Blockchain Hyperledger is an umbrella project of open-source blockchains and related tools initiated by the Linux Foundation in December 2015. Hyperledger doesn't support cryptocurrencies and doesn't represent a traditional blockchain system; instead, it has a unique infrastructure built to advance cross-industry collaboration. It includes modular blockchain frameworks and libraries which businesses can leverage for specific applications. Hyperledger was designed to advance blockchain technology by identifying a cross-industry standard platform for distributed ledgers. It aims to nurture an open, standardized, and enterprise-grade distributed ledger framework and codebase. Its principal goal is to improve the reliability, performance, and overall robustness of blockchain systems, making them suitable for global business transactions. Key components of Hyperledger include Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger Composer. Hyperledger Fabric is a blockchain framework that helps design and implement blockchain business networks. Hyperledger Composer, on the other hand, is a set of collaboration tools for building blockchain business networks, accelerating the development of smart contracts. Transactions in Hyperledger follow a defined flow. First, the client application sends a transaction proposal to endorsing peers. The peers simulate the transaction, returning an endorsement if the proposal is correct. The application then sends the endorsed proposal to the ordering service, which orders the transaction into a block and delivers it to the peers for validation and commitment to the ledger. Blockchain Hyperledger project has several key types or frameworks that each serve different use cases. Here are a few notable ones: Fabric is a modular and flexible architecture that is designed to support pluggable implementations of various functions. It is a framework for permissioned networks where all participants have known identities. The fabric allows components, such as consensus and membership services, to be plug-and-play, making it a great option for enterprises. Besu is an Ethereum client designed to be enterprise-friendly for both public and private permissioned network use cases. It can run on the Ethereum public network, private networks, and test networks such as Rinkeby, Ropsten, and Görli. Sawtooth is a blockchain framework that makes it easy to build, deploy, and run distributed ledgers. It provides a highly modular and flexible platform for implementing transaction-based updates to the shared state between untrusted parties coordinated by consensus algorithms. Indy is a distributed ledger purpose-built for decentralized identity. It provides tools, libraries, and reusable components for creating and using independent digital identities rooted in blockchains or other distributed ledgers. Iroha is a simple blockchain platform easy to incorporate into infrastructural projects requiring distributed ledger technology. It features simple construction, modern, domain-driven C++ design, and an emphasis on mobile application development. Burrow is a permissioned Ethereum smart-contract blockchain node built to be part of the Hyperledger framework. It executes Ethereum EVM smart contract code on a permissioned virtual machine. Consensus in Hyperledger is the process of agreeing on the order and confirming the correctness of the set of transactions that constitute a block. Unlike other blockchain systems, Hyperledger allows for flexibility in its consensus protocols as it doesn’t have a native cryptocurrency and doesn’t require mining, leading to improved performance and scalability. Hyperledger supports pluggable consensus protocols that enable it to be more effectively used in a range of use cases. Depending on the needs of the network, different consensus protocols can be implemented. Some of these include Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), Raft, and Kafka. Hyperledger provides an advanced and secure foundation for developing applications or solutions with a modular architecture. Its design provides confidentiality, resilience, flexibility, and scalability, which are critical for secure business transactions. Hyperledger supports a variety of blockchain consensus algorithms, making it adaptable to a wide array of business needs. This flexibility allows for interoperability, as businesses can choose a consensus protocol that suits their specific use case and requirements. With its modular architecture, Hyperledger offers exceptional scalability. It can process a high number of transactions per second compared to other blockchain platforms, meeting the needs of various industries, including finance and supply chain management. Hyperledger is an open-source project hosted by the Linux Foundation. It's supported by a large, active community of developers who continuously work to improve its functionalities and performance. Hyperledger's advanced functionalities come with increased complexity. It requires a certain level of expertise to set up, manage, and troubleshoot, which might be challenging for those without a technical background. Like any new technology, businesses may face resistance when adopting Hyperledger. People may be hesitant to transition from traditional methods to a new, blockchain-based approach. Therefore, change management becomes critical in the successful implementation of Hyperledger. Deploying a blockchain solution such as Hyperledger also involves dealing with regulatory and compliance issues. Depending on the industry and region, specific rules and regulations may govern the use of blockchain technology. Hyperledger comes with built-in security features that ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the transactions. These include permissioned network models, where participants are known to each other, and the use of cryptography for securing transaction data. Despite its security features, Hyperledger is not impervious to potential vulnerabilities and threats. This includes the risk of smart contract vulnerabilities, privacy breaches, and the threat of network nodes acting maliciously. Blockchain Hyperledger, a project initiated by the Linux Foundation, offers a unique and modular infrastructure to accelerate cross-industry blockchain technologies. Key frameworks such as Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger Composer form their foundation, aiding in constructing efficient business networks. With a suite of types like Fabric, Besu, Sawtooth, Indy, Iroha, and Burrow, Hyperledger caters to a wide array of enterprise requirements, providing flexibility and adaptability. Its strength lies in its robust security, scalability, and the support of a vigorous open-source community. However, like any technology, it has its challenges, such as technical complexity, adoption resistance, and regulatory issues. Despite these, with its inherent security features and ability to handle potential threats, Hyperledger stands as a strong contender in the field of blockchain technologies, offering substantial benefits for businesses looking to implement blockchain systems.What Is Blockchain Hyperledger?
Function of Blockchain Hyperledger
Core Components of Hyperledger
Understanding Transaction Flow in Hyperledger
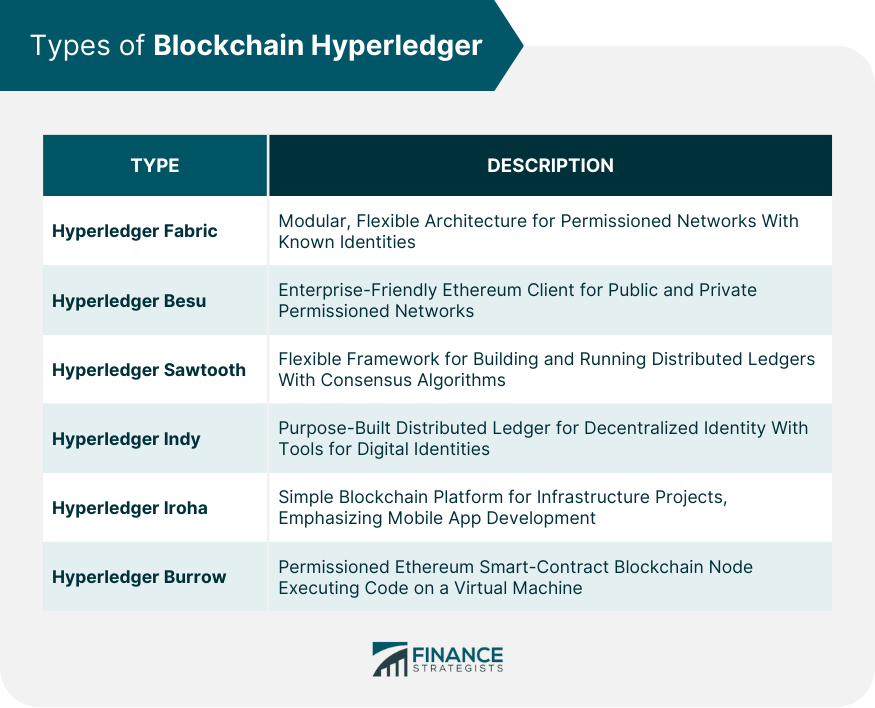
Types of Blockchain Hyperledger
Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Besu
Hyperledger Sawtooth
Hyperledger Indy
Hyperledger Iroha
Hyperledger Burrow
Consensus Mechanism in Blockchain Hyperledger
Role of Consensus
Different Consensus Protocols in Hyperledger
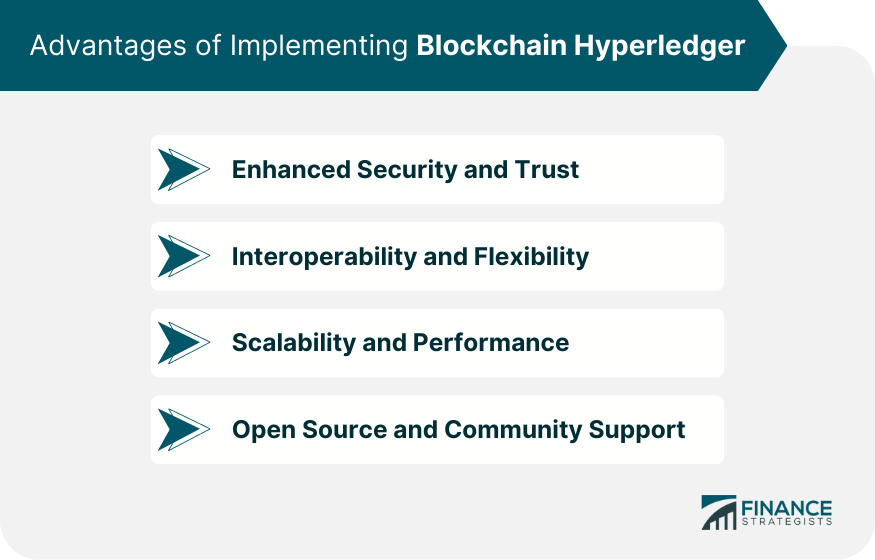
Advantages of Implementing Blockchain Hyperledger
Enhanced Security and Trust
Interoperability and Flexibility
Scalability and Performance
Open Source and Community Support
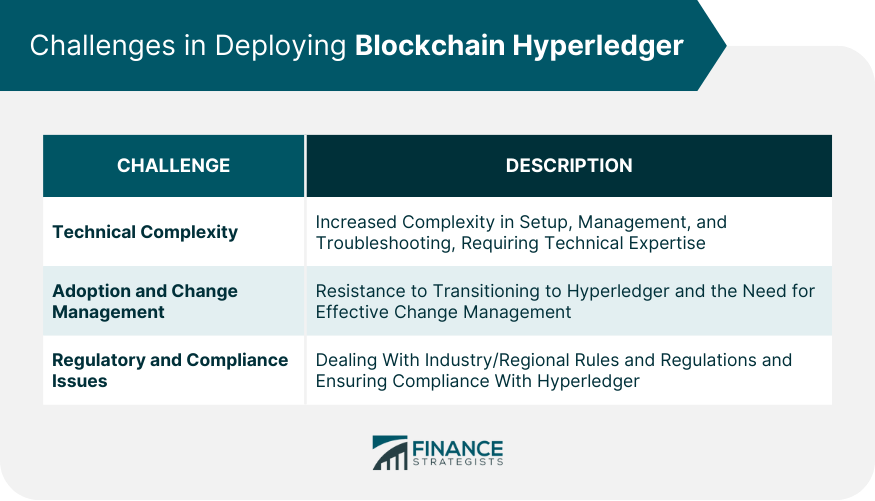
Challenges in Deploying Blockchain Hyperledger
Technical Complexity
Adoption and Change Management
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Exploring the Security Aspects of Blockchain Hyperledger
Inherent Security Features
Potential Vulnerabilities and Threats
Conclusion
Blockchain Hyperledger FAQs
Blockchain Hyperledger is an open-source project launched by the Linux Foundation that provides a standardized, enterprise-grade platform for distributed ledgers. It doesn't support cryptocurrencies and instead focuses on creating cross-industry standards for blockchain systems.
Key components include Hyperledger Fabric, a blockchain framework for designing and implementing business networks, and Hyperledger Composer, a suite of collaboration tools for building blockchain business networks.
Hyperledger enables flexible consensus protocols as it doesn’t have a native cryptocurrency and doesn’t require mining. It supports various pluggable consensus protocols that can be used according to the needs of the network, including Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), Raft, and Kafka.
Hyperledger offers enhanced security and trust, interoperability and flexibility, excellent scalability, and strong community support due to its open-source nature.
Deploying Hyperledger can involve technical complexity, adoption and change management challenges, and potential regulatory and compliance issues. Despite its robust security features, there are also potential vulnerabilities and threats to consider, such as smart contract vulnerabilities and privacy breaches.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











