What Is Blockchain Identity Management?
Blockchain identity management refers to the use of blockchain technology to manage and validate digital identities.
It ensures that identities are uniquely owned and controlled by individuals or organizations themselves, rather than a centralized authority.
Leveraging blockchain's inherent characteristics of decentralization, immutability, and security, this concept embodies the core of a new era of identity management.
These identities, securely anchored on the blockchain, can include a plethora of digital data such as personal credentials, corporate details, or transaction records, significantly simplifying identity verification processes while enhancing security.
How Blockchain Identity Management Works
Instead of the typical centralized authority model, a decentralized approach is applied where users have greater control over their identities.
Each user is assigned a unique digital identity, encapsulating their personal or organizational information.
Once assigned, this digital identity is recorded on the blockchain, the decentralized ledger technology.
Herein lies the security strength - these records cannot be modified, duplicated, or deleted without the user's consent due to blockchain's immutable nature.
Every transaction or request for identity verification triggers a consensus process across multiple nodes within the network, ensuring every identity interaction's validity and integrity.
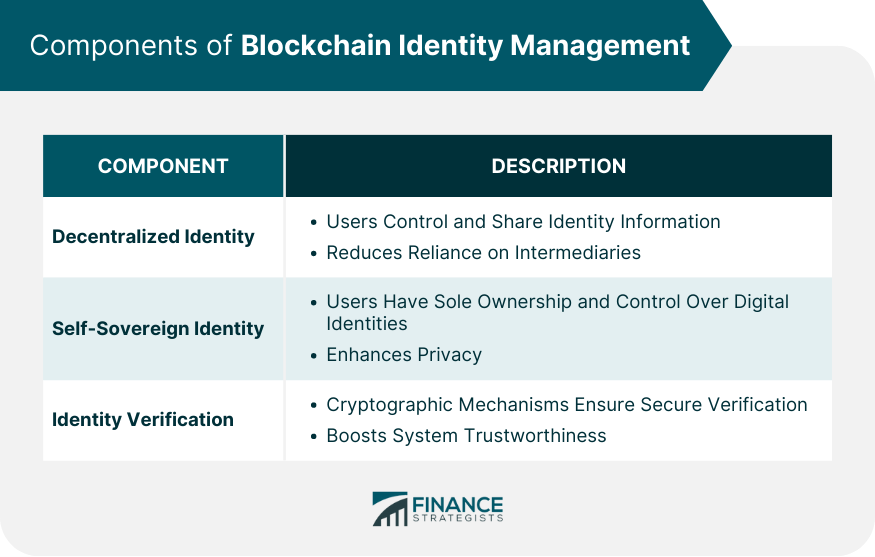
Components of Blockchain Identity Management
Decentralized Identity
In stark contrast to the traditional centralized model, the decentralized approach hands the reins of identity control back to the individuals or organizations.
It empowers users to manage their identities, dictating what information to share, with whom, and for how long.
A decentralized identity framework is both immutable and transparent. It ensures the identity ownership remains with the users while providing seamless access to services.
Additionally, it cuts down the reliance on third-party intermediaries, reducing potential vulnerabilities and privacy risks inherent in centralized systems.
Self-Sovereign Identity
The concept of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) is a cornerstone of blockchain identity management.
SSI is a digital identity model where individuals or entities have sole ownership over their digital and analog identities.
It grants users the authority to control their identity-related data, verifying and managing them without an intermediary.
SSI not only preserves user autonomy but also amplifies the level of privacy and security.
With SSI, users can selectively disclose their identity information, avoiding unnecessary data exposure.
Moreover, the blockchain-based decentralized system significantly reduces the risk of data breaches, giving the users unparalleled control and security.
Identity Verification Mechanisms
These mechanisms verify the authenticity of the digital identity and any associated transactions.
Based on cryptographic principles, these processes involve generating keys for each identity, ensuring secure access and interaction.
In a blockchain ecosystem, the validation process uses consensus algorithms. This decentralized validation ensures that no single entity has control over the verification process, enhancing the system's trustworthiness.
Further, the immutable nature of blockchain ensures that once the identity is validated, it cannot be tampered with, boosting the security and reliability of the system.
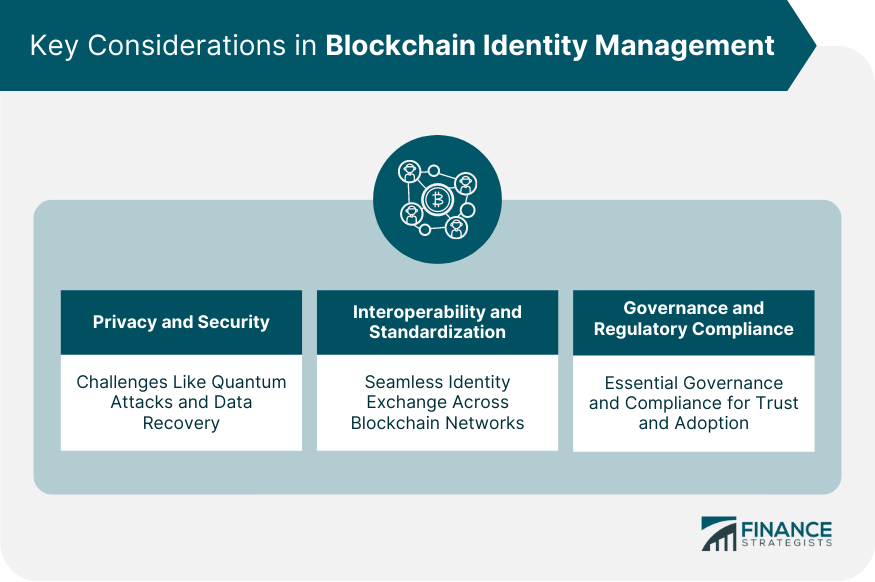
Key Considerations in Blockchain Identity Management
Privacy and Security
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized nature and robust cryptographic techniques, offers superior privacy and security features.
However, while blockchain enhances data privacy by giving individuals control over their data, it also presents a unique set of challenges, such as vulnerability to quantum attacks or potential issues regarding data recovery.
In addition, blockchain's immutability could pose privacy concerns. Once data is stored on a blockchain, it's nearly impossible to erase it, even when an individual's "right to be forgotten" under regulations like the GDPR comes into play.
Developers and stakeholders must carefully consider these aspects when designing and implementing blockchain-based identity management solutions.
Interoperability and Standardization
For blockchain identity management to function efficiently, interoperability and standardization are essential.
Different blockchain networks should be able to communicate and interact with each other, ensuring seamless exchange and recognition of identities.
Standardization, on the other hand, can promote consistency in the way digital identities are created and managed, enhancing user experience and security.
However, achieving interoperability and standardization in a highly fragmented blockchain landscape can be challenging.
It requires the collaboration of various stakeholders, including technology providers, users, and regulators, to agree on common standards and protocols.
Governance and Regulatory Compliance
Incorporating blockchain into identity management implicates several legal and regulatory concerns.
Navigating the complexities of data privacy laws, cross-border data transfers, and specific sectoral regulations can be particularly challenging.
Therefore, a well-defined governance model is crucial for maintaining accountability, transparency, and compliance.
Moreover, to promote trust and wide-scale adoption, blockchain identity management solutions should be developed and operated in compliance with relevant regulations.
This includes privacy laws like GDPR, cybersecurity regulations, and industry-specific rules. This necessitates continuous dialogue with regulators and a comprehensive understanding of the legislative landscape.
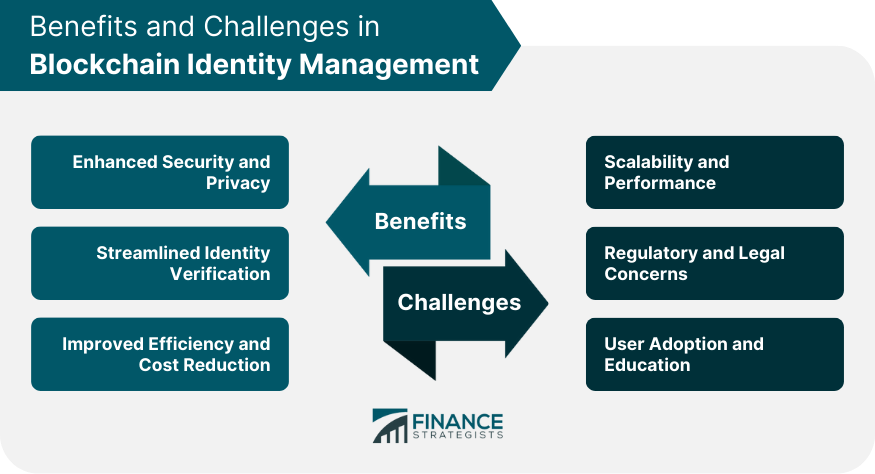
Benefits of Blockchain Identity Management
Enhanced Security and Privacy
By giving individuals control over their data, it significantly reduces the risk of data breaches common in centralized systems.
The cryptographic security measures used in blockchain, such as public-private key pairs, provide a robust layer of security.
At the same time, the selective disclosure of data inherent in the self-sovereign identity model bolsters privacy protections.
Moreover, the decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates single points of failure. In the event of a security incident, only a fraction of the data would be at risk, rather than a whole database.
This approach to identity management therefore represents a significant leap forward in terms of both security and privacy.
Streamlined Identity Verification
With blockchain identity management, the identity verification process becomes more streamlined and efficient. Traditional methods often involve time-consuming manual checks and are subject to errors.
Blockchain, on the other hand, enables automated, instant verification of identities, saving both time and costs.
Blockchain-based identities are unique, verifiable, and non-replicable, ensuring that the verification process is seamless and reliable.
These identities can be used across multiple platforms, reducing the need for multiple logins and credentials, thus simplifying user experience while enhancing security.
Improved Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Blockchain identity management also brings about significant improvements in efficiency and cost reduction.
By eliminating intermediaries, streamlining verification processes, and enabling reusable digital identities, it can significantly reduce operational costs.
Moreover, the efficiency gains from instant, automated verification can accelerate service delivery and improve customer experiences.
The decentralized model also reduces the need for extensive IT infrastructure for managing identities, leading to lower maintenance costs.
Furthermore, the transparency and traceability of blockchain can help minimize fraud and related costs, adding to the economic benefits.
Challenges of Blockchain Identity Management
Scalability and Performance
Blockchains, especially public ones, can suffer from limited transaction throughput and slow transaction times.
As the number of users increases, the system's performance might not scale linearly, potentially causing inefficiencies and delays.
Addressing these challenges requires technological improvements and new architectural designs.
Solutions like sharding, off-chain transactions, and Layer 2 protocols are being explored to enhance the scalability and performance of blockchain systems.
Regulatory And Legal Concerns
The technology is still relatively new, and many jurisdictions around the world are still working to understand it and develop relevant regulatory frameworks.
These frameworks need to strike a balance between enabling innovation, protecting users, and ensuring legal compliance.
Legal uncertainties include issues of data privacy, jurisdiction, and liability, among others.
For instance, the challenge presents itself in the form of executing the 'Right to be Forgotten,' as mandated by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), on an immutable blockchain structure.
Comprehensive solutions to these legal and regulatory hurdles need to be meticulously articulated and addressed.
User Adoption and Education
For most people, blockchain technology is complex and difficult to understand. As such, there's a steep learning curve involved in understanding and using blockchain-based systems.
Users need to feel comfortable with the technology, and they need to understand the benefits it brings, such as enhanced privacy and security.
Furthermore, many people are wary of new technologies, especially those that involve sensitive information such as personal identities.
To overcome these challenges, substantial efforts are needed to educate people about the benefits of blockchain identity management, and user-friendly interfaces need to be developed to promote widespread adoption.
Use Cases of Blockchain Identity Management
Know Your Customer (KYC) Processes
In an increasingly digital world, businesses, particularly financial institutions, need efficient, reliable ways to carry out KYC processes.
Blockchain identity management can revolutionize these processes. By using blockchain-based identities, businesses can verify customer information quickly and reliably.
These identities are not only more secure but are also reusable across different platforms, eliminating the need for customers to undergo the same KYC processes multiple times.
Moreover, with a blockchain-based KYC process, businesses can achieve substantial cost savings and improve customer experiences.
Secure Digital Identity Verification
Secure digital identity verification is another critical use case for blockchain identity management.
As more services move online, the need for secure, reliable digital identities becomes paramount. Blockchain can offer a solution to this by providing unique, verifiable, and secure digital identities.
In this context, blockchain could be used for a variety of applications, from accessing online services to digital signatures in electronic documents.
By using blockchain-based identities, these processes can be made more secure, efficient, and user-friendly.
Streamlined Authentication and Authorization
Blockchain identity management can also streamline authentication and authorization processes.
In traditional systems, these processes often rely on passwords or tokens, which can be easily lost, stolen, or forgotten.
With blockchain, authentication and authorization can be based on digital identities, which are more secure and easier to manage.
A blockchain-based identity could be used to access a building, log in to a computer system, or authorize a transaction.
Such a system would not only enhance security but also improve user experiences by eliminating the need for multiple passwords or tokens.
Conclusion
Blockchain identity management refers to the use of blockchain technology to manage and validate digital identities.
It ensures that identities are uniquely owned and controlled by individuals or organizations themselves, rather than a centralized authority.
Blockchain identity management leverages the decentralized, immutable, and secure nature of blockchain to revolutionize the way identities are managed and verified.
This approach enables enhanced security and privacy, streamlined identity verification processes, and improved efficiency and cost reduction.
However, challenges such as scalability, regulatory compliance, and user adoption need to be addressed.
Despite these challenges, blockchain identity management holds great promise in transforming traditional identity systems and empowering individuals and organizations with greater control over their digital identities.
Blockchain Identity Management FAQs
Blockchain Identity Management is a new approach to managing digital identities. It leverages the decentralized, transparent, and secure nature of blockchain technology to give individuals or organizations control over their identities.
By decentralizing identity control and using robust cryptographic techniques, blockchain identity management enhances both security and privacy. It minimizes the risk of data breaches and provides a more secure platform for storing and sharing personal data.
Some of the main challenges include scalability and performance issues, regulatory and legal uncertainties, and hurdles in user adoption and education. It's important to address these challenges effectively to realize the full potential of blockchain identity management.
By providing unique, verifiable, and secure digital identities, blockchain identity management can streamline KYC processes. It allows businesses to verify customer information quickly, reliably, and securely. Moreover, these identities are reusable across platforms, eliminating the need for customers to undergo the same KYC processes multiple times.
Blockchain identity management has the potential to impact numerous sectors. In finance, it can streamline KYC processes and enhance online transaction security. In healthcare, it can facilitate secure sharing of medical records. In education, it can enable reliable verification of academic credentials. The possibilities are vast, pointing to a future where digital identities are secure, efficient, and user-centric.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











