Blockchain in Metaverse denotes the incorporation of a decentralized and transparent ledger system into a collective virtual shared space. This digital realm, termed the metaverse, emerges from the intersection of virtually augmented physical reality and the physical persistence of virtual space. Within this digital ecosystem, blockchain enables the creation, ownership, trading, and security of digital assets in an immutable and transparent manner. Blockchain brings to the fore the idea of true digital ownership facilitated through asset tokenization. This process allows users to own, trade, and potentially profit from their digital assets, such as virtual real estate, digital art, and more, much like the way one would deal with physical assets. Furthermore, with its inherent qualities of trust, transparency, and security, blockchain technology serves as the foundation upon which the metaverse can confidently rest, making every transaction and interaction reliable, verifiable, and secure. The backbone of blockchain technology within the metaverse comprises of complex systems like decentralized networks, distributed ledgers, cryptographic algorithms, and consensus protocols. These decentralized networks eliminate the need for central authorities, promoting direct peer-to-peer interactions. Any transaction that occurs within this network is captured in blocks on the distributed ledger. Cryptographic algorithms provide an added layer of security, ensuring the data is secure and immutable. In the metaverse, smart contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps) are critical components of blockchain technology. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They facilitate transactions without intermediaries, with the contract automatically executed when pre-set conditions are met. On the other hand, DApps are applications that are built on the blockchain network, providing various functionalities within the metaverse, such as gaming, finance, and social networking. In the world of the metaverse, blockchain technology introduces the possibility of true digital ownership. This is achieved through asset tokenization. Tokenization involves converting rights to an asset into a digital token on a blockchain. These tokens, representative of digital assets, grant users verifiable ownership rights. The implications are profound for in-game assets, virtual real estate, and digital collectibles, among other forms of digital assets. True digital ownership becomes a reality through blockchain's asset tokenization. Much like the physical world, these assets can be traded, sold, or held for potential future appreciation. This opens up new economic opportunities within the metaverse, as users can capitalize on their digital assets. The decentralization aspect of blockchain technology has the potential to make the metaverse more accessible and financially inclusive. By eliminating intermediaries, transactions and interactions become more straightforward. Moreover, the universal accessibility of cryptocurrencies can help foster financial inclusion, even reaching those traditionally excluded from financial systems. The fusion of blockchain technology with the metaverse can revolutionize the retail and commerce industry. By enabling the creation of immersive e-commerce experiences, users can engage in interactive and lifelike shopping experiences, transforming traditional commerce. The encrypted and immutable nature of blockchain records enhances user privacy and data security within the metaverse. The transparency and security of blockchain technology help build trust among users, which is crucial for the mass adoption of the metaverse. The integration of blockchain into the metaverse isn't without its challenges. One of these is the technical complexity of blockchain technology, which can pose a significant barrier to entry for many users. Additionally, due to the nascent stage of both blockchain and metaverse technologies, the accessibility of these technologies for non-technical users can be a challenge. Regulatory and legal uncertainties surrounding the use of blockchain and cryptocurrencies also pose significant challenges. The issues of jurisdiction, tax implications, and legal recognition of digital assets are still open for debate and will require international cooperation to address. Blockchains, particularly those that use the proof-of-work consensus mechanism, can be energy-intensive. This could raise sustainability concerns, particularly as the scale of the metaverse expands. Like any financial system, the use of blockchain in the metaverse is susceptible to financial scams and cybersecurity threats. The risk of fraud, hacking, and phishing attacks necessitates robust security measures and regulatory oversight to protect users and their assets. Several blockchain platforms are at the forefront of metaverse development, each offering unique features and capabilities. Platforms such as Ethereum, with its robust smart contract functionality, underpin many decentralized virtual worlds. Similarly, the Flow blockchain, the technology behind the popular NBA Top Shot, is another leading player capable of handling high volumes of transactions. While Ethereum is renowned for its comprehensive smart contract capabilities, Flow distinguishes itself with its scalability and low transaction costs. Other platforms like Polkadot and Cosmos offer interoperability features, while some platforms focus on delivering high-speed transactions. The choice of platform largely depends on the specific use case and requirements of the metaverse application. Blockchain technology has given rise to a virtual real estate market within the metaverse. Users can buy, sell, or lease virtual land, with all transactions verified through the blockchain. This has created new investment opportunities, and significant real-world capital is starting to flow into this virtual real estate market. The influence of blockchain extends to virtual goods and services within the metaverse. Tokenization allows users to own, trade, or sell their in-game assets as they see fit. This introduces a whole new level of economic incentive for participation in the metaverse. The impact of blockchain on in-game economies and decentralized finance (DeFi) within the metaverse is equally significant. Through tokenization and DeFi, users can lend, borrow, earn interest, and trade digital assets, transforming the metaverse into a self-sustaining economy. Blockchain's integration into the metaverse revolutionizes digital ecosystems, providing a decentralized, transparent ledger system fostering true digital ownership and increased accessibility. It catalyzes an evolution in digital economies, impacting virtual real estate, goods, services, and DeFi, through sophisticated mechanisms such as decentralized networks, distributed ledgers, cryptographic algorithms, smart contracts, and DApps. As advantageous as this innovation is, it's not devoid of challenges. Technical complexities, regulatory uncertainties, sustainability issues, and cybersecurity threats are hurdles to overcome as this technology proliferates. Pioneering platforms like Ethereum and Flow, among others, offer unique features, pushing the boundaries of what's achievable in the metaverse. The blockchain-metaverse convergence has the potential to reshape our digital future, bringing with it new wealth creation opportunities and, with it, new wealth management needs. As you navigate this emerging landscape, it's crucial to seek the expertise of wealth management professionals who understand the dynamics of these transformative technologies. What Is Blockchain in Metaverse?
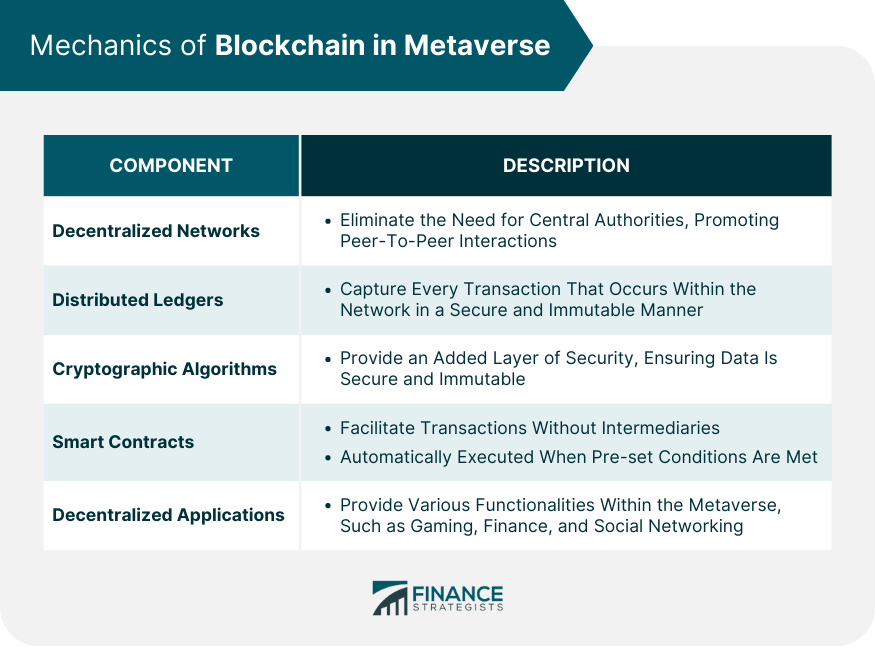
Mechanics of Blockchain in Metaverse
Infrastructure and Mechanisms
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Digital Ownership and Asset Tokenization
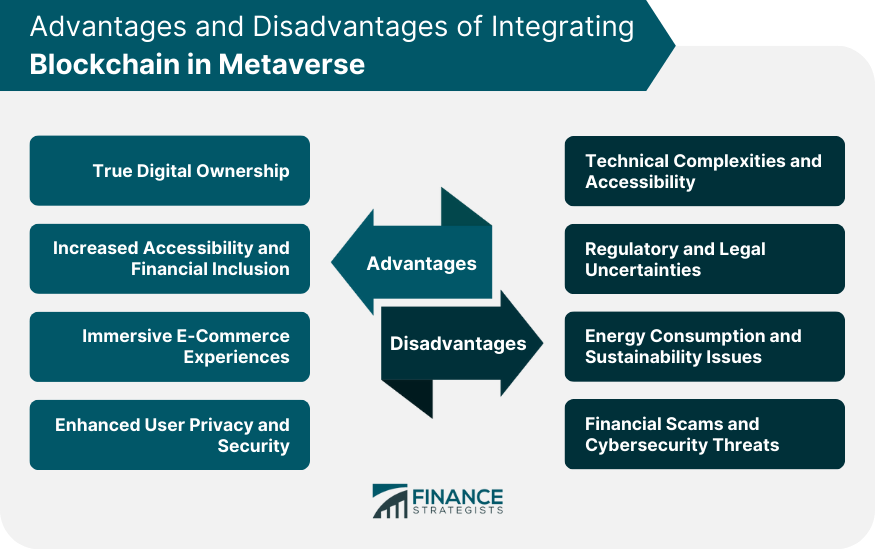
Advantages of Integrating Blockchain in Metaverse
Realization of True Digital Ownership
Increased Accessibility and Financial Inclusion
Creation of Immersive E-commerce Experiences
Provision of Enhanced User Privacy and Security
Challenges of Implementing Blockchain in Metaverse
Navigating Technical Complexities and Accessibility
Addressing Regulatory and Legal Uncertainties
Managing Energy Consumption and Sustainability
Mitigating Financial Scams and Cybersecurity Threats
Prominent Blockchain Platforms in the Metaverse
Examination of Leading Platforms
Comparison of Features and Capabilities
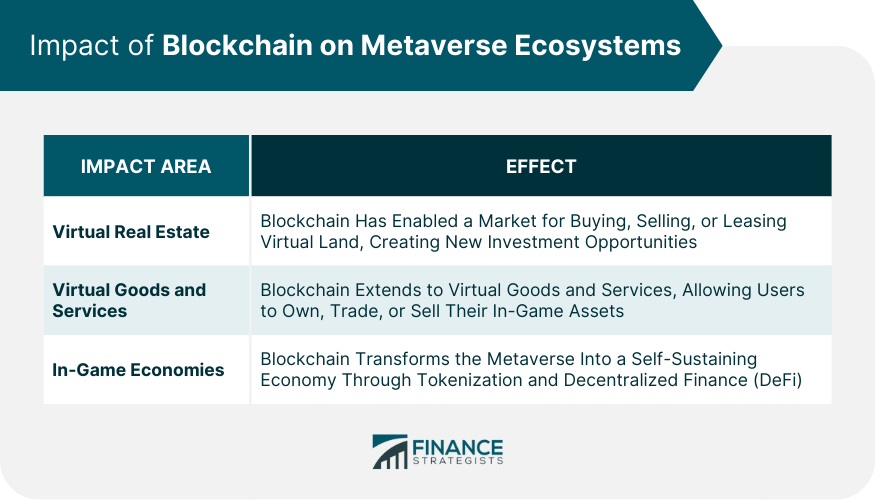
Impact of Blockchain on Metaverse Ecosystems
Effect on Virtual Real Estate
Influence on Virtual Goods and Services
Impact on In-Game Economies and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The Bottom Line
Blockchain in Metaverse FAQs
Blockchain in the metaverse enables true digital ownership, secure transactions, and the creation of a decentralized, user-driven economy.
Advantages include enhanced user privacy, true digital ownership, increased accessibility, and immersive e-commerce experiences.
Challenges involve technical complexities, regulatory uncertainties, sustainability issues, and potential cybersecurity threats.
Platforms like Ethereum, Flow, Polkadot, and Cosmos provide robust functionalities such as smart contracts and interoperability that enhance the metaverse experience.
Blockchain transforms metaverse ecosystems by enabling new opportunities in virtual real estate, goods and services, and in-game economies.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











