Blockchain in the Financial Industry refers to the application of blockchain technology, a form of distributed ledger technology, within various financial services. It serves to streamline operations, increase transparency, reduce fraud, and decrease costs by providing a secure, immutable, and decentralized system for conducting and recording transactions. This technology impacts the reader by fundamentally transforming how financial transactions are carried out, eliminating the need for intermediaries, and offering more efficient, secure, and transparent financial systems. The technology finds a broad range of applications, from facilitating peer-to-peer transactions and tokenizing assets to executing smart contracts and enhancing audit and compliance procedures. With blockchain, the financial industry stands on the cusp of a major revolution that could redefine the way we manage, trade, and interact with financial assets. In the financial industry, blockchain facilitates transactions by allowing direct peer-to-peer transfers of assets. These transactions are added to a shared ledger and confirmed by network participants, reducing the need for intermediaries and making the process more efficient and less costly. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts encoded on a blockchain. They automatically execute transactions when predetermined conditions are met. In the financial industry, smart contracts can be used for various applications, such as executing trades or releasing funds. Tokenization is the process of turning real-world assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. These tokens can represent assets like stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities, enabling more accessible and more efficient trading and management. Blockchain technology can also streamline audits and compliance. The transparency and immutability of blockchain records simplify the audit process, while smart contracts can be used to automatically enforce regulatory compliance. Blockchain technology can significantly increase efficiency and speed in the financial industry. By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes with smart contracts, blockchain can accelerate transaction settlement times and streamline operations. Blockchain's transparent and immutable ledger provides a trustworthy record of transactions. This feature improves traceability and reduces the risk of fraud and corruption. Blockchain's decentralized and cryptographic nature enhances security. It's nearly impossible to alter data once added to the blockchain, reducing the risk of fraud and cyberattacks. Blockchain can help financial institutions save costs in various ways. It reduces the need for intermediaries, lowers operational costs by automating processes, and decreases fraud and error-related costs through enhanced security and transparency. Regulatory challenges are a significant hurdle for blockchain adoption in the financial industry. The technology's decentralized nature and potential for anonymity raise regulatory concerns about money laundering and other illegal activities. Scalability is another challenge for blockchain in the financial industry. The current transaction processing capacity of most blockchains is significantly lower than traditional financial systems, posing a challenge for widespread adoption. Interoperability, or the ability of different blockchain systems to work together, is a significant challenge. The financial industry needs a standard way to communicate across different blockchain platforms. There is a lack of standardization in the blockchain industry, with different platforms using different protocols and standards. This lack of consistency can hamper adoption and integration into existing financial systems. Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is one of the most prominent applications of blockchain in the financial industry. DeFi platforms use blockchain technology to offer financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries. Blockchain technology can also streamline cross-border payments, which are traditionally slow and expensive. By using blockchain, financial institutions can settle cross-border payments instantly and at lower costs. Blockchain can be used for identity verification in financial services. By storing identity data on a blockchain, financial institutions can streamline the identity verification process and enhance security. In the insurance industry, blockchain can simplify and streamline the claims processing procedure. Smart contracts can automate claim verification and payment, reducing processing time and costs. Blockchain's integration into the financial industry has dramatically improved transactional efficiency, security, and transparency. By facilitating direct peer-to-peer transfers, automating processes via smart contracts, and enabling asset tokenization, blockchain has significantly streamlined financial operations. However, widespread adoption is still challenged by regulatory concerns, scalability issues, and a lack of interoperability and standardization. Notably, the technology has found prominent applications in DeFi platforms, cross-border payments, identity verification, and insurance claim processing. As the technology matures, standardization improves, and regulatory bodies become more acquainted with its potential, blockchain's impact on the financial industry is anticipated to grow even more profound. This technology holds the potential to reshape the financial landscape by reducing costs, eliminating intermediaries, and increasing overall operational efficiency.What Is Blockchain in the Financial Industry?
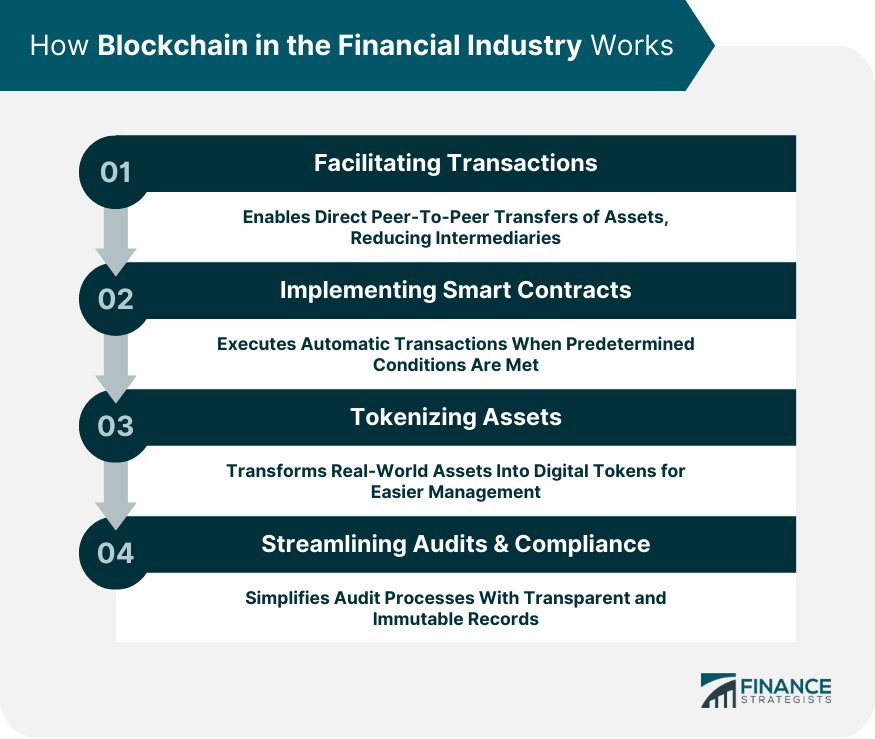
How Blockchain in the Financial Industry Works
Facilitating Transactions
Implementing Smart Contracts
Tokenizing Assets
Streamlining Audits and Compliance
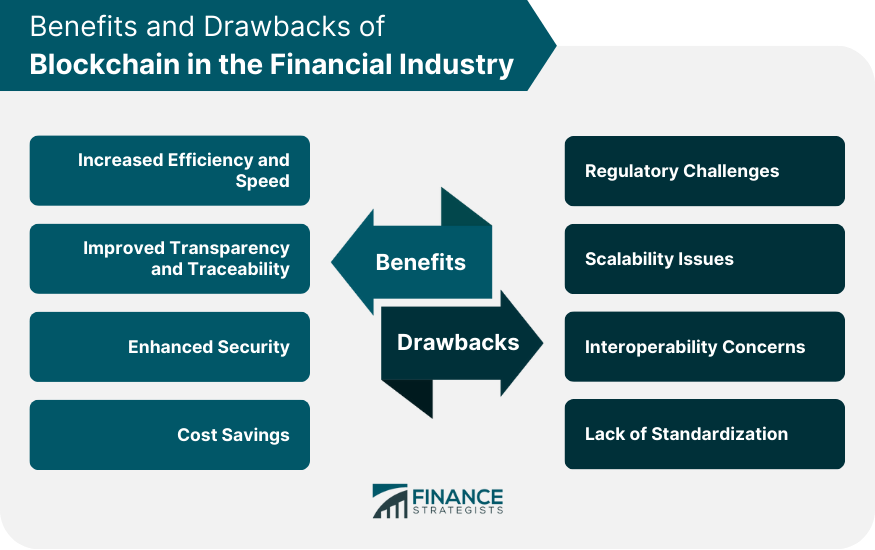
Benefits of Blockchain in the Financial Industry
Increased Efficiency and Speed
Improved Transparency and Traceability
Enhanced Security
Cost Savings
Drawbacks and Challenges of Blockchain in the Financial Industry
Regulatory Challenges
Scalability Issues
Interoperability Concerns
Lack of Standardization
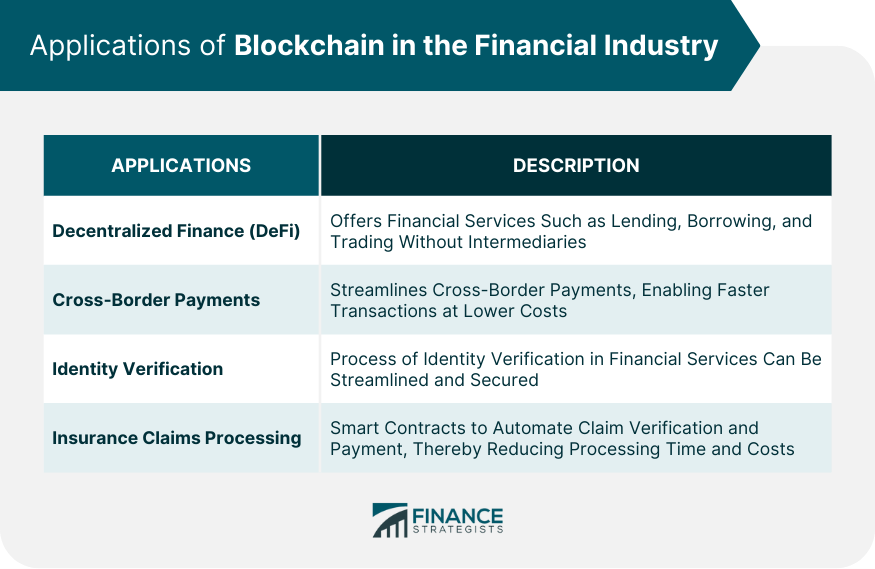
Applications of Blockchain in the Financial Industry
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Cross-Border Payments
Identity Verification
Insurance Claims Processing
Conclusion
Blockchain in Financial Industry FAQs
Blockchain plays a crucial role in the financial industry by streamlining operations, improving transparency, reducing fraud, and lowering costs. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature allows for efficient and secure transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Blockchain improves efficiency and speed in the financial industry by facilitating direct peer-to-peer transactions and automating processes with smart contracts. These features eliminate the need for intermediaries and reduce transaction settlement times.
Some challenges faced by blockchain in the financial industry include regulatory issues due to its decentralized nature, scalability concerns with transaction processing capacity, interoperability problems among different blockchain platforms, and lack of standardization in the blockchain industry.
In the financial industry, decentralized finance (DeFi) uses blockchain to offer financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without traditional financial intermediaries. It utilizes blockchain's secure and transparent nature to build trust among users.
Blockchain has a significant impact on cross-border payments in the financial industry. It allows for the direct transfer of assets across borders, reducing transaction times from days to minutes. Additionally, it reduces the cost associated with these transactions by eliminating the need for intermediaries.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











