access to the assets associated with a blockchain address, it is crucial to store them securely. The loss of private keys results in the permanent loss of digital assets, making secure storage practices paramount. To safeguard blockchain addresses and the assets they hold from cyber threats, it is essential to regularly update security measures. Implementing strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and utilizing secure digital wallets are recommended security practices. Users must remain vigilant to avoid falling victim to scams. Phishing attempts, fraudulent platforms, and various other forms of cybercrime pose risks to blockchain address security. Awareness and cautiousness are key to preventing the loss of digital assets. Blockchain addresses are digital identifiers unique to each user on the blockchain, facilitating secure transactions and digital asset management. Through complex cryptographic algorithms, addresses are created from public and private keys. The advantages of blockchain addresses include robust security, control over personal finance, and decentralized transactions. However, limitations such as difficulty in understanding and irreversibility of transactions exist. Practical applications include digital asset management and identity verification. Precautions involve the secure storage of private keys, regular security updates, and awareness of scams. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, understanding and utilizing blockchain addresses remain essential for users to navigate this transformative landscape safely and effectively.Definition of Blockchain Address
How a Blockchain Address Works
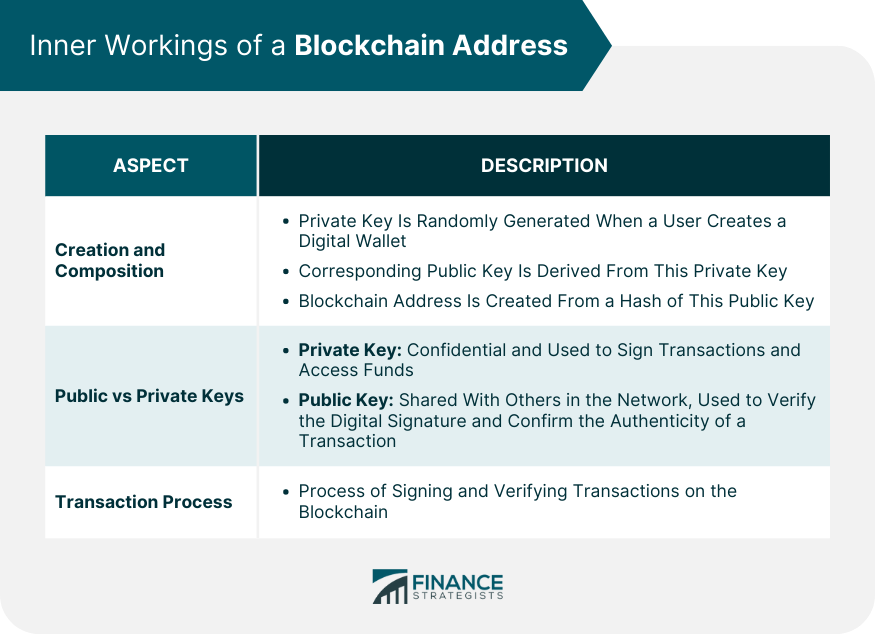
Creation and Composition
Public vs Private Keys
Transaction Process
Practical Applications and Use Cases of Blockchain Addresses
Digital Asset Management
Identity Verification and Authentication
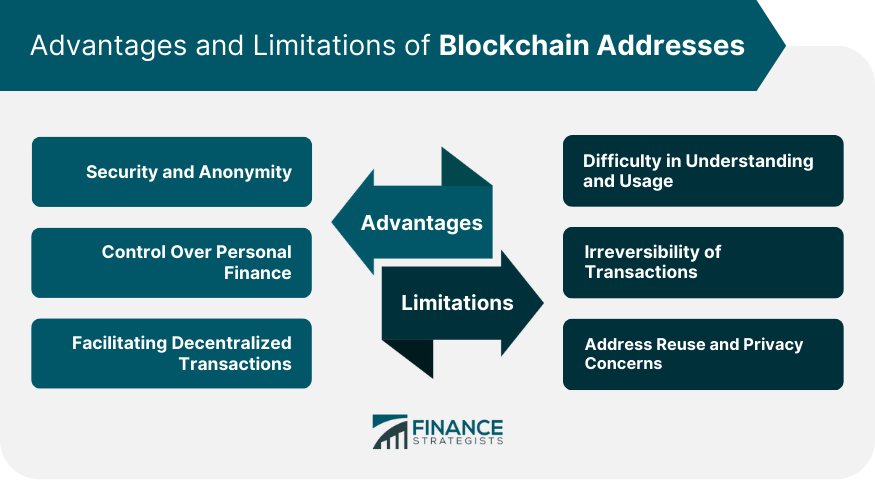
Advantages of Blockchain Addresses
Security and Anonymity
Control Over Personal Finance
Facilitating Decentralized Transactions
Limitations of Blockchain Addresses
Difficulty in Understanding and Usage
Irreversibility of Transactions
Address Reuse and Privacy Concerns
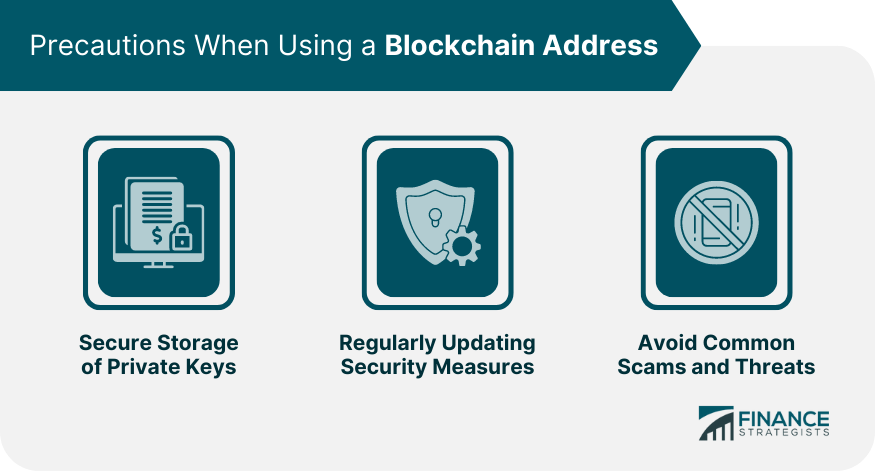
Precautions When Using a Blockchain Address
Secure Storage of Private Keys
Regularly Updating Security Measures
Avoiding Common Scams and Threats
Conclusion
Blockchain Address FAQs
A blockchain address is a unique digital identifier used for sending and receiving digital assets within the blockchain network.
Blockchain addresses are created using complex cryptographic algorithms that generate a pair of public and private keys.
Public keys are shared with others to verify transactions, while private keys remain confidential and are used to sign transactions and access funds.
Yes, blockchain addresses offer robust security with nearly impossible-to-crack cryptographic keys, while transactions remain transparent and the address owner's identity remains anonymous.
Securely store your private keys, regularly update security measures, and stay vigilant to avoid scams or cyber threats that could result in the loss of your digital assets.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











