A Blockchain DNS, also known as a Blockchain Domain Name System, is a revolutionary approach that combines blockchain technology with traditional DNS systems. By leveraging blockchain's decentralization, immutability, and security features, a Blockchain DNS improves upon conventional DNS systems by offering enhanced privacy, security, and control over domain names. Traditional DNS, while being a critical component of the internet, operates under centralized control, making it susceptible to hacking, censorship, and other issues. A Blockchain DNS, on the other hand, leverages a distributed network of nodes, each holding a copy of a ledger that records all domain name registrations and transfers, ensuring a more secure and censorship-resistant system. In a Blockchain DNS, domain name records are stored on a public blockchain. Each domain name corresponds to a unique blockchain address. Each transaction (like domain name registration, update, or transfer) is recorded as a transaction on the blockchain. When a user requests a domain name, the Blockchain DNS looks up the blockchain ledger for the corresponding address and resolves the domain. Since the data on the blockchain is immutable and distributed across multiple nodes, the domain name records are secure from tampering and cannot be altered without consensus from the network. One key function of a Blockchain DNS is to maintain secure and immutable records of domain name registrations and transactions. Because each transaction is recorded on the blockchain and validated by the network, the records are tamper-proof and can't be altered retroactively. This ensures that the ownership and transaction history of a domain name is always accurate and transparent. Furthermore, the cryptographic protection offered by blockchain technology ensures that these records are highly secure against hacking and fraudulent activities. Another important function of a Blockchain DNS is to provide decentralized domain name resolution. Unlike traditional DNS systems, which rely on a central authority to resolve domain names, a Blockchain DNS operates on a network of distributed nodes. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain ledger, so it can independently verify and resolve domain name requests. This not only makes the system more resilient to attacks but also prevents censorship and control by a single entity. By leveraging the distributed nature of blockchain technology, a Blockchain DNS can effectively mitigate DNS attacks like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Because there is no central point of failure, it's difficult for attackers to disrupt the system by targeting a single server or node. Similarly, a Blockchain DNS can resist censorship efforts. Since domain name records are stored on a public, decentralized network, they can't be easily blocked or removed by any single entity, ensuring that users can always access the domain names they want. Blockchain DNS offers significant advantages for the finance industry, especially in terms of security and data integrity. By storing domain name records on a secure, immutable blockchain, financial institutions can ensure that their digital assets and transactions are protected from tampering and fraud. Moreover, the cryptographic security measures inherent in blockchain technology can protect sensitive financial data from cyberattacks, further enhancing the trustworthiness and reliability of financial services. Every transaction, whether it's a domain name registration or a financial transaction, is recorded on the blockchain and can be viewed by anyone on the network. This transparency helps to reduce fraud and corruption by making it difficult to alter or hide transactions. In addition, the immutable nature of blockchain records makes it easier for auditors to verify transactions, improving the efficiency and accuracy of financial audits. Blockchain DNS can also help mitigate the risks associated with single points of failure in financial systems. Traditional DNS systems, with their centralized structure, are vulnerable to attacks or failures at their central points. In contrast, the decentralized structure of a Blockchain DNS distributes the data across numerous nodes, making the system highly resilient to attacks and technical failures. This robustness and resilience can be particularly beneficial for financial institutions, which need to ensure uninterrupted access to their services. Because every transaction needs to be recorded on the blockchain and validated by the network, Blockchain DNS can struggle with high volumes of transactions, potentially leading to slower processing times. Moreover, as the size of the blockchain grows, it can become increasingly difficult for individual nodes to store and manage the entire ledger. These scalability issues could limit the feasibility of Blockchain DNS for large-scale financial applications, at least with current technology. Another challenge for Blockchain DNS in finance is regulatory and compliance complexities. Given the decentralized and borderless nature of blockchain technology, it can be difficult to apply traditional regulatory frameworks and compliance standards to Blockchain DNS systems. For instance, issues such as data privacy, consumer protection, and anti-money laundering (AML) can become more complex in a blockchain context. Financial institutions adopting Blockchain DNS would need to navigate these complexities to ensure they remain compliant with relevant laws and regulations. Despite the potential benefits of blockchain technology, many financial institutions are still hesitant to adopt it due to perceived risks, lack of technical expertise, or resistance to change. In addition, integrating a new technology like Blockchain DNS into existing IT infrastructure can be complex and costly, requiring significant time and resources. This limited adoption and integration can slow down the potential impact of Blockchain DNS on the finance industry. Blockchain DNS is a revolutionary approach that combines the power of blockchain technology with traditional DNS systems. It offers a decentralized and secure framework for managing domain names in the finance industry and beyond. Blockchain DNS provides enhanced security, improved transparency, and resilience against single points of failure. By leveraging blockchain's immutability and distributed nature, it ensures secure and immutable record-keeping, preventing tampering and fraud. It enables decentralized domain name resolution, avoiding censorship and control by a central authority. Blockchain DNS offers advantages such as enhanced security and data integrity, improved transparency and auditability, and mitigation of single point-of-failure risks. However, challenges such as scalability, regulatory complexities, and limited adoption and integration need to be addressed. Despite these challenges, the potential of Blockchain DNS to transform the finance sector and revolutionize domain name management is immense.What is a Blockchain DNS?
How Does a Blockchain DNS Work
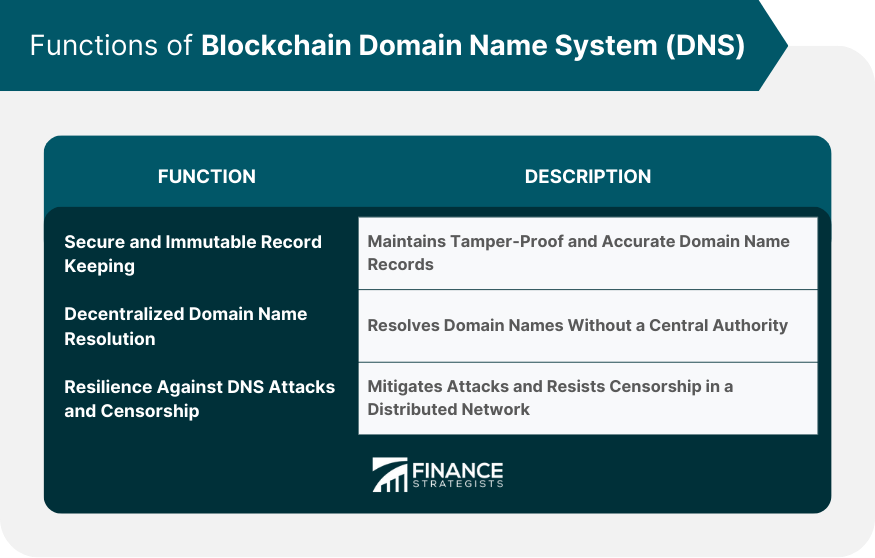
Function of Blockchain DNS
Secure and Immutable Record Keeping
Decentralized Domain Name Resolution
Resilience against DNS Attacks and Censorship
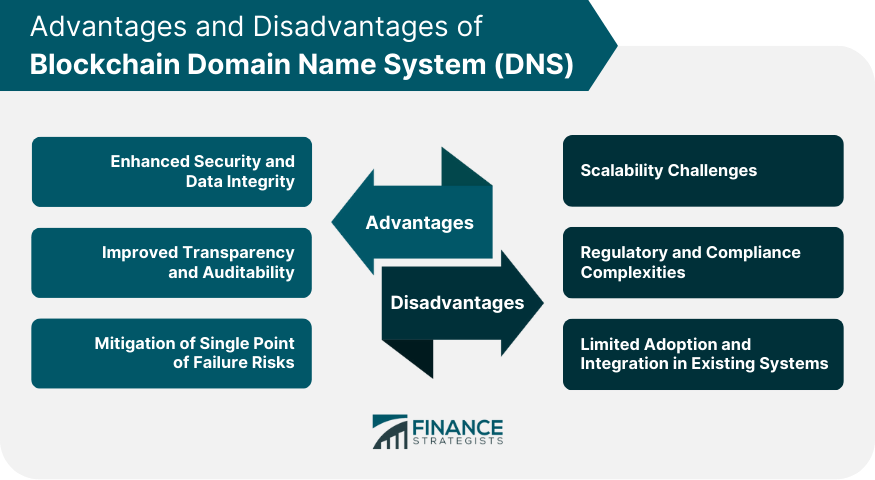
Advantages of Blockchain Domain Name System (DNS)
Enhanced Security and Data Integrity
Improved Transparency and Auditability
Mitigation of Single Point of Failure Risks
Disadvantages of Blockchain Domain Name System (DNS)
Scalability Challenges
Regulatory and Compliance Complexities
Limited Adoption and Integration in Existing Systems
Conclusion
Blockchain DNS FAQs
A Blockchain DNS, or Blockchain Domain Name System, is a system that uses blockchain technology to store and manage domain name records in a decentralized and secure manner.
In a Blockchain DNS, domain name records are stored on a blockchain. Each domain name corresponds to a unique blockchain address, and transactions related to domain names (like registration, update, or transfer) are recorded as transactions on the blockchain.
Advantages of Blockchain DNS in finance include enhanced security and data integrity, improved transparency and auditability, and mitigation of single point of failure risks.
Challenges of Blockchain DNS in finance include scalability issues, regulatory and compliance complexities, and limited adoption and integration in existing systems.
While Blockchain DNS is more resilient to certain types of attacks due to its decentralized nature, it's not completely immune. Vulnerabilities can still exist, especially in areas like smart contract design or user endpoints. However, continuous developments and improvements in blockchain technology are helping to mitigate these risks.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











