What Is Blockchain in the Energy Industry?
Blockchain in the energy industry refers to the application of blockchain technology in energy-related transactions and management.
This innovative technology serves as a dxecentralized ledger that records and verifies all energy transactions in real-time, shared across a network of computers.
This technology promotes transparency and efficiency in the energy sector, especially in energy trading. For instance, blockchain can facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals to buy and sell energy directly without the need for intermediaries.
Additionally, blockchain can improve grid management, enabling more efficient distribution of energy resources. It also allows for the verification of renewable energy certificates, thereby promoting the use of renewable energy sources.
Despite a few challenges like the complex nature of the technology and high energy consumption, blockchain holds considerable potential in transforming the energy industry.
Purpose and Importance
Blockchain technology holds the potential to revolutionize the energy sector. Its primary purpose in this industry is to increase efficiency, transparency, and security in energy transactions.
It offers a decentralized, reliable, and verifiable platform that can facilitate direct peer-to-peer energy transactions, thereby reducing reliance on intermediaries and lowering transaction costs.
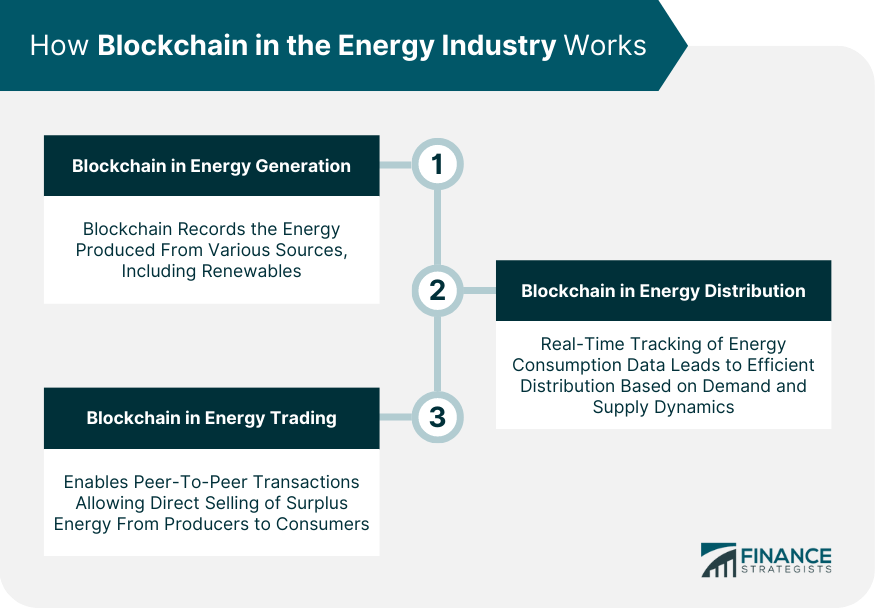
How Blockchain in the Energy Industry Works
Energy Generation
In the realm of energy generation, blockchain enables the recording of energy produced by various sources, including renewable sources like solar and wind power.
Energy producers can register their production data on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and verifiability of their production volumes.
Energy Distribution
Blockchain can also revolutionize the energy distribution process. It can facilitate real-time tracking of energy consumption data, allowing for efficient energy distribution based on real-time demand and supply dynamics.
This can lead to optimized energy distribution, reduction of losses, and improved energy efficiency.
Energy Trading
In energy trading, blockchain can enable peer-to-peer transactions, where energy producers can sell their surplus energy directly to consumers.
This type of transaction, known as peer-to-peer energy trading, can be recorded and verified on the blockchain, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction costs.
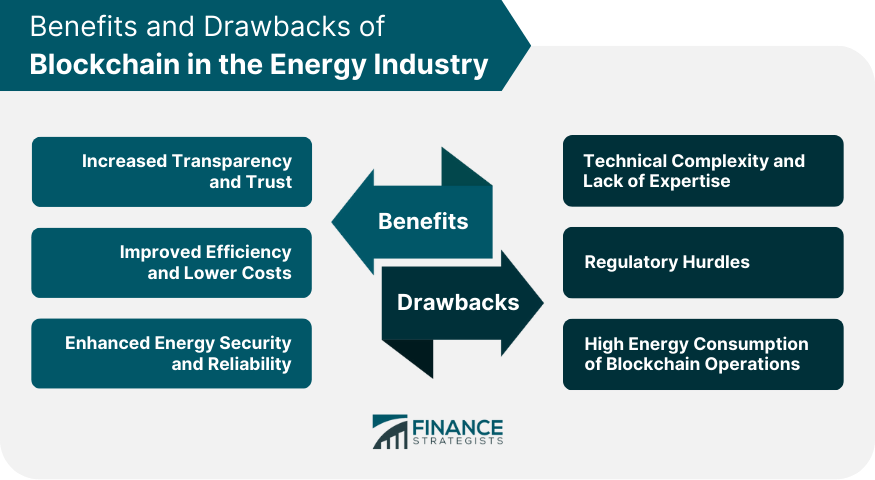
Benefits of Blockchain in the Energy Industry
Increased Transparency and Trust
Blockchain provides a transparent and verifiable record of all transactions, enhancing trust among participants in the energy market.
This can lead to increased participation in energy markets, especially from small-scale energy producers and consumers.
Improved Efficiency and Lower Costs
By enabling peer-to-peer transactions and eliminating intermediaries, blockchain can significantly reduce transaction costs in the energy sector.
Additionally, the real-time tracking of energy production and consumption can lead to improved efficiency in energy distribution.
Enhanced Energy Security and Reliability
Blockchain can enhance energy security by enabling a decentralized energy system, where energy consumers can source their energy directly from producers.
This can reduce reliance on centralized energy grids, improving energy reliability, especially in regions prone to grid failures.
Drawbacks and Challenges of Blockchain in the Energy Industry
Technical Complexity and Lack of Expertise
Implementing blockchain in the energy sector requires technical expertise and an understanding of both blockchain technology and energy systems. This complexity can be a significant hurdle, especially for smaller energy companies.
Regulatory Hurdles
The energy sector is highly regulated, and the use of blockchain in this sector can face regulatory hurdles. Regulations concerning energy trading, data privacy, and cybersecurity can all impact the adoption of blockchain in the energy industry.
High Energy Consumption of Blockchain Operations
Blockchain operations, especially those based on proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, can consume significant amounts of energy.
This can be a significant drawback, especially considering the growing concern over the environmental impact of energy consumption.
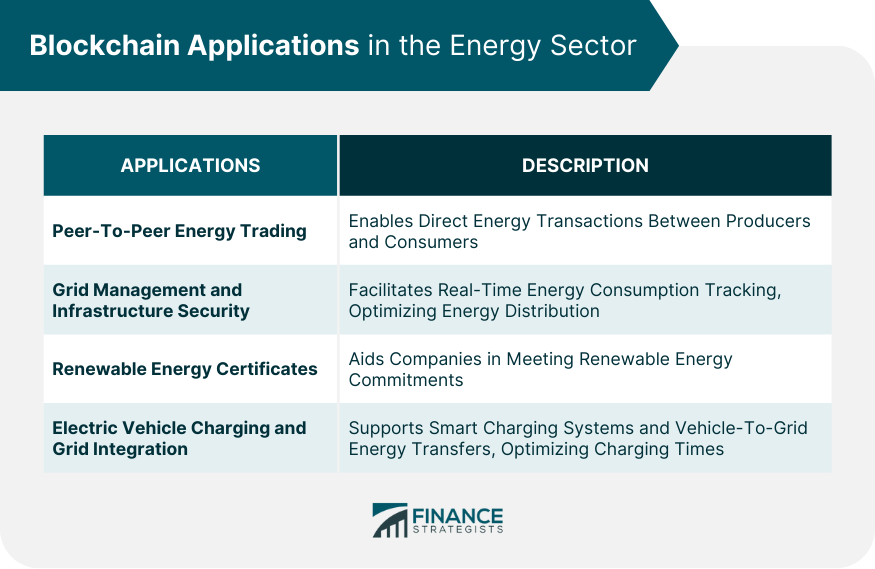
Blockchain Applications in the Energy Sector
Peer-To-Peer Energy Trading
One of the primary applications of blockchain in the energy sector is peer-to-peer energy trading.
Blockchain technology can enable direct trading between energy producers and consumers, allowing for more efficient use of energy resources and lower energy costs.
Grid Management and Infrastructure Security
Blockchain can enhance grid management and infrastructure security. It can enable real-time tracking of energy consumption, which can help in managing energy loads on the grid.
Additionally, the secure nature of blockchain can help protect energy infrastructure from cyber threats.
Renewable Energy Certificates
Blockchain can facilitate the issuance and trading of renewable energy certificates (RECs). RECs represent the environmental attributes of renewable energy production and can be traded separately from the actual electricity.
Blockchain can ensure the transparency and authenticity of RECs, making it easier for companies to meet their renewable energy commitments and for regulators to verify compliance.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging and Grid Integration
Blockchain can also support the integration of electric vehicles (EVs) with the energy grid. It can enable smart charging systems where EVs can communicate with the grid to optimize charging times based on grid loads and electricity prices.
Moreover, EVs can sell back excess energy to the grid, a process known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) energy transfer, with transactions recorded and verified on the blockchain.
Conclusion
Blockchain's transformative potential in the energy industry is becoming increasingly apparent. It holds the promise of revolutionizing energy markets by increasing transparency, efficiency, and security in energy transactions.
The applications of blockchain, from peer-to-peer energy trading to grid management and from renewable energy certificates to electric vehicle grid integration, can fundamentally reshape the energy landscape.
However, realizing this potential has its challenges. Technical complexity, regulatory hurdles, and the high energy consumption of blockchain operations represent significant obstacles.
Overcoming these will require concerted efforts from stakeholders in the energy industry and beyond.
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain in the energy industry looks promising, with the potential for profound and far-reaching impacts.
Blockchain in the Energy Industry FAQs
Blockchain in the energy industry refers to the use of blockchain technology to facilitate energy transactions, improve grid management, ensure transparency in energy trading, and enhance renewable energy distribution. It is a decentralized ledger that records energy transactions and shares them across a network of computers.
Blockchain works by recording energy transactions, such as buying and selling energy, on a decentralized ledger. These transactions are verified by multiple participants in the network, enhancing the transparency and security of the transactions. It enables peer-to-peer energy trading, efficient grid management, and the verification of renewable energy certificates.
The benefits of using blockchain in the energy industry include enhanced transparency in energy transactions, increased efficiency in energy trading and grid management, and improved tracking of renewable energy distribution. It can also support electric vehicle charging and grid integration.
Challenges include the complexity of the technology, regulatory hurdles, and the high energy consumption of some blockchain operations. Overcoming these challenges requires technological advancements and regulatory support.
Practical applications include peer-to-peer energy trading, grid management, tracking renewable energy certificates, and electric vehicle charging and grid integration. Blockchain can ensure the transparency, efficiency, and security of these processes.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











