Blockchain wallets, at the heart of digital asset management, are software applications that facilitate the monitoring, management, and transaction of cryptocurrencies. Unlike traditional wallets, they serve as digital interfaces for interacting with various blockchain networks, where they store a user's public and private cryptographic keys. The private key enables access to digital assets, while the public key acts as an address for receiving funds. In the fast-paced realm of digital finance, blockchain wallets offer a crucial blend of security and accessibility. They provide a secure environment for storing and transacting digital assets, allowing users to engage with the blockchain network anytime, anywhere. This makes them an indispensable tool for anyone participating in the digital economy. Blockchain wallets rely heavily on cryptography for their operations. Each transaction processed through a blockchain wallet is secured using complex cryptographic algorithms. These algorithms ensure that once a transaction is added to the blockchain after verification, it's immutable and cannot be modified or tampered with, providing a robust level of security and trust. When you initiate a transaction using a blockchain wallet, the network needs to verify it. This verification process involves miners who solve complicated mathematical problems to authenticate the transaction. Once it has been validated, it's added to a 'block' of transactions. This block, in turn, is linked to the existing blockchain, creating an unalterable record of the transaction. A blockchain wallet interacts with blockchain networks to execute transactions. When you initiate a transaction, your wallet broadcasts the details to the network. Nodes, which are computers maintaining the blockchain, then validate the transaction and add it to the blockchain. An essential aspect of blockchain wallet operations revolves around public and private keys. A private key is akin to a password that allows the spending of cryptocurrencies from the wallet. A public key, contrastingly, functions as a public address where others can send funds. Hot wallets refer to blockchain wallets that are constantly connected to the internet. They offer convenience and are easy to use, making them suitable for frequent transactions. However, their constant internet connectivity also makes them more vulnerable to online threats, which users must consider. Cold wallets, in contrast, are offline wallets. They provide a higher level of security by storing digital assets offline, making them less susceptible to online threats. They are particularly suitable for storing large amounts of digital assets over a long period, although they might lack the convenience of hot wallets. Compared to traditional banking systems, blockchain wallets offer a higher level of security. The combination of cryptographic encryption and decentralization reduces the risk of single-point failures and unauthorized access. Moreover, many wallets offer two-factor authentication, adding an extra layer of security. One of the unique advantages of a blockchain wallet is that it gives users complete control over their digital assets. Unlike traditional banking, where the bank has ultimate control over user funds, blockchain wallets provide users with full ownership of their digital assets. Blockchain wallets are not just for storing and transacting digital currencies. They are also designed to interact with smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) built on the blockchain. This versatility makes blockchain wallets an essential tool in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. Transactions made via a blockchain wallet are transparent and verifiable on the blockchain. This transparency fosters trust, as users can always validate the authenticity of transactions. The technology behind blockchain wallets can be daunting for beginners. To effectively and securely use a blockchain wallet requires a level of technical knowledge that may present a steep learning curve for many. Blockchain wallets, despite their enhanced security, are not entirely immune to digital threats like hacking and phishing. Users must adhere to best practices in digital security to safeguard their assets, which often requires a robust understanding of digital security principles and regular updating of security protocols. A significant risk associated with blockchain wallets is the loss of access to digital assets due to private key mismanagement. The private key associated with a blockchain wallet is the only way to access the stored funds. If this key is lost, the user loses access to their digital assets with no mechanism for recovery. Choosing a blockchain wallet that fits your needs requires careful consideration. Factors such as security requirements, types of digital currencies to be stored, and users' technical proficiency play a significant role in the decision-making process. For instance, a hardware wallet (a type of cold wallet) might be suitable for those who prioritize security, while a mobile wallet (a type of hot wallet) might be more suitable for those needing regular access to their digital assets. There is a wide variety of blockchain wallet options available, each with its unique features and security measures. Some of the popular blockchain wallets include Trezor and Ledger (hardware wallets), and MyEtherWallet and MetaMask (web-based wallets). It is advisable for users to conduct thorough research and choose a wallet that best fits their specific needs and circumstances. Blockchain wallets serve as the backbone of digital asset management, offering a secure and efficient medium to store and transact digital currencies. Their enhanced security measures, transparency, and the control they offer to users signify a marked improvement over traditional financial systems. However, they are not without their challenges, with technological complexity and potential loss due to private key mismanagement being some of them. By understanding the working of blockchain wallets and their pros and cons, users can make informed decisions and effectively navigate the world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies. The future is sure to bring more innovation and user-friendly features in this domain, but the onus of using these wallets securely and effectively will always lie with the user.What Is a Blockchain Wallet?
How a Blockchain Wallet Works
Cryptographic Security
Transaction Verification and Record
Interaction With Blockchain Networks
Public and Private Keys
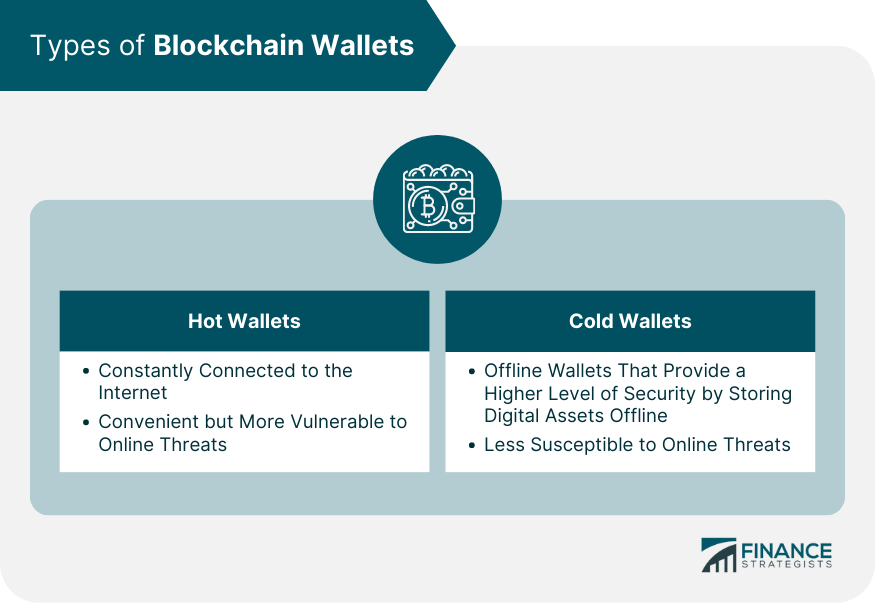
Types of Blockchain Wallets
Hot Wallets
Cold Wallets
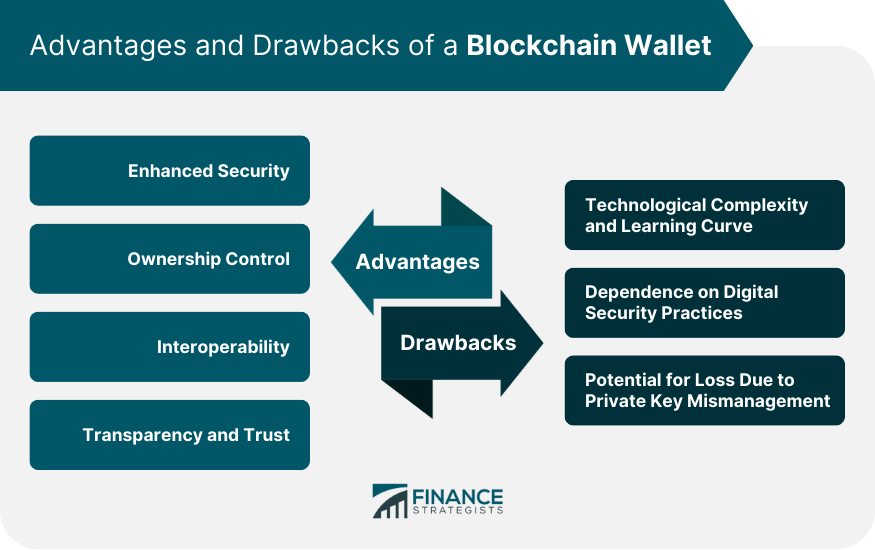
Advantages of a Blockchain Wallet
Enhanced Security
Ownership Control
Interoperability With Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Applications
Transparency and Trust
Drawbacks of a Blockchain Wallet
Technological Complexity and Learning Curve
Dependence on Digital Security Practices
Potential for Loss Due to Private Key Mismanagement
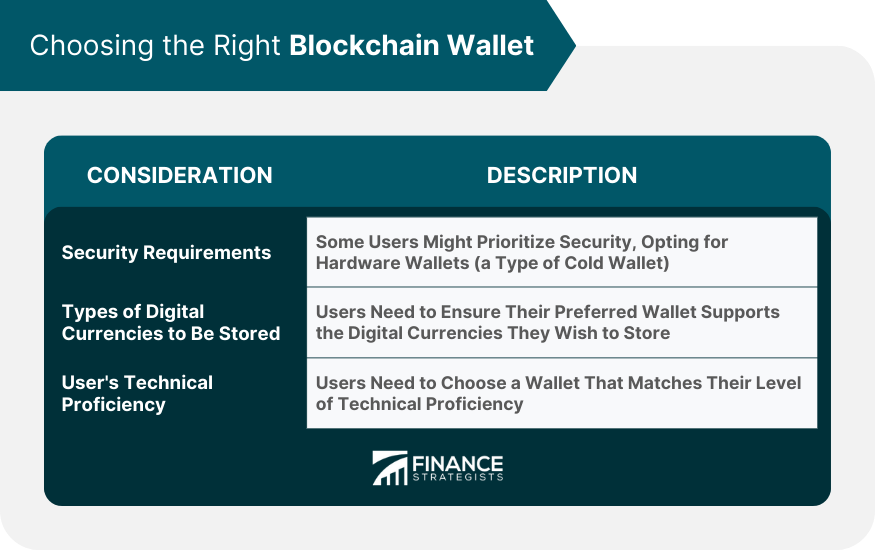
Choosing the Right Blockchain Wallet
Final Thoughts
Blockchain Wallet FAQs
A blockchain wallet is a digital interface that allows users to monitor, manage, and transact their cryptocurrencies. It is where a user's public and private cryptographic keys are stored. The private key enables access to digital assets, while the public key functions as a recipient address for digital funds.
Blockchain wallets offer enhanced security through cryptographic encryption and decentralization. They give users complete control over their digital assets and allow interaction with cryptocurrencies and blockchain applications like smart contracts and DApps. All transactions made via a blockchain wallet are transparent and verifiable on the blockchain, fostering trust.
The technology behind blockchain wallets can be complex and require a certain level of technical knowledge. Despite their enhanced security, they are not immune to digital threats like hacking and phishing. Also, if the private key of a blockchain wallet is lost, the user loses access to their digital assets without any recovery mechanism.
Hot wallets are blockchain wallets that are constantly connected to the internet, offering convenience but being more vulnerable to online threats. Cold wallets, on the other hand, are offline wallets that provide a higher level of security by storing digital assets offline, making them less susceptible to online threats.
Choosing a blockchain wallet requires careful consideration of factors such as security requirements, the types of digital currencies to be stored, and the user's technical proficiency. It's recommended to conduct thorough research and choose a wallet that best fits your specific needs and circumstances. Popular options include hardware wallets like Trezor and Ledger and web-based wallets like MyEtherWallet and MetaMask.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











