Blockchain in the automotive industry refers to the application of decentralized ledger technology to various aspects of the automotive sector. The technology securely records and verifies transactions across a network of participants, bringing enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency to operations. Key applications include supply chain management, where blockchain can track and authenticate every transaction, vehicle authentication through creating a digital twin and facilitating contracts and transactions through smart contracts. The result is a more streamlined and secure operational process, reinforcing data security, consumer trust, and the overall efficiency of the automotive industry. Despite its complexities, blockchain technology represents a transformative tool in the digital evolution of the automotive sector. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) forms the backbone of blockchain technology. It offers an immutable and transparent ledger distributed across a network of computers called nodes. In the automotive industry, DLT allows for the secure tracking of vehicle parts, ensuring the authenticity of components and protecting against counterfeiting. Smart contracts, a unique feature of blockchain, are self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code. In automotive transactions, smart contracts automate processes such as vehicle leasing, insurance, and sales, thereby reducing the need for middlemen and reducing costs. Several leading automotive companies, including BMW, Ford, and Renault, are exploring blockchain applications to enhance their operations. These companies have used blockchain for use cases ranging from supply chain transparency to automated vehicle payments. Startups are also driving innovation in the field, introducing novel applications of blockchain in the automotive sector. Companies like FOAM are creating spatial protocols for autonomous cars, while others like CarVertical are focusing on vehicle history reports using blockchain technology. The blockchain ecosystem is a complex network of technology providers, regulators, and users. Automotive companies need to understand this ecosystem, including various blockchain platforms and the regulatory landscape, before embarking on their blockchain journey. A successful blockchain implementation requires collaboration between different stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, and competitors. Automotive companies should focus on building these collaborative networks for a successful implementation. The regulatory environment for blockchain is still evolving. Automotive companies need to closely monitor this landscape and ensure their blockchain implementation is compliant with existing and emerging regulations. Blockchain technology has the potential to significantly disrupt the automotive industry's value chain. It enables direct interaction between manufacturers and customers, potentially eliminating intermediaries. It can also facilitate new business models like peer-to-peer car sharing or leasing. By increasing transparency and trust, blockchain can transform the relationship between automotive companies and customers. It enables new services, like car history verification, and improves existing ones, like leasing and insurance. Blockchain can unlock new revenue streams for automotive companies by enabling new business models. Additionally, by automating various processes, it can lead to cost reductions. Blockchain technology allows for unprecedented supply chain transparency. Every component's journey can be traced from the raw material stage to the final product, reducing the risk of counterfeit parts entering the supply chain and improving quality control. Blockchain technology simplifies and streamlines transactions by automating them through smart contracts. It removes intermediaries, reduces the time taken for settlements, and reduces transaction costs. With a secure and unalterable ledger, blockchain technology ensures the security and authenticity of vehicle data. It protects against data breaches and offers a reliable platform for data sharing among trusted parties. Blockchain technology enhances customer trust through transparency. Customers can verify the history and authenticity of a vehicle, which increases confidence in the purchase. Furthermore, it enables secure customer interaction, facilitating services like vehicle leasing, ride-sharing, and pay-per-use insurance. Implementing blockchain technology in the automotive industry is technically complex. It involves overcoming challenges related to blockchain's scalability, speed, and energy consumption. Interoperability between different blockchain systems is another issue that needs to be addressed. Blockchain technology faces regulatory challenges due to its disruptive nature. Regulations related to data privacy, cross-border transactions, and smart contracts are still evolving, creating a level of uncertainty for automotive companies considering blockchain adoption. Integrating blockchain technology with existing systems is a significant challenge. Many automotive companies use legacy systems for operations, and integrating these with blockchain technology may require substantial time and resources. While blockchain ensures data security, concerns around data privacy persist. Because of the transparent nature of the blockchain, ensuring private data is not accessible by unwanted parties can be a significant concern. Blockchain is a relatively new technology with associated risks. Automotive companies need to adopt a phased approach to implementation, starting with pilot projects before going for full-scale implementation. Additionally, they should invest in blockchain education and training to build internal capabilities. Legal and regulatory risks are among the most significant challenges for blockchain implementation. Companies need to engage with legal experts and closely follow the evolving regulatory landscape to mitigate these risks. Blockchain implementation involves operational and financial risks. Companies need to ensure the integration of blockchain with existing systems and processes. Financial risks can be mitigated by careful budgeting and cost management. Blockchain technology has the potential to reshape the automotive industry by enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency. Understanding the blockchain ecosystem, building collaborative networks, and navigating the regulatory environment are essential considerations for implementing blockchain in the automotive industry. The impact of blockchain on automotive business models includes potential shifts in the value chain, changing customer relationships and services, and new revenue streams. Blockchain offers benefits such as enhanced supply chain transparency, streamlined transactions, improved data security and authenticity, and increased customer trust and interaction. However, challenges related to technical complexity, scalability, regulatory compliance, integration with existing systems, and data privacy must be addressed. Risk mitigation strategies involving phased implementation, legal and regulatory engagement, and operational and financial considerations can help overcome these challenges. By embracing blockchain technology strategically, the automotive industry can unlock its transformative potential and drive innovation in areas such as supply chain management, vehicle authentication, and streamlined transactions.What Is Blockchain in the Automotive Industry?
How Blockchain Works in the Automotive Industry
Key Players in Blockchain Application in the Automotive Industry
Major Automotive Companies
Innovative Startups
Practical Considerations for Implementing Blockchain in the Automotive Industry
Understanding the Blockchain Ecosystem
Building Collaborative Blockchain Networks
Navigating the Regulatory Environment
Impact of Blockchain on Automotive Business Models
Potential Shifts in the Value Chain
Changing Customer Relationships and Services
New Revenue Streams and Cost Structures
Benefits of Blockchain in the Automotive Industry
Enhanced Supply Chain Transparency
Streamlined Automotive Transactions
Improved Vehicle Data Security and Authenticity
Increased Customer Trust and Interaction
Challenges of Implementing Blockchain in the Automotive Industry
Technical Complexity and Scalability
Regulatory Challenges
Integration With Existing Systems
Data Privacy Concerns
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Blockchain Implementation in the Automotive Industry
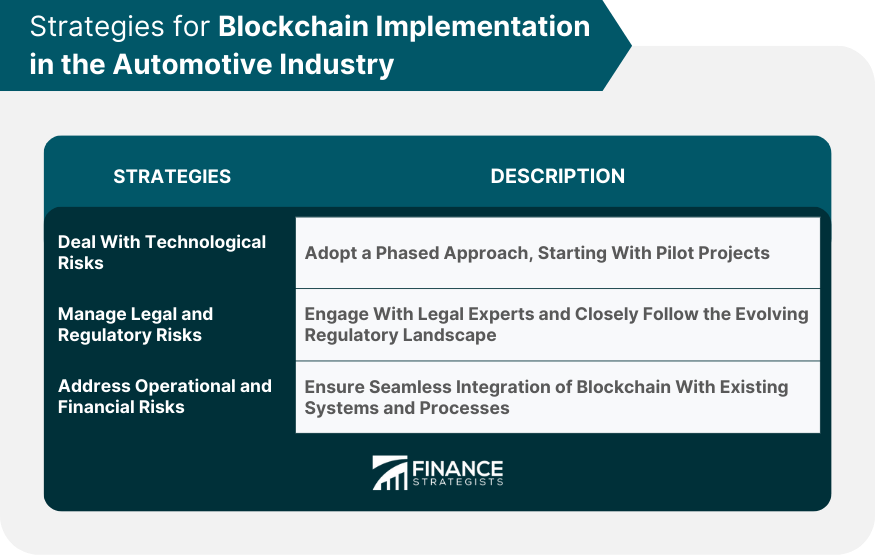
Dealing With Technological Risks
Managing Legal and Regulatory Risks
Addressing Operational and Financial Risks
Conclusion
Blockchain in the Automotive Industry FAQs
Blockchain technology provides enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency in the automotive industry. It is used for tracking and authenticating every transaction in the supply chain, vehicle authentication, and automating contracts and transactions.
Blockchain improves supply chain management by providing an unalterable record of every transaction, from raw material procurement to final product. This enables better quality control and prevents the entry of counterfeit parts into the supply chain.
Adopting blockchain technology in the automotive industry comes with technical complexities, regulatory uncertainties, difficulties in integrating with existing systems, and concerns about data privacy.
Several leading automotive companies, including BMW, Ford, and Renault, are exploring blockchain applications. In addition, innovative startups like FOAM and CarVertical are introducing novel blockchain applications in the sector.
Blockchain has the potential to disrupt the automotive industry's value chain, facilitate direct interaction between manufacturers and customers, and enable new business models like peer-to-peer car sharing or leasing. It can also transform customer relationships and unlock new revenue streams.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











