At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers or nodes. The key characteristics of blockchain include transparency, security, immutability, and decentralization. A distributed ledger refers to a database that is shared among multiple participants or nodes in a network. In the case of blockchain, this ledger contains a chronological record of all transactions, which are bundled together into blocks. Each block is linked to the previous one, forming a chain of blocks—hence the name blockchain. Decentralization is a fundamental aspect of blockchain technology. Unlike traditional systems where a central authority controls the data and transactions, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network where no single entity has complete control. Instead, consensus algorithms are used to validate and agree upon transactions, ensuring the integrity and security of the blockchain. One of the notable features of blockchain is its immutability. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes extremely difficult to alter or tamper with. This immutability is achieved through cryptographic hashing, where each block contains a unique identifier based on the information within it. Any attempt to modify a block would require changing the entire chain, making it highly impractical and easily detectable. Transparency is another inherent characteristic of blockchain. Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is visible to all participants in the network. This transparency fosters trust and accountability as it allows for public verification of transactions without the need for intermediaries. However, this transparency also raises concerns regarding privacy, especially when dealing with sensitive information. Centralized systems, where data is stored and controlled by a single entity, pose significant privacy risks. In such systems, individuals have limited control over their personal information, making them vulnerable to data breaches, identity theft, and surveillance. Organizations with centralized databases are attractive targets for hackers seeking to exploit the wealth of data they possess. Numerous high-profile data breaches have highlighted the extent of privacy vulnerabilities in centralized systems. From the Equifax breach compromising the personal data of millions to social media giants facing privacy scandals, these incidents have exposed the dire consequences of weak privacy protections. Such breaches can have severe financial, reputational, and emotional repercussions for individuals and organizations alike. The growing concern over privacy violations has fueled the demand for enhanced privacy solutions. Users are increasingly seeking more control over their personal data, requiring robust mechanisms that protect their privacy without compromising security. This demand has paved the way for blockchain technology, which offers innovative approaches to privacy protection. Blockchain employs encryption and cryptographic techniques to safeguard the privacy of its participants. Transactions recorded on the blockchain are encrypted, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure. Public-key cryptography, for instance, allows users to interact with the blockchain using cryptographic keys, ensuring that their identities are protected. Blockchain offers pseudonymity, which means that participants are identified by cryptographic addresses rather than their real-world identities. This provides a layer of privacy by reducing the direct association between individuals and their transactions. While transactions are visible on the blockchain, it is challenging to link them back to specific individuals without additional information. Anonymity can also be achieved through certain blockchain implementations. Privacy-focused cryptocurrencies like Monero and Zcash use advanced cryptographic techniques to obfuscate transaction details, making it extremely difficult to trace the flow of funds and identify the parties involved. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements encoded on the blockchain, can incorporate privacy settings. These contracts enable selective disclosure of information, allowing parties to reveal only necessary details while keeping the rest confidential. This feature is particularly useful in sensitive business scenarios where privacy is essential, such as supply chain management or medical data sharing. The integration of privacy settings within smart contracts allows for granular control over data visibility, ensuring that sensitive information remains hidden from unauthorized parties. Privacy-focused blockchains also provide configurable options for participants to customize their privacy preferences according to their specific requirements. Blockchain technology introduces a delicate balance between transparency and privacy, addressing the needs of various use cases and participants in the network. Blockchain networks strive to strike a balance between transparency and privacy, as both aspects hold significance in different contexts. Transparency is essential for public trust, auditability, and accountability, enabling anyone to verify transactions on the blockchain. However, complete transparency may not be desirable in scenarios where certain data should remain private. To maintain this delicate balance, blockchain networks often employ mechanisms that allow for selective disclosure and encryption of sensitive information. By implementing privacy-enhancing techniques, blockchain networks can protect confidentiality while maintaining the necessary level of transparency for public validation. Public blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, offer a high degree of transparency while providing pseudonymous transactions. Participants on these networks are identified by cryptographic addresses instead of their real-world identities, preserving a level of privacy. While transaction details are visible on the public ledger, tracing these transactions back to specific individuals without additional information is challenging. Pseudonymity ensures a level of privacy on public blockchains, making it difficult to directly link transactions to real-world identities. However, it's worth noting that pseudonymity is not synonymous with complete anonymity, as additional information or external factors can potentially reveal the identities behind these cryptographic addresses. In contrast to public blockchains, private and permissioned blockchains prioritize privacy by restricting access to a limited set of participants. These networks are typically used by organizations and consortiums that require a higher level of control over data and transactions. Private blockchains offer a higher degree of privacy by allowing only authorized participants to access and verify transactions. The visibility of the blockchain can be limited to a select group, enabling confidential transactions within the network. Permissioned blockchains provide even greater control over privacy by allowing predefined entities to participate in the consensus process and access sensitive data. Private and permissioned blockchains are particularly relevant in industries where confidentiality is crucial, such as healthcare, finance, and supply chain management. By granting access only to trusted parties, these blockchain networks enhance privacy while still leveraging the benefits of decentralized technology. Blockchain technology incorporates various privacy-enhancing technologies to further protect sensitive information and ensure confidentiality. Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are cryptographic techniques that enable the verification of information without revealing the actual data. ZKPs allow for proving the correctness of a statement without disclosing the underlying details, ensuring privacy while providing cryptographic assurance. One specific type of zero-knowledge proof is zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge). zk-SNARKs are highly efficient proofs that allow for the verification of encrypted data without revealing the original values. This technology has been instrumental in privacy-focused blockchains, enabling secure transactions and preserving confidentiality. Ring signatures provide an additional layer of privacy by obfuscating the identity of the signer in a transaction. In a ring signature scheme, multiple public keys are combined, making it impossible to determine which specific key corresponds to the actual signer. This technique ensures that the source of a transaction remains anonymous, further protecting privacy on the blockchain. Confidential transactions enhance privacy by encrypting transaction amounts. Instead of publicly revealing the exact values transferred, confidential transactions employ cryptographic techniques to mask the actual amounts. This way, participants can verify the validity of transactions while maintaining confidentiality. Off-chain solutions involve conducting transactions or storing data outside the main blockchain, providing an additional layer of privacy. Off-chain channels, such as the Lightning Network for Bitcoin, enable users to perform fast and private micro-transactions without burdening the main blockchain with every single transaction detail. Privacy layers, such as the TumbleBit protocol, facilitate anonymization of transactions by obfuscating the transaction history and ensuring privacy in a scalable manner. These layers work alongside the main blockchain, offering enhanced privacy features while leveraging the security and decentralization of the underlying blockchain network. Decentralized identity (DID) systems aim to give individuals greater control over their personal information. In traditional systems, individuals often have limited control over their digital identities, relying on centralized authorities to manage and validate their credentials. DID systems, built on blockchain technology, offer a more secure and privacy-focused alternative. DID systems enable users to create and manage their identities using cryptographic keys. These identities can be verified by interacting with the blockchain, removing the need for intermediaries. By decentralizing identity management, individuals gain more control over their personal data, ensuring privacy and reducing the risk of data breaches. Self-sovereign identity (SSI) is a concept closely tied to decentralized identity systems. SSI empowers individuals to have complete ownership and control over their personal information, allowing them to selectively disclose data as needed. SSI enables users to share specific attributes or credentials without revealing their entire identity, preserving privacy in various digital interactions. By utilizing blockchain technology, SSI ensures that individuals maintain control over their identity, minimizing the reliance on centralized entities for identity verification. This decentralized approach enhances privacy and reduces the risk of personal data being exposed or misused. Blockchain plays a crucial role in enabling self-sovereign identity by providing the necessary infrastructure for secure and decentralized identity management. The immutability and transparency of blockchain ensure that identity-related transactions and verifications are tamper-proof and publicly auditable. By leveraging blockchain's features, such as cryptographic hashing, smart contracts, and decentralized consensus, self-sovereign identity systems can offer robust privacy protection and empower individuals to have full control over their personal information. As blockchain technology evolves and gains adoption, it is crucial to address privacy considerations within the framework of data protection regulations. Organizations implementing blockchain solutions must ensure compliance with relevant regulations, such as the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or similar laws in different jurisdictions. Blockchain developers and users must carefully design and implement privacy features that align with data protection regulations. Privacy-enhancing techniques, such as encryption, pseudonymity, and selective disclosure, should be employed to uphold individuals' rights to privacy while meeting legal requirements. Implementing privacy on the blockchain present unique challenges and risks. Balancing privacy and transparency requires thoughtful design and consideration of trade-offs. While blockchain technology offers privacy features, improper implementation or configuration can lead to unintended data leaks or breaches. Additionally, blockchain scalability and performance considerations can impact privacy. As transaction volumes increase, maintaining privacy becomes more challenging, especially in public blockchains where every transaction is visible to all participants. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research, innovation, and collaboration among technologists, regulators, and industry experts to establish best practices and guidelines for privacy in blockchain implementations. The field of blockchain privacy is continually evolving, driven by ongoing research and development efforts. Several emerging trends and technologies hold promise for further enhancing privacy on the blockchain. Improvements in zero-knowledge proofs, such as zk-STARKs and zk-Rollups, aimto enhance the efficiency and scalability of privacy features on the blockchain. These advancements will enable a wider range of applications and use cases without compromising privacy. Another area of development is the integration of privacy-focused cryptocurrencies into mainstream adoption. Privacy coins like Monero and Zcash continue to innovate and refine their cryptographic techniques, providing robust privacy solutions for users who prioritize anonymity in their transactions. Furthermore, advancements in decentralized identity systems and self-sovereign identity are expected to shape the future of blockchain privacy. As these technologies mature, individuals will have even greater control over their personal data, enabling seamless and privacy-enhanced interactions in various digital ecosystems. Blockchain technology represents a new era of privacy protection, fusing transparency, decentralization, and cryptography. Through encryption, pseudonymity, and selective disclosure, blockchain bolsters privacy while retaining essential transparency for public trust. This balance is ensured through pseudonymous transactions on public blockchains and increased privacy features on private blockchains. Techniques like zero-knowledge proofs and ring signatures further enhance privacy. Decentralized and self-sovereign identities allow individuals more control over personal data, decreasing reliance on central entities. Despite privacy challenges and the need for data protection compliance, continuous research, and innovation are addressing these. Progress in zero-knowledge proofs, privacy-oriented cryptocurrencies, and decentralized identities hold promise. As blockchain adoption grows, prioritizing privacy rights and fostering further research is critical. By leveraging blockchain technology and privacy-enhancing techniques, we can envision a future of harmonious coexistence between privacy and security, empowering individuals and building trust in digital interactions.Overview of Blockchain Technology
Understanding Blockchain's Immutability and Transparency
Privacy Challenges in Traditional Systems
Overview of Privacy Concerns in Centralized Systems
Examples of Data Breaches and Privacy Violations
Need for Improved Privacy Solutions
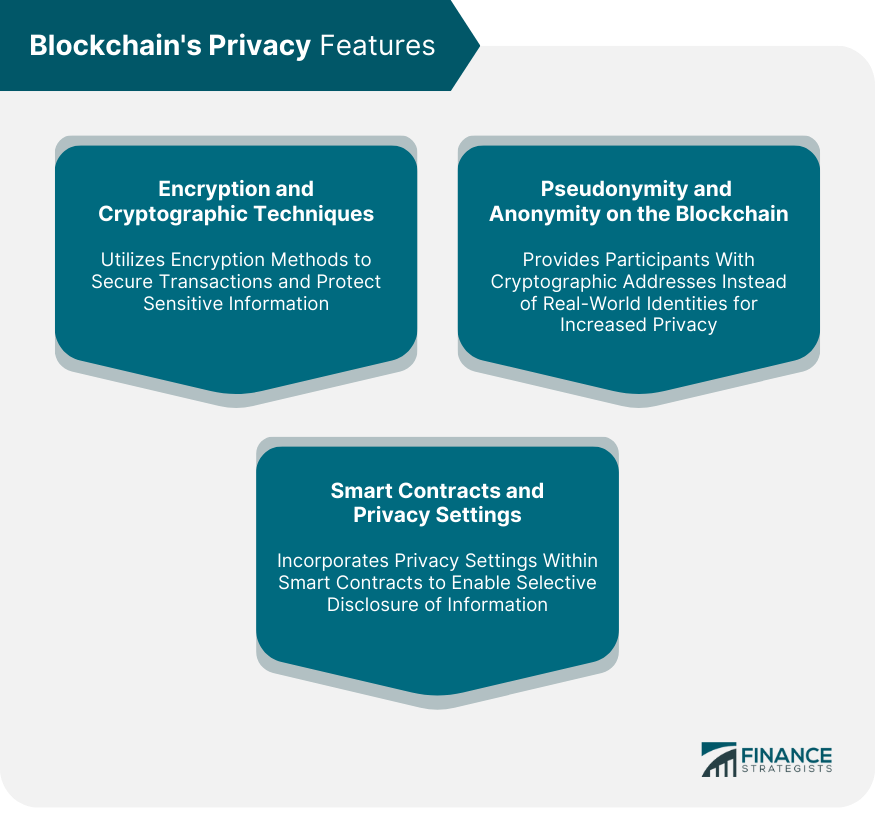
Blockchain's Privacy Features
Encryption and Cryptographic Techniques
Pseudonymity and Anonymity on the Blockchain
Smart Contracts and Privacy Settings
Transparency vs Privacy on the Blockchain
Balancing Transparency and Privacy in Blockchain Networks
Public Blockchains and Pseudonymous Transactions
Private and Permissioned Blockchains for Enhanced Privacy
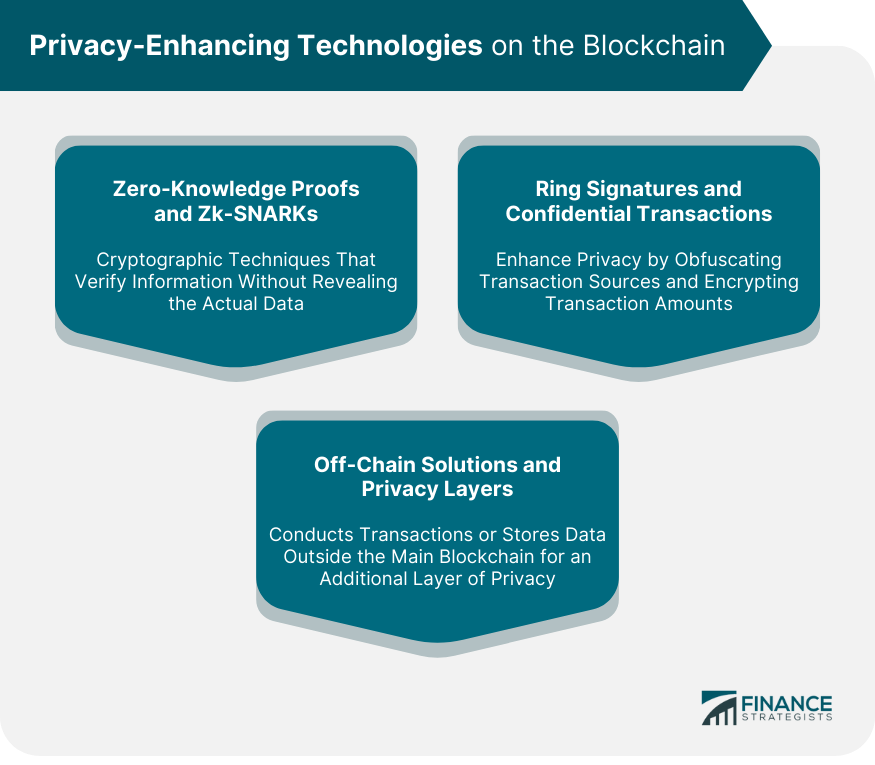
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies on the Blockchain
Zero-Knowledge Proofs and zk-SNARKs
Ring Signatures and Confidential Transactions
Off-Chain Solutions and Privacy Layers
Decentralized Identity and Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
Introduction to Decentralized Identity Systems
Benefits of SSI in Protecting Privacy
Blockchain's Role in Enabling Self-Sovereign Identity
Privacy Considerations in Blockchain Adoption
Compliance With Data Protection Regulations
Risks and Challenges in Implementing Privacy on the Blockchain
Emerging Trends and Future Developments in Blockchain Privacy
The Bottom Line
How Does Blockchain Protect Privacy? FAQs
Blockchain offers encryption, pseudonymity, and smart contracts with privacy settings.
Through techniques like zero-knowledge proofs, ring signatures, and confidential transactions.
SSI empowers individuals to control their personal data and identities using decentralized systems.
Yes, blockchain networks achieve a balance by providing selective disclosure and pseudonymous transactions.
Blockchain enables secure transactions, enhances control over personal data, and fosters trust in the digital realm.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











