A blockchain network is a type of distributed digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers or nodes in a manner that the recorded transactions cannot be altered retroactively. It forms the backbone of blockchain technology, ensuring transparency, decentralization, and security. The purpose of a blockchain network is to enable secure, peer-to-peer transactions through a decentralized system, eliminating the need for intermediaries and enhancing the efficiency of data transfer. It accomplishes this through a series of individual components working together, including node applications, a shared ledger, a consensus algorithm, a virtual machine, and smart contracts. These components ensure the smooth operation of the network, each fulfilling a specific role, from validating transactions and maintaining a record of transactions to executing automated contracts. The blockchain network has transformative applications across various industries, from finance to supply chain management. A standard blockchain network is composed of several core components, each of which plays a crucial role in the operation and maintenance of the network. A node application, or simply a node, is the fundamental unit of a blockchain network. Each node stores a copy of the blockchain ledger and participates in the validation and verification of transactions on the network. The shared ledger is a decentralized and distributed database where all transactions on the blockchain network are recorded. It is accessible to all nodes in the network, which ensures transparency and prevents fraud or manipulation of transaction data. The consensus algorithm is the mechanism by which nodes in the blockchain network agree on the validity of transactions. Different blockchain networks use different consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), to secure the network and ensure that all nodes are in agreement. In the context of a blockchain network, a virtual machine (VM) is a software emulation of a computer system that executes smart contracts. It is responsible for processing the instructions encoded in smart contracts and determining the outcome of their execution. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They are stored on the blockchain network and automatically execute predefined functions when certain conditions are met. Each component of a blockchain network plays a distinctive role and serves a specific function in the overall operation of the network. Nodes, as the fundamental units of a blockchain network, play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the network. They store and update the blockchain ledger, validate and relay transactions, and participate in the consensus process. The shared ledger serves as the universal record of all transactions across the blockchain network. By maintaining a transparent and tamper-proof log of all transactions, the shared ledger ensures the integrity of the data and fosters trust among network participants. Consensus algorithms are at the heart of the decentralization feature of blockchain networks. They ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the state of the shared ledger. This agreement, or consensus, prevents double-spending, fraud, and other forms of manipulation. The virtual machine is crucial for executing smart contracts on the blockchain network. It interprets and executes the instructions in the smart contract code, thereby automating transactions and other processes on the network without the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts serves to automate the execution of agreements on the blockchain network. They eliminate the need for intermediaries, increase transaction efficiency, and ensure the execution of agreements is transparent and tamper-proof. The unique benefits of each component of a blockchain network contribute to the overall advantages of blockchain technology. Node Application: Contribute to the decentralization and security of the blockchain network. By storing copies of the ledger and participating in the consensus process, nodes help prevent fraud and ensure the integrity of the network. Shared Ledger: Fosters transparency and trust among participants in the blockchain network. Its immutability ensures the integrity of transaction data, while its accessibility allows anyone on the network to verify the transactions. Consensus Algorithm: Contribute to the security and decentralization of the blockchain network. They ensure all nodes agree on the state of the shared ledger, preventing double-spending and other forms of fraud. Virtual Machine: Enables the automation of processes on the blockchain network through the execution of smart contracts. This leads to increased transaction efficiency and a reduction in the need for intermediaries. Smart Contracts: Automate the execution of agreements on the blockchain network, leading to increased efficiency and trust. They also eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and potential points of failure. Despite their benefits, each component of a blockchain network also comes with its own set of challenges that need to be addressed. Node Application: Running a node can be resource-intensive, requiring significant computing power and storage space. Shared Ledger: The shared ledger, while ensuring transparency, can also raise privacy concerns. Since transaction data is visible to all participants on the network, appropriate measures must be in place to protect sensitive information. Consensus Algorithm: Certain consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work, can be energy-intensive and contribute to environmental concerns. Virtual Machine: The execution of smart contracts on a virtual machine can be subject to what is known as the "halting problem," which is an issue in deciding whether a given smart contract can be executed indefinitely. This can lead to inefficiencies and security concerns. Smart Contracts: While smart contracts can automate transactions, they can also be susceptible to bugs and vulnerabilities in their code. The components of a blockchain network do not exist in isolation. They interact in a manner that ensures the functionality, security, and efficiency of the network as a whole. Nodes and the shared ledger interact closely in a blockchain network. Nodes maintain and update the shared ledger, while the shared ledger provides a transparent and immutable record of transactions for the nodes to validate. The consensus algorithm, virtual machine, and smart contracts work together to automate and secure transactions on the blockchain network. The consensus algorithm ensures agreement on the validity of transactions, the virtual machine executes the smart contracts, and the smart contracts automate the transactions based on predefined rules. The interplay of the components of a blockchain network strikes a balance between security and efficiency. While the consensus algorithm and shared ledger provide security through decentralization and transparency, the virtual machine and smart contracts enhance efficiency by automating transactions and processes on the network. Understanding the components of a blockchain network offers valuable insight into the operation, strengths, and potential challenges of blockchain technology. Each component — node application, shared ledger, consensus algorithm, virtual machine, and smart contracts — plays a critical role in establishing the network's functionality, security, and efficiency. Despite the inherent challenges associated with each component, their symbiotic interaction provides the blockchain network with its unique advantages, transforming various sectors from finance to healthcare. As the understanding and development of these components continue, the potential of blockchain technology expands, promising a more decentralized, transparent, and efficient future.Blockchain Network Overview
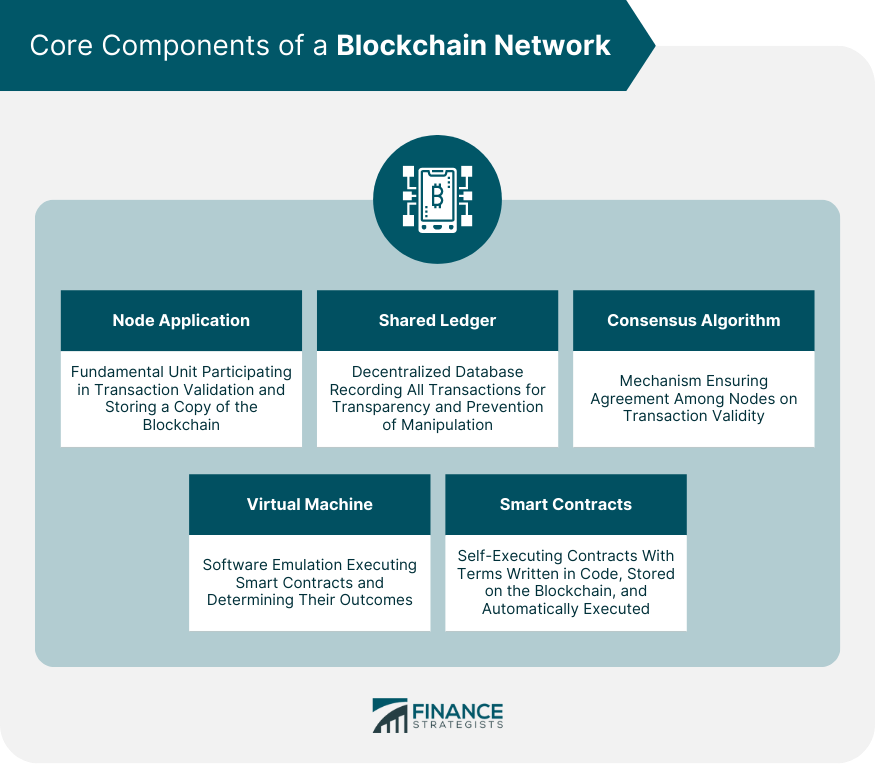
Core Components of a Blockchain Network
Node Application
Shared Ledger
Consensus Algorithm
Virtual Machine
Smart Contracts
Understanding the Role and Function of Each Blockchain Network Component
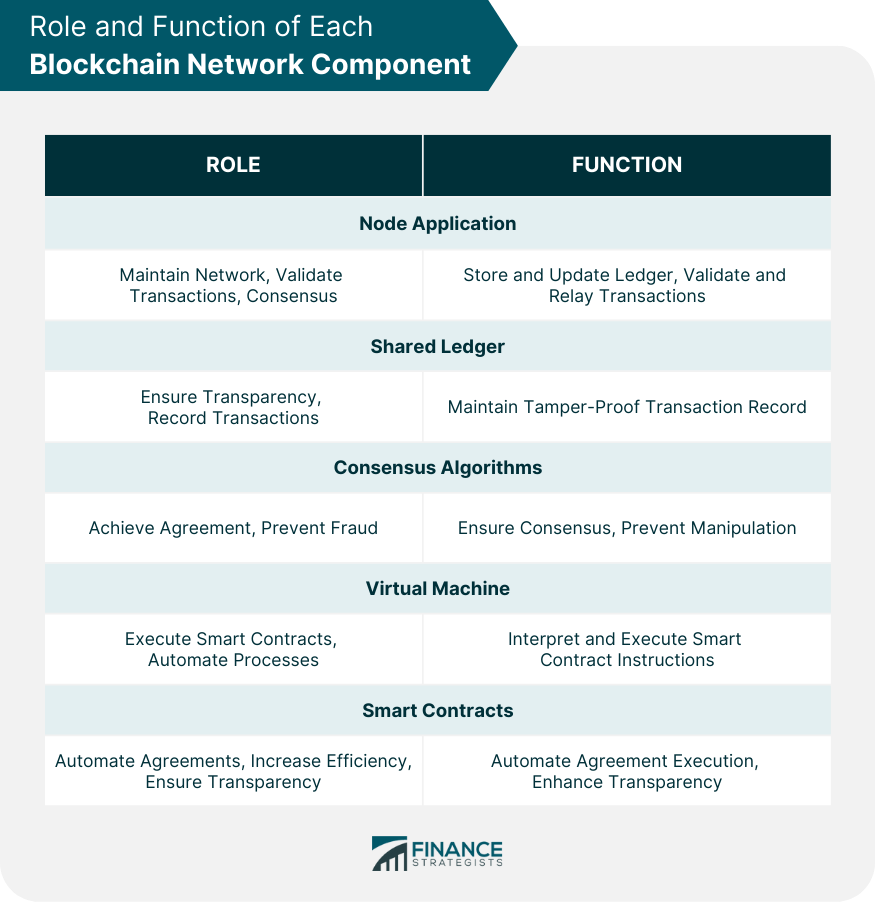
Role of Node Application in the Network
Function of Shared Ledgers
Understanding Consensus Algorithms
Importance of the Virtual Machine
Application of Smart Contracts
Benefits of Each Component in a Blockchain Network
Challenges Associated With Each Blockchain Network Component
This can limit the number of individuals or organizations willing or able to run full nodes, potentially affecting the level of decentralization in the network.
Furthermore, achieving consensus in a large, distributed network can be time-consuming and potentially slow down transaction processing times.
Moreover, once deployed, smart contracts cannot be modified, which can pose challenges if errors are discovered after deployment.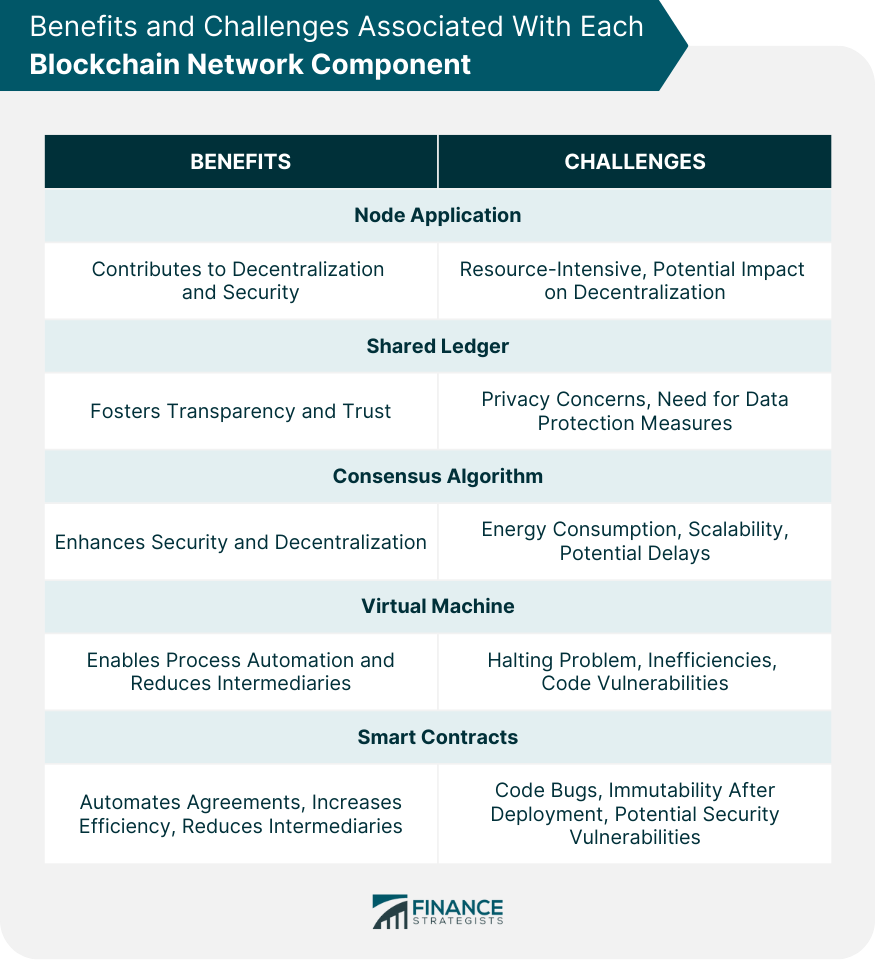
Interplay of Components in a Blockchain Network
Symbiotic Relationship Between Nodes and Shared Ledgers
How Consensus Algorithms, Virtual Machines, and Smart Contracts Work Together
Balance of Security and Efficiency in Blockchain Network Components
Conclusion
Components of Blockchain Network FAQs
The key components of a blockchain network are the node application, shared ledger, consensus algorithm, virtual machine, and smart contracts. Together, these elements allow the blockchain to operate securely and efficiently.
Nodes and the shared ledger have a symbiotic relationship. Nodes store and update the shared ledger, validate and relay transactions, and participate in the consensus process. The shared ledger provides a transparent and immutable record of transactions for the nodes to validate.
The consensus algorithm is crucial as it ensures all nodes in the network agree on the state of the shared ledger. This agreement, or consensus, prevents double-spending, fraud, and other forms of manipulation, thereby maintaining the integrity of the blockchain.
Smart contracts automate the execution of agreements on the blockchain network, leading to increased efficiency and trust. They also eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and potential points of failure.
Challenges include the resource-intensiveness of running a node, privacy concerns due to the transparency of the shared ledger, the energy consumption of certain consensus algorithms, the "halting problem" in virtual machine execution, and the susceptibility of smart contracts to bugs and code vulnerabilities.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











