Blockchain in Industries refers to the application and integration of blockchain technology across various industrial sectors. This transformational technology, originally the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. The purpose of utilizing blockchain in industries is to introduce new levels of transparency, security, and efficiency. Industries such as finance, healthcare, supply chain, energy, real estate, and the public sector have started leveraging blockchain's potential to drive fundamental changes. Blockchain revolutionizes industries by facilitating faster cross-border payments, improving supply chain traceability, enhancing healthcare data security, and enabling real-time, secure data exchanges, fostering innovation and growth. Implementing blockchain across different industries requires a well-planned and methodical approach. The first step usually involves identifying the problem areas where blockchain can offer significant improvements. These are typically areas where transparency, data security, and operational efficiency are of utmost concern. Key considerations when implementing blockchain in an industry setting include understanding the technology's capabilities, the specific requirements of the industry, regulatory considerations, and the readiness of the industry to adopt the technology. A thorough understanding of these factors can guide the decision-making process and ensure the successful deployment of blockchain technology. Blockchain has made significant inroads in the financial industry. It forms the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, and it has been instrumental in introducing innovations such as decentralized finance (DeFi). From facilitating cross-border payments to streamlining securities trading, blockchain is revolutionizing the financial landscape. In the healthcare sector, blockchain is used to ensure the privacy, security, and interoperability of health data. Offering a decentralized approach to data management, it allows for the creation of a single, unchangeable patient health record, improving care coordination and outcomes. In supply chains, blockchain provides unparalleled visibility and traceability. It allows for real-time tracking of goods from production to delivery, reducing the likelihood of counterfeit products entering the supply chain and improving operational efficiency. In the energy sector, blockchain is facilitating peer-to-peer energy trading, enabling consumers to buy and sell excess renewable energy directly with one another. In real estate, blockchain is streamlining transactions by eliminating the need for intermediaries, reducing costs, and speeding up the process. It also adds transparency by providing a secure, immutable record of property ownership. Public sector entities are leveraging blockchain for a range of applications, from maintaining land registries to improving public service delivery and transparency. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures a high degree of transparency. As every transaction is recorded across a network of computers, it's virtually impossible to alter past transactions. This immutability fosters a high level of trust, as parties involved can verify transactions independently. In industries like supply chain and finance, this feature drastically reduces the risk of fraudulent activities. For instance, in supply chains, stakeholders can trace a product's journey from manufacturing to the end consumer, creating an ecosystem where the product's authenticity is verifiable. Blockchain's robust security features make it an attractive choice for industries dealing with sensitive data. It uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data, rendering it extremely resistant to cyber threats. This security is critical in sectors like healthcare, where patient confidentiality is paramount. By creating a secure, immutable record of patient data, blockchain can help mitigate risks of data breaches, thereby protecting both healthcare providers and patients. Blockchain technology significantly optimizes business operations by eliminating intermediaries and streamlining processes. This is achieved through smart contracts - self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. These contracts automate routine tasks, thereby speeding up the transaction process considerably. Financial institutions can leverage this to expedite settlements, while supply chains can use it to automate logistics processes. The result is an overall increase in operational efficiency and productivity. Cost reduction is another profound benefit of blockchain. Transaction costs can be reduced by eliminating middlemen, thereby simplifying the transaction process. Moreover, compliance costs can be reduced as the transparency provided by blockchain simplifies the audit process. These cost reductions can be particularly beneficial for financial institutions, which often incur significant expenses due to complex regulatory compliance requirements. By improving transparency and reducing reliance on intermediaries, blockchain can pave the way for considerable cost savings across all industries. The pioneering nature of blockchain technology implies a high degree of complexity. Grasping the nuances of blockchain requires a steep learning curve and specialized knowledge. This complexity often acts as a deterrent for organizations considering the technology, especially those without access to dedicated blockchain experts. Overcoming this obstacle often necessitates investing in education and training to develop in-house blockchain expertise. Given its disruptive potential, blockchain often finds itself in a regulatory gray area. As a relatively nascent technology, most countries are still trying to understand blockchain's implications, leading to an absence of clear, definitive regulations. This lack of legal clarity can create uncertainty for organizations planning to implement blockchain, as they may find it challenging to comply with evolving regulations and ensure their blockchain applications are legally sound. With various types of blockchain platforms in existence, each with distinct capabilities, a significant challenge arises - the lack of standardization. Organizations can find it overwhelming to choose the right platform that suits their specific needs. Developing common standards that streamline the selection process is crucial to encouraging the widespread adoption of blockchain technology. Interoperability, or the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and interact seamlessly, is a substantial challenge that impedes the technology's full potential. As industries often deal with multiple blockchain networks, it's vital to ensure that these networks can exchange and make use of information efficiently. Addressing interoperability issues can propel the blockchain industry forward by enabling more integrated and versatile applications. The implementation of blockchain technology across industries holds enormous potential for transformative change. It's redefining the landscapes of industries like finance, healthcare, supply chain, and more by offering enhanced transparency, fortified security, increased efficiency, and cost reduction. However, its complexity, regulatory ambiguity, lack of standardization, and interoperability issues present significant challenges. By addressing these hurdles and fostering a broader understanding of blockchain's benefits and applications, industries can harness this revolutionary technology to its full potential. The coming years will undoubtedly witness blockchain's increasingly vital role in driving innovation, efficiency, and growth across various sectors.Blockchain in Industries Overview
How Blockchain Is Implemented in Various Industries
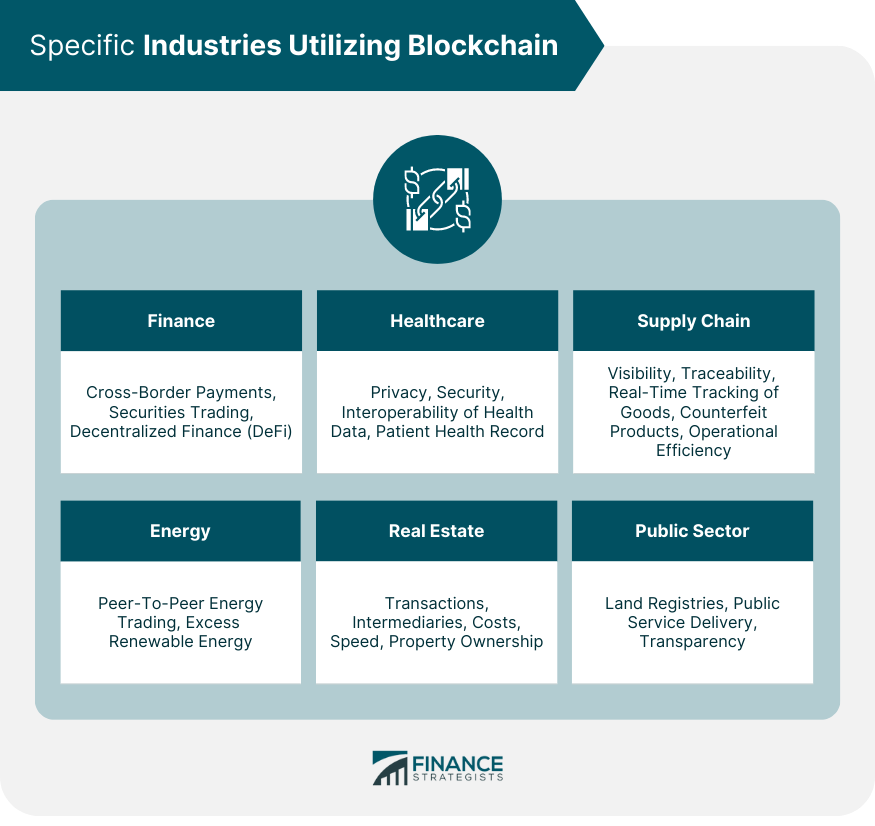
Specific Industries Utilizing Blockchain
Finance Industry
Healthcare Industry
Supply Chain Industry
Energy Industry
Real Estate Industry
Public Sector
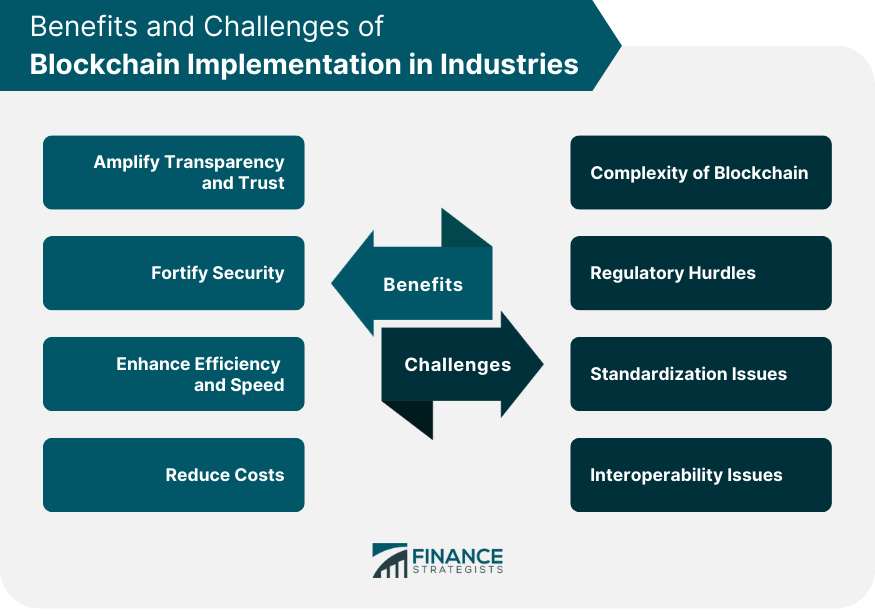
Benefits of Blockchain in Industries
Amplify Transparency and Trust
Fortify Security
Enhance Efficiency and Speed
Reduce Costs
Challenges of Blockchain Implementation in Industries
Complexity of Blockchain Technology
Regulatory Hurdles Encountered
Standardization Issues in Blockchain
Interoperability Issues
Conclusion
Blockchain in Industries FAQs
'Blockchain in Industries' refers to the use of blockchain technology across various industrial sectors. It involves leveraging blockchain's unique features, such as its decentralized nature and transparency, to transform business operations and drive industry-level changes.
Blockchain technology is utilized across numerous industries, including finance, healthcare, supply chain, energy, real estate, and the public sector. In each of these industries, blockchain is leveraged to improve transparency, security, efficiency, and trust.
The benefits of implementing blockchain in industries include increased transparency and trust, enhanced security, improved efficiency and speed, and reduced costs. These benefits stem from blockchain's immutable record-keeping, decentralized nature, and capacity for automating processes.
The challenges of implementing blockchain in industries include its technical complexity, regulatory challenges, lack of standardization, and interoperability issues. Overcoming these challenges requires both technological advancement and legislative support.
Blockchain is transforming industry operations by changing the way transactions are conducted, data is stored and managed, and value is created and transferred. It streamlines operations, eliminates intermediaries, automates processes, and introduces new business models, leading to increased efficiency and potential for growth.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











