Enterprise blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology designed for use in corporate environments. Unlike public blockchains that are open to anyone, enterprise blockchains are permissioned, meaning only authorized users can participate in network activities. This offers a blend of the decentralization benefits of blockchain with the control typically required in a business setting. The primary purpose of enterprise blockchain is to enhance business processes. By utilizing blockchain’s key traits of transparency, security, and immutability, businesses can achieve improved efficiency and lower costs. Its importance is recognized in various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more, as it offers a novel way to manage data and streamline operations. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) forms the core of any blockchain system. In an enterprise blockchain, the ledger is shared among the permitted participants, and every participant has an identical copy. Any changes made are reflected across all copies, which promotes transparency and trust among the users. Smart contracts, another essential aspect of blockchain technology, are self-executing contracts. The terms of the agreement are directly written into lines of code. For businesses, this automates contractual processes, minimizing the need for intermediaries and reducing potential errors and delays. Enterprise blockchains operate in a decentralized manner, with no single authority having complete control. Instead, all participants collectively make decisions, contributing to the system's resilience and making it more difficult for any one party to manipulate the data. To maintain the integrity of the system, enterprise blockchains employ various consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Authority or Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance. These mechanisms ensure that only valid transactions are recorded on the blockchain and help to prevent double-spending or other fraudulent activities. Every participant in the blockchain network runs a node application. This application allows them to propose, validate, and record transactions, ensuring the continued operation and integrity of the blockchain. The shared ledger records all transactions that occur within the network. Given its distributed nature, it's almost impossible to alter a transaction once it's been recorded, lending the enterprise blockchain its characteristic immutability. Enterprise blockchains require consensus algorithms to ensure all nodes agree on the state of the distributed ledger. This agreement maintains trust within the network and prevents fraudulent transactions from being recorded. The virtual machine executes the smart contracts on the blockchain. It runs the code when triggered by a transaction, and the results are recorded on the blockchain. Before implementing an enterprise blockchain, businesses must consider various factors, including their specific needs, potential benefits, and the readiness of their existing infrastructure to integrate with blockchain technology. Other considerations include regulatory compliance, technological expertise, and potential risk factors. Once the decision is made to proceed, the implementation process begins with identifying a suitable blockchain platform and designing the network architecture. This is followed by the development and testing phases, before finally launching the network and integrating it into the existing business infrastructure. After the implementation, continuous management and support are essential for the successful operation of the enterprise blockchain. This includes regular monitoring, resolving technical issues, and making necessary updates and improvements. Enterprise blockchain can provide real-time visibility and traceability in the supply chain, which helps in reducing fraud, optimizing logistics, and improving overall efficiency. Financial institutions can leverage enterprise blockchain to streamline transactions, enhance security, and reduce costs. By using blockchain technology, these institutions can automate various processes and eliminate the need for intermediaries, which results in faster, more efficient services. Blockchain can help healthcare providers securely manage patient data, enable interoperability between different systems, and even streamline the drug supply chain. By storing medical records on a blockchain, the data remains secure and easily accessible, promoting better patient care. Blockchain can simplify the process of buying, selling, and managing real estate by reducing fraud, speeding up transactions, and providing a clear, immutable record of ownership. This eliminates the need for many traditional real estate processes, which are often slow and opaque. Blockchain can provide a decentralized identity verification system, increasing security and reducing the risk of identity theft. With blockchain, users can control their personal data, which can be verified without being shared, enhancing both security and privacy. Due to their decentralized nature and the use of cryptographic techniques, enterprise blockchains offer enhanced security compared to traditional systems. Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it is almost impossible to alter or delete. With enterprise blockchain, all transactions are recorded on a single, shared ledger. This means that all network participants can view these transactions, resulting in unprecedented levels of transparency. Enterprise blockchain can provide an auditable trail of all transactions, which is particularly useful in supply chain management. This improved traceability can help prevent fraud and errors, as well as improve accountability. By automating and streamlining processes through smart contracts, enterprise blockchain can significantly increase operational efficiency and speed. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing delays and lowering costs. Enterprise blockchain can lead to significant cost savings by eliminating intermediaries, automating processes, and reducing fraud and errors. Additionally, improved efficiency and speed can also contribute to lower operational costs. Implementing and managing enterprise blockchain can be complex and may require significant technological expertise. This complexity can present a barrier for some organizations, especially those without the necessary technical resources. Given the relative novelty of blockchain technology, the regulatory environment is still evolving. This can create uncertainty and make it more challenging for businesses to ensure compliance when using blockchain. Integrating blockchain technology with existing IT infrastructure can be challenging and time-consuming. Incompatibility issues could arise, and significant changes may be required to existing systems. While blockchain can provide significant benefits, it can also present scalability challenges. As the number of transactions increases, the computational power required to process and verify these transactions can also increase, potentially leading to performance issues. Although blockchain can enhance security, it may raise concerns about privacy and confidentiality, particularly in sectors dealing with sensitive data. It's crucial for businesses to ensure they manage and protect data in accordance with relevant regulations. Enterprise blockchain, with its blend of decentralization and control, presents a transformative approach to conducting business. Its primary advantage lies in its ability to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in business operations across multiple sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. Key components like smart contracts and consensus algorithms automate processes, while distributed ledger technology ensures immutability and trust. Despite the potential challenges in terms of technological complexity, regulatory compliance, and scalability, the benefits clearly outweigh the risks. As organizations increasingly recognize the potential of enterprise blockchain, we are likely to witness broader adoption, ultimately leading to more efficient, transparent, and secure business environments. The emergence of blockchain in enterprise operations signifies a new era of business, where data is not just an asset, but also a driver of innovation and growth.What Is Enterprise Blockchain?
How Enterprise Blockchain Works
Role of Distributed Ledger Technology
Understanding Smart Contracts
Decentralization and Trust in the System
Validation and Consensus Mechanisms
Key Components of Enterprise Blockchain
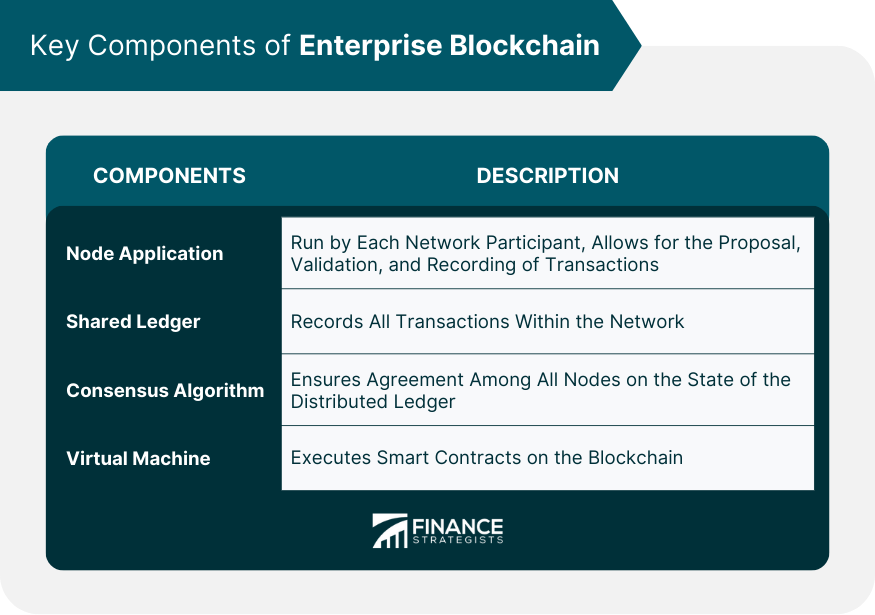
Node Application
Shared Ledger
Consensus Algorithm
Virtual Machine
Implementing Enterprise Blockchain
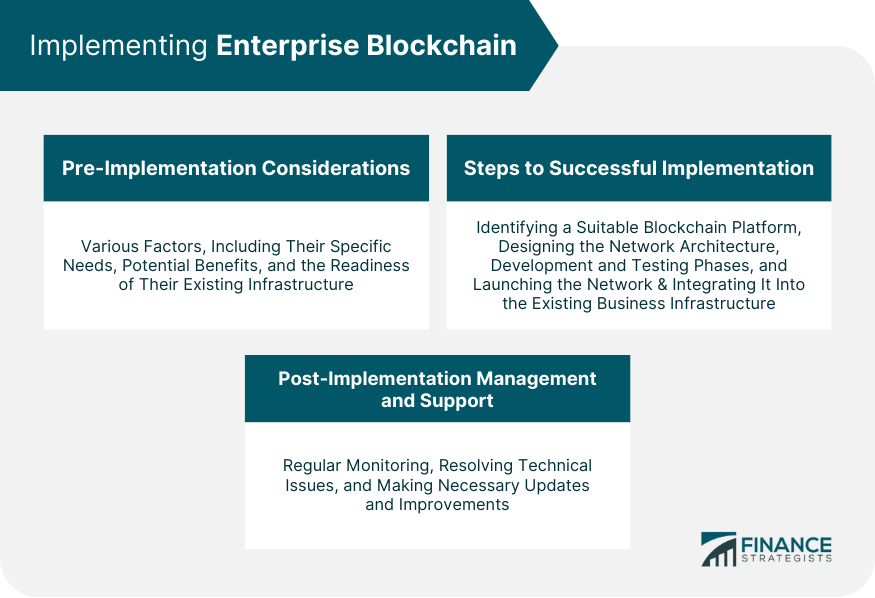
Pre-Implementation Considerations
Steps to Successful Implementation
Post-Implementation Management and Support
Use Cases of Enterprise Blockchain
Supply Chain Management
Financial Services and Transactions
Healthcare and Patient Data Management
Real Estate and Asset Management
Identity Verification and Security
Benefits of Enterprise Blockchain
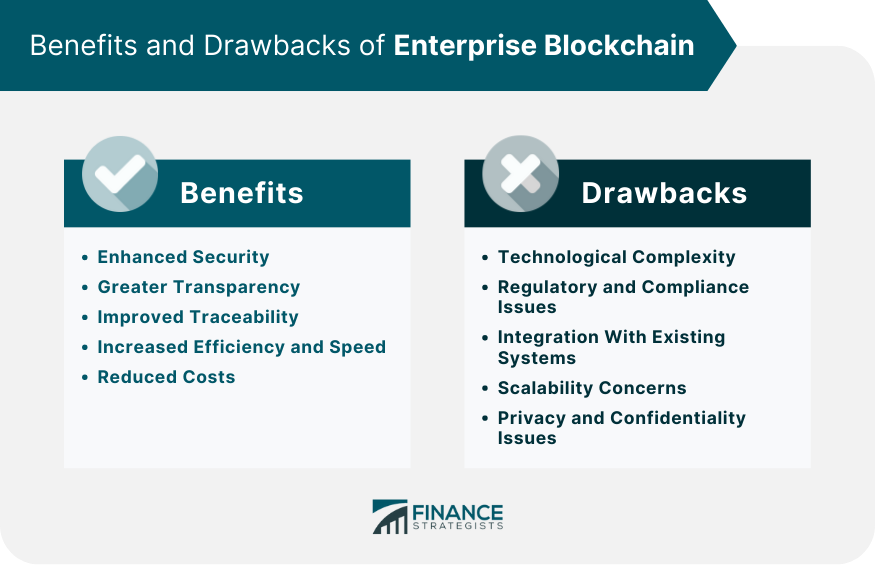
Enhanced Security
Greater Transparency
Improved Traceability
Increased Efficiency and Speed
Reduced Costs
Drawbacks and Challenges of Enterprise Blockchain
Technological Complexity
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Integration With Existing Systems
Scalability Concerns
Privacy and Confidentiality Issues
Conclusion
Enterprise Blockchain FAQs
An enterprise blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology designed specifically for business applications. It is a permissioned blockchain, which means only authorized participants can join and interact within the network. It combines the advantages of blockchain technology, like transparency, security, and immutability, with the control typically needed in a corporate environment.
Enterprise blockchain works through a shared, distributed ledger where every participant holds an identical copy of all transactions. It uses smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with terms written into code, to automate processes. The system is decentralized, with collective decision-making. Various consensus mechanisms are in place to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the system.
Enterprise blockchain has a wide range of use cases across various sectors. In supply chain management, it can provide traceability and visibility. Financial institutions can use it to streamline transactions, improve security, and reduce costs. Healthcare providers can use blockchain for secure patient data management. It can also be used in real estate and asset management for transparent transactions and clear record-keeping. Additionally, it provides a secure platform for identity verification.
Implementing enterprise blockchain can lead to enhanced security, greater transparency, improved traceability, and increased efficiency. Because it eliminates the need for intermediaries and automates processes via smart contracts, it can significantly reduce operational costs.
Despite its numerous advantages, enterprise blockchain also presents several challenges. The technology is complex, which may present a barrier for some organizations. It can also be difficult to integrate with existing systems. Regulatory and compliance issues, scalability concerns, and privacy and confidentiality issues are other potential challenges. However, with the right strategies and expertise, these challenges can be effectively managed.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











