Blockchain technology, originally designed as the underlying system for Bitcoin, has found applications in many sectors, including education. The term 'Blockchain in Education' refers to the use of this distributed ledger technology to streamline and revolutionize several processes within the educational ecosystem. In its simplest terms, blockchain is a transparent, secure, and immutable ledger that records transactions. When applied to education, this technology can foster trust and efficiency by providing a secure way to store and share educational records, credentials, and other important information. One of the most significant ways blockchain is utilized in education is through the decentralization of educational records. In a traditional setup, student records are stored in centralized databases maintained by educational institutions. This centralized approach is often fraught with challenges, including data breaches and cumbersome record transfer processes. In contrast, a blockchain-based system decentralizes these records. Each student can have their digital portfolio stored in the blockchain, which can include their academic records, certifications, extra-curricular activities, and other achievements. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that these records are secure, immutable, and can be accessed anytime, anywhere. Blockchain technology can also provide a secure method for sharing and verifying educational credentials. Traditional methods of verifying educational certificates often involve time-consuming and error-prone processes. Blockchain can simplify this by creating digital certificates that are stored on the blockchain. These certificates can be shared with potential employers or other institutions who can quickly and securely verify the authenticity of the credentials directly on the blockchain. Another promising application of blockchain in education is the use of gamification and tokenization to enhance the learning process. By using blockchain, educational institutions can issue digital tokens to students as a form of reward for their academic performance, participation, or engagement. This tokenization can create a more interactive and motivating learning environment, promoting better learning outcomes. One of the most significant advantages of blockchain in education is the enhanced security and authenticity it provides. Blockchain's inherent characteristics—transparency, immutability, and security—ensure that educational records and credentials stored on it are safe from unauthorized alterations or breaches. This increased security not only safeguards important educational data but also adds a level of authenticity and trust that is often lacking in traditional educational systems. As mentioned earlier, blockchain can also revolutionize the process of credential verification. Blockchain-based credentials can be verified instantly and transparently, eliminating the need for intermediaries. This can drastically reduce the time and resources required for credential verification, benefiting educational institutions, students, and employers alike. Blockchain can also pave the way for personalized and self-paced learning. By storing a comprehensive record of a student's academic journey, blockchain can help create personalized learning plans based on the student's strengths, weaknesses, and preferences. Moreover, the use of tokenization can motivate students to learn at their own pace, rewarding them for their progress and achievements. Blockchain could also potentially facilitate global collaboration and resource sharing in education. By providing a universal and secure platform for sharing educational records and resources, blockchain can help foster global educational collaborations, enabling students and educators from around the world to learn from and contribute to a shared educational resource pool. One of the main hurdles is the technological infrastructure required to support blockchain. Many educational institutions may lack the necessary technical resources and expertise to implement and maintain a blockchain-based system. Moreover, the adoption of blockchain in education also requires significant change management efforts. Students, educators, and other stakeholders will need to understand and accept this new technology, which can be a slow and challenging process. Data privacy is another major concern when implementing blockchain in education. Although blockchain can enhance the security of educational data, it also raises questions about who can access this data and how it can be used. Furthermore, regulatory frameworks for blockchain technology are still evolving, which can create uncertainty and potential legal issues. Another challenge of implementing blockchain in education is the potential for inequities in access. While blockchain can offer many benefits to students and educators, these benefits may not be equally accessible to all. For example, students without reliable internet access or digital literacy skills may be left behind in a blockchain-based educational system. To overcome the technological challenges of implementing blockchain, educational institutions need to invest in creating a tech-ready infrastructure. This could involve upgrading existing IT systems, investing in cloud storage, and providing technical training for staff. Furthermore, a phased approach to implementation could also help mitigate risks and allow for learning and adjustments along the way. To address data privacy and regulatory concerns, a clear and robust regulatory framework needs to be established. This could involve working with legal experts, policymakers, and technologists to create guidelines and regulations that protect students' data privacy while allowing for the efficient use of blockchain technology. To prevent inequities in access, strategies need to be developed to ensure that all students can benefit from blockchain technology. This could include providing digital literacy training, ensuring access to reliable internet services, and creating inclusive policies and practices. The real-world impact of blockchain in education can be seen in the changes it brings to the verification and accreditation processes. With blockchain, these processes become faster, easier, and more transparent, benefiting students, educational institutions, and employers. The use of blockchain in education can also contribute to the evolution of personalized learning. By storing a comprehensive record of each student's learning journey, educators can tailor instruction to each student's needs and preferences, improving learning outcomes. Furthermore, blockchain's potential to facilitate global collaboration and resource sharing can transform international learning experiences. Students and educators can share and access resources on a secure, universal platform, enabling cross-cultural learning and collaborations. Blockchain technology holds immense potential for revolutionizing the education sector. Through its secure and transparent nature, blockchain enhances the storage and sharing of educational records, improves the verification of credentials, and brings innovation to the learning process with gamification and tokenization. It paves the way for personalized, self-paced learning and fosters global collaboration. However, challenges persist, including technical infrastructure requirements, adoption hurdles, data privacy concerns, and access disparities. For successful implementation, robust strategies such as creating a tech-ready infrastructure, developing a clear regulatory framework, and ensuring equitable access are essential. The transformative power of blockchain in education is already visible in changed verification processes, personalized learning, and enhanced international collaboration. Embracing blockchain technology can be the next significant step toward an efficient, inclusive, and future-oriented education system.What Is Blockchain in Education?
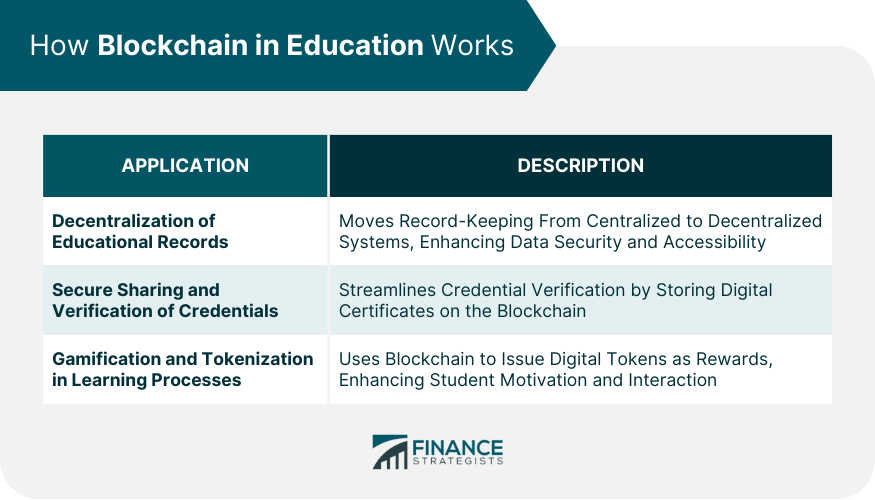
How Blockchain in Education Works
Decentralization of Educational Records
Secure Sharing and Verification of Credentials
Gamification and Tokenization in Learning Processes
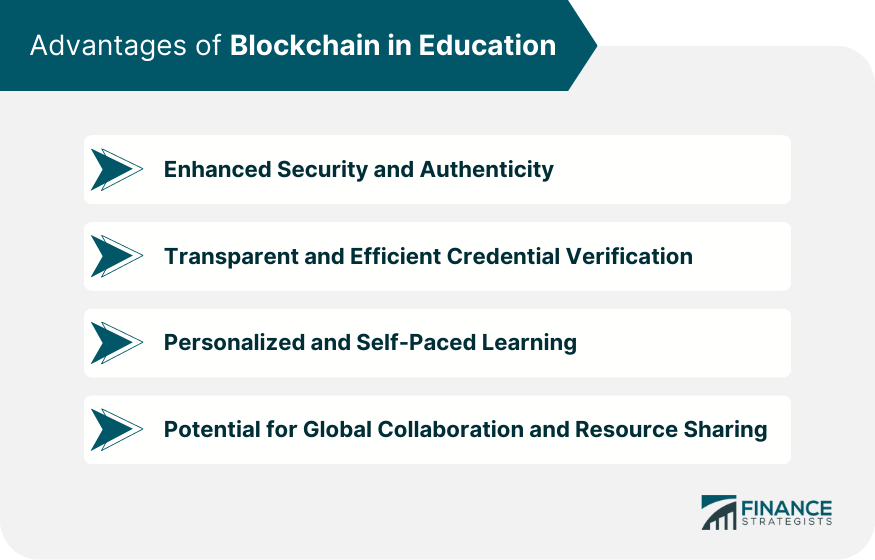
Advantages of Blockchain in Education
Enhanced Security and Authenticity
Transparent and Efficient Credential Verification
Personalized and Self-Paced Learning
Potential for Global Collaboration and Resource Sharing
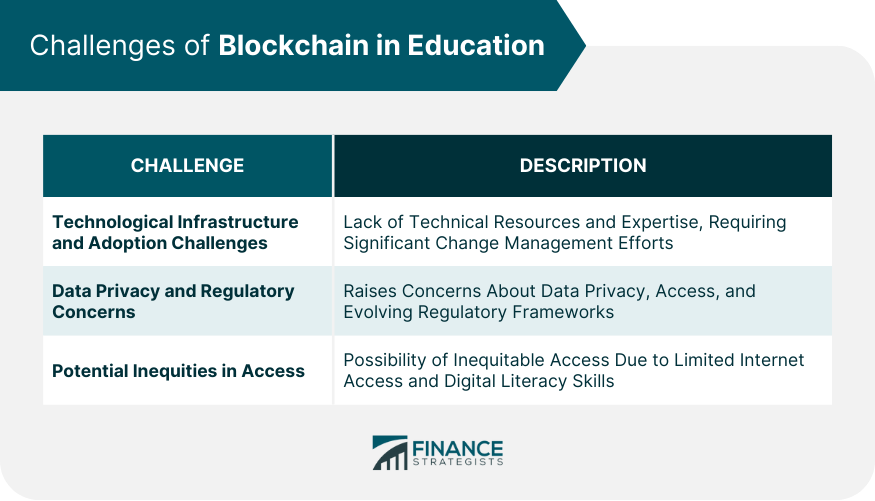
Challenges of Blockchain in Education
Technological Infrastructure and Adoption Challenges
Data Privacy and Regulatory Concerns
Potential Inequities in Access
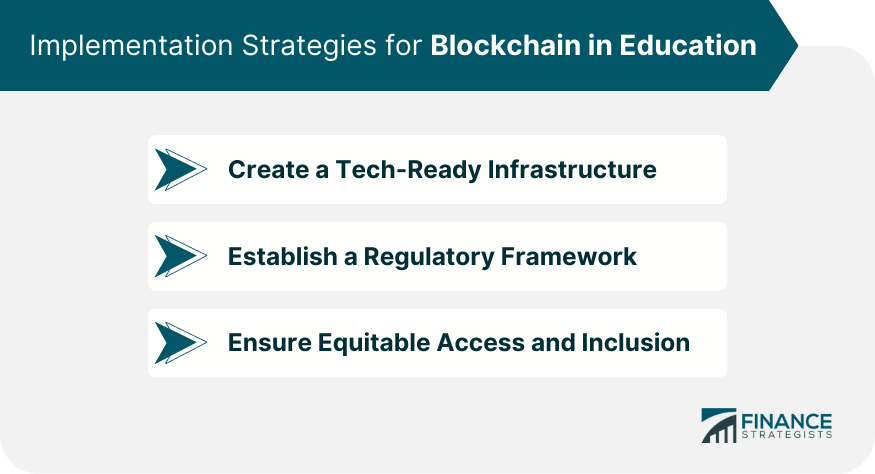
Implementation Strategies for Blockchain in Education
Create a Tech-Ready Infrastructure
Establish a Regulatory Framework
Ensure Equitable Access and Inclusion
Real-World Impact of Blockchain in Education
Changes in Verification and Accreditation Processes
Evolution of Personalized Learning
Influence on International Collaboration and Learning Experiences
Bottom Line
Blockchain in Education FAQs
Blockchain in Education refers to the application of blockchain technology, a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger system, in the education sector. It enables the decentralization of educational records, secure sharing, and verification of credentials, and can enhance the learning process through gamification and tokenization.
Blockchain technology enhances security in education by providing a secure platform to store educational records and credentials. Its transparency, immutability, and decentralization make it difficult for unauthorized alterations or breaches, thereby safeguarding important educational data.
Blockchain technology can streamline the process of credential verification by storing digital certificates on the blockchain. These can be shared with potential employers or other institutions who can quickly and securely verify the authenticity of the credentials directly on the blockchain, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Some challenges of implementing blockchain in education include the technological infrastructure required to support blockchain, adoption challenges, data privacy and regulatory concerns, and potential inequities in access. Ensuring that all students can benefit from the technology and protecting students' data privacy are crucial considerations.
To successfully implement blockchain in education, it's important to create a tech-ready infrastructure, establish a clear regulatory framework to address data privacy and regulatory concerns, and develop strategies to ensure equitable access and inclusion, such as digital literacy training and access to reliable internet services.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











