Blockchain technology is the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. It is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that stores data in a chain of blocks, offering security and transparency. Democracy is the system of government where power is vested in the people. It is pivotal to society as it fosters equality, encourages participation, and values freedom of speech and thought. Blockchain technology has the potential to significantly impact democracy by enhancing transparency, accountability, and trust in democratic processes. Through its immutable and decentralized nature, blockchain can ensure that data and transactions are securely recorded and tamper-proof, addressing concerns of election fraud and manipulation. Blockchain-based voting systems can enable verifiable and auditable elections, increasing voter confidence. Decentralized governance mechanisms facilitated by blockchain can foster more inclusive decision-making processes, allowing citizens to participate directly in policy-making. Blockchain has the capacity to revolutionize democratic systems by promoting fairness, security, and citizen empowerment. Blockchain can support democratic processes by ensuring transparent, secure, and efficient systems for voting, identity management, and campaign financing. The immutability of the blockchain can help foster trust in democratic processes, which is often lacking in conventional systems. Blockchain, with its decentralized and transparent nature, is compatible with the principles of democracy. It can decentralize power and put it back into the hands of individuals. By leveraging blockchain technology, we can envision a democratic model where intermediaries are no longer required, and individuals have a more direct role in the decision-making process. The traditional voting system has been marred by various issues such as accessibility, transparency, and security. Blockchain technology presents a promising solution to these problems. A blockchain-based voting system can ensure transparency by enabling voters to track their votes and verify the final count. The immutability of blockchain ensures the votes cannot be tampered with, offering a high level of security. Countries like Estonia and Russia have already experimented with blockchain-based voting during elections. Mobile voting platform Voatz has also used blockchain to enable secure remote voting in West Virginia, United States. These blockchain-based voting initiatives have demonstrated the potential for more efficient, transparent, and secure electoral processes. Campaign financing has often been a contentious issue, with allegations of hidden contributions and illicit funds. Blockchain technology could offer a solution to these challenges. By leveraging blockchain, all campaign contributions could be recorded in a transparent, immutable ledger. This would enable the public to see exactly who is funding a campaign, promoting transparency and trust. Blockchain can also enable micro-donations, allowing more individuals to contribute to political campaigns and reducing dependence on large donors. Projects such as the Democracy.Earth Foundation are exploring blockchain for this purpose, aiming to make political funding more transparent and democratic. Identity management is critical in any democratic process. It ensures that only eligible citizens can vote and prevents fraudulent activities such as double voting. Blockchain can be used to create secure, verifiable digital identities. This can improve access to voting, particularly for diaspora and displaced populations who may not have access to traditional identity documents. A digital identity stored on a blockchain can be more secure than traditional methods of identity verification. It reduces the risk of identity theft and fraud, as the data is stored across multiple nodes and is encrypted. Estonia is a pioneer in this area, with its e-residency program offering digital identities for entrepreneurs worldwide. Blockchain's immutable and transparent nature can significantly enhance transparency and accountability in democratic processes. With blockchain, every transaction or vote is recorded and can be viewed by anyone, making it nearly impossible to manipulate results or hide illicit activities. This could restore public trust in democratic processes, which is often undermined by allegations of corruption or manipulation. Moreover, in the context of public spending, blockchain could provide a transparent record of how funds are being used, holding governments more accountable. Blockchain can ensure that every transaction, contract, or grant is recorded and made public, making it easier for citizens to scrutinize public spending. Blockchain technology can revolutionize voting systems by making them more secure and tamper-proof. With blockchain-based voting, each vote is recorded as a transaction on the blockchain, which is then verified by the network. Once recorded, the vote cannot be changed, ensuring that the final vote count is accurate. Moreover, blockchain could also offer solutions for remote voting, making the voting process more accessible. Remote voting systems based on blockchain can offer security and integrity, ensuring that only eligible voterscan vote and that each vote is accurately recorded. This could make democratic processes more inclusive and encourage higher voter turnout. Decentralization is a core principle of both blockchain and democracy. By leveraging blockchain, we can create decentralized governance mechanisms that give individuals more control over their data and decision-making processes. This could make democracy more participatory, as citizens could have a direct say in decisions that affect them, rather than relying solely on elected representatives. Blockchain can enable decentralized decision-making platforms where citizens can propose, discuss, and vote on issues directly. This could revolutionize the way democracy operates, fostering a more engaged and empowered citizenry. Projects like Bitnation and Democracy Earth are exploring this potential, using blockchain to create decentralized governance platforms. Blockchains, particularly public ones, can process only a limited number of transactions per second. This could be problematic in a large-scale voting scenario where millions of votes need to be processed in a short time. Furthermore, the verification process in blockchain, known as mining, requires significant computational power and energy. These scalability and performance issues could hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain in democratic processes. However, researchers and developers are exploring solutions, such as sharding and layer 2 protocols, to address these challenges. Another challenge in implementing blockchain in democracy is privacy and data protection. While blockchain can provide transparency, it can also expose sensitive data. For example, in a blockchain-based voting system, it would be essential to ensure that the identity of voters is not revealed. This presents a paradox: while transparency is necessary for trust, privacy is crucial for security and freedom. Moreover, once data is stored on a blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted. This could pose challenges in the context of data protection regulations, such as the right to be forgotten under the GDPR. Developers and policymakers would need to find a balance between transparency and privacy when implementing blockchain in democratic processes. Implementing blockchain in democratic processes would also require careful consideration of accessibility and inclusivity. While blockchain could potentially make voting more accessible, it could also exclude those who do not have access to the necessary technology or internet connection. Furthermore, using blockchain for democratic processes would require a certain level of digital literacy. If not addressed, this could lead to a digital divide, where only those with the necessary skills and resources can participate in the democratic process. Policymakers and developers would need to ensure that blockchain-based democratic processes are accessible and inclusive to all citizens. Blockchain and democracy, both underpinned by principles of decentralization and transparency, present a compelling intersection. The potential of blockchain to enhance democratic processes—through secure and transparent voting systems, accountable campaign financing, and verifiable digital identities—is significant. While blockchain can offer many benefits to democracy—including enhanced transparency and accountability, secure and tamper-proof voting, and decentralized governance—it also presents certain challenges. Scalability and performance issues, privacy and data protection concerns, and accessibility and inclusivity considerations must be addressed to realize the full potential of blockchain in democracy. If the challenges can be addressed, blockchain could revolutionize democratic processes, fostering a more transparent, secure, and participatory democracy.Overview of Blockchain Technology and Democracy
Relationship Between Blockchain and Democracy
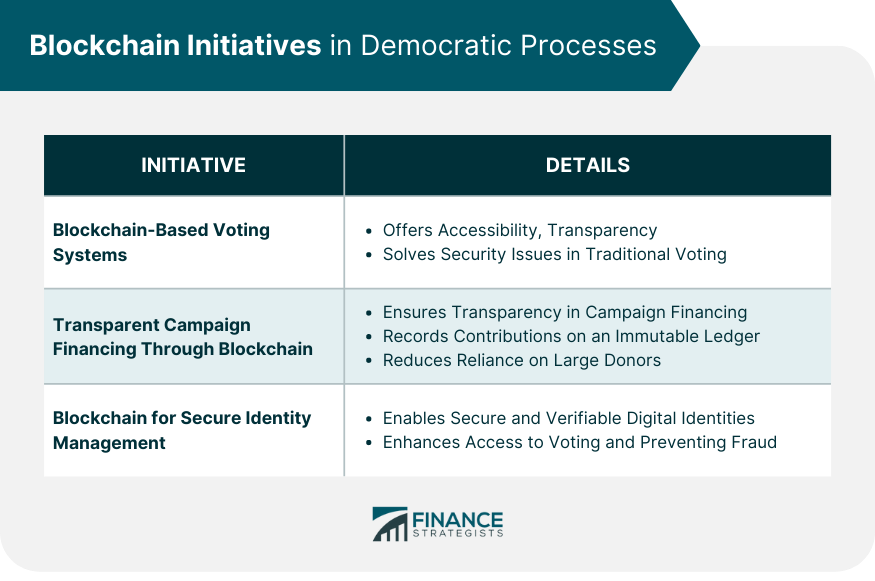
Blockchain Initiatives in Democratic Processes
Blockchain-Based Voting Systems
Transparent Campaign Financing Through Blockchain
Blockchain for Secure and Verifiable Identity Management
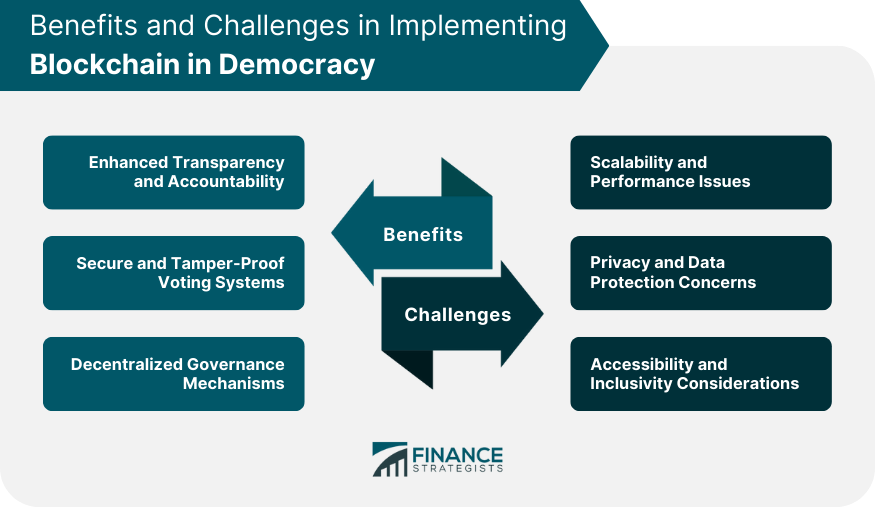
Benefits of Blockchain for Democracy
Enhanced Transparency and Accountability
Secure and Tamper-Proof Voting Systems
Decentralized Governance Mechanisms
Challenges in Implementing Blockchain in Democracy
Scalability and Performance Issues
Privacy and Data Protection Concerns
Accessibility and Inclusivity Considerations
Conclusion
Blockchain and Democracy FAQs
Blockchain technology can provide a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof platform for voting. Each vote is recorded as a transaction on the blockchain, which is then verified by the network. Once recorded, the vote cannot be changed, ensuring that the final vote count is accurate. Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate remote voting, making the voting process more accessible.
Blockchain can bring transparency to campaign financing by recording all campaign contributions on an immutable ledger. This allows the public to track funding sources and promotes accountability. Additionally, blockchain can enable micro-donations, reducing dependence on large donors and allowing more people to contribute to political campaigns.
Implementing blockchain in democratic processes presents several challenges, including scalability and performance issues, privacy and data protection concerns, and accessibility and inclusivity considerations. Overcoming these challenges will require technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and efforts to ensure digital literacy and access.
Blockchain technology, with its decentralization feature, can enable new forms of governance where individuals have more control over decision-making processes. It can foster decentralized platforms where citizens can propose, discuss, and vote on issues directly, leading to more participatory and inclusive democratic processes.
Countries like Estonia and Russia have made strides in integrating blockchain into their democratic processes. Estonia uses blockchain for secure digital identities and e-governance, while Moscow has used a blockchain-based system for its "Active Citizen" project, allowing citizens to vote on city decisions. These implementations demonstrate the potential of blockchain in enhancing democratic processes.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











