Alternative investments have gained significant attention from investors looking to diversify their portfolios and potentially enhance their returns. In the simplest terms, alternative investments are financial assets that do not fall into the conventional investment categories, such as stocks or bonds. They provide an alternative (hence the name) avenue for those who seek to venture outside the confines of traditional asset classes. Financial advisor Matt Williamson encapsulates the allure of these investments, stating, "Alternative investments offer a unique proposition, breaking the traditional investment mold to unlock diverse opportunities and potential for significant returns." "Their intrinsic value lies not just in their return potential but in their capability to hedge against market volatility, making them indispensable in a strategically diversified portfolio." The significance of alternative investments lies in their potential to diversify an investment portfolio. Diversification involves spreading investments across different types of assets to reduce exposure to any single asset or risk. A well-diversified portfolio often contains a mix of stocks, bonds, and alternative investments. This mix can potentially reduce volatility and increase returns. Real estate investments encompass more than just buying a house or land. They include a wide range of options, such as residential and commercial properties, along with Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). Residential real estate involves properties used for living purposes, like apartments and houses. Commercial real estate, on the other hand, includes business-oriented properties like offices, malls, and warehouses. REITs provide a unique option for investing in real estate. These companies own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate, offering investors a way to invest in portfolios of real estate assets without having to buy or manage properties themselves. Private equity represents a type of investment involving equity (ownership) in businesses that are not publicly traded. This category includes venture capital, leveraged buyouts, and growth capital. Venture capital investments typically target startups with high growth potential. Leveraged buyouts involve buying a controlling stake in established companies with borrowed funds, intending to improve their operations and profitability. Growth capital investments are aimed at mature businesses needing capital to expand or restructure operations, enter new markets, or finance a significant acquisition. Hedge funds are investment pools that employ different strategies to earn active returns for their investors. These strategies might involve short-selling, using derivatives for leverage, and investing in domestic and international markets. Hedge funds can potentially generate high returns, but they also come with increased risks and are generally less regulated than other types of investments. As such, they are usually limited to accredited or institutional investors who can absorb these risks. Commodities are tangible assets like gold, oil, and agricultural products. Investors can invest in physical commodities by purchasing them directly or through futures contracts where the investor agrees to buy or sell a commodity at a future date for a specified price. Cryptocurrencies represent a relatively new but rapidly growing category of alternative investments. Notable cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and a growing list of others, each with unique features and uses. While cryptocurrencies can provide high returns due to their price volatility, they also come with substantial risk. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies can lead to potential regulatory issues, and the technology behind them is complex and difficult to understand. Collectibles are physical items of value due to their rarity or demand. Art, wine, classic cars, and rare coins are some examples of collectibles that investors might consider. The value of collectibles can be highly subjective and can fluctuate greatly based on trends and personal preferences. This section will draw a comparative analysis between the risks and returns of alternative investments and those of traditional investments like stocks and bonds. When it comes to alternative investments, each asset class carries its unique set of risks. For instance, real estate investments may face market fluctuations and property-specific issues, while cryptocurrencies are susceptible to extreme volatility and regulatory changes. Private equity and hedge funds often involve higher risk due to their complex nature and limited liquidity. Despite their inherent risks, alternative investments can offer substantial returns. Private equity can provide high returns from successful startups or turnaround ventures. Real estate and commodities can deliver steady income and appreciation, while cryptocurrencies have demonstrated unprecedented price surges in recent years. In comparison to stocks and bonds, alternative investments can offer a higher risk-reward profile. While the potential for higher returns exists, so does the risk of substantial losses. Therefore, understanding each investment's risk-return dynamics is crucial before embarking on alternative investment strategies. This section delves into how alternative investments can bolster diversification. Portfolio diversification involves spreading investments across different asset classes to minimize risk exposure. The goal is to construct a portfolio that can withstand market volatility and generate consistent returns over the long term. Alternative investments can enhance diversification due to their low correlation with traditional asset classes. This means that they might perform differently than stocks and bonds under the same market conditions, potentially reducing portfolio volatility and improving returns. In alternative investments, two elements take the spotlight: regulation and transparency. The regulatory environment for alternative investments differs significantly from traditional investments. For instance, hedge funds and private equity funds face less stringent regulation compared to mutual funds, while regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrencies are still developing. Alternative investments often lack the transparency characteristic of traditional asset classes. Prices for these investments may not be readily available, and information about their underlying assets can be challenging to obtain. This opacity can add another layer of risk for investors. In comparison to stocks and bonds, alternative investments often have lower levels of regulation and transparency. Investors must consider these factors and their implications on risk and return when exploring alternative investments. Given the complex nature of these investments, professional advice is often beneficial for navigating the landscape of alternative investments. Alternative investments represent a broad category of financial assets that extend beyond the traditional confines of stocks and bonds. Alternative investments, spanning from real estate and private equity to cryptocurrencies and collectibles, offer opportunities beyond traditional asset classes like stocks and bonds. Their diverse nature provides the potential for portfolio diversification, potentially mitigating risk and boosting returns. Yet, this diversity also harbors inherent challenges, including heightened risk, less regulation, and diminished transparency. This makes understanding each investment's risk-return profile critical. As their regulatory environment evolves, particularly for newer entrants like cryptocurrencies, the landscape of alternative investments continues to shift. Despite these complexities and challenges, alternative investments present a compelling prospect for those seeking to venture beyond traditional investment avenuesAlternative Investments Overview

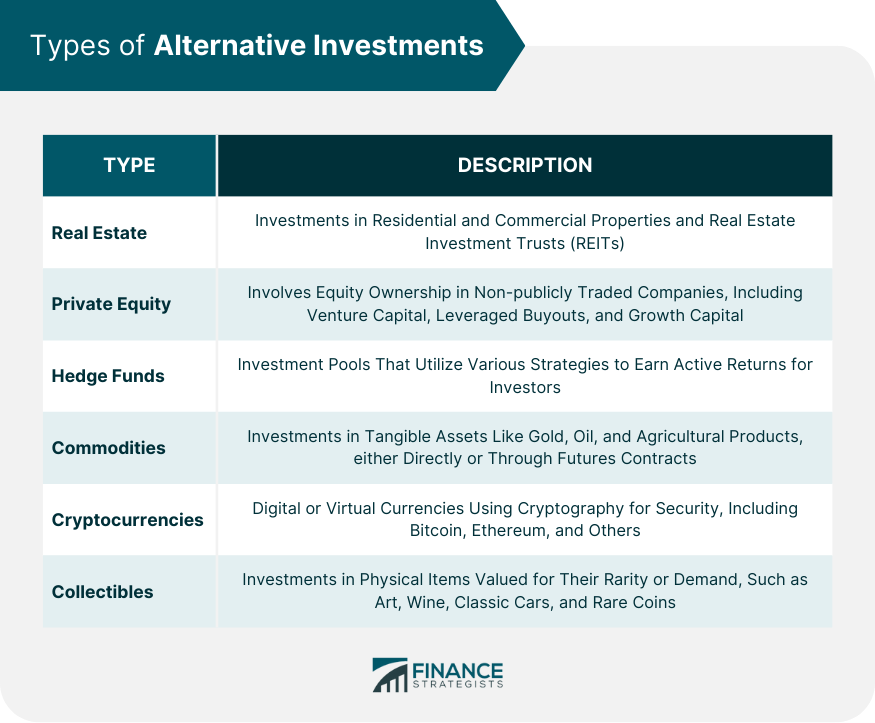
Types of Alternative Investments
Real Estate
Private Equity
Hedge Funds
Commodities
Cryptocurrencies
Collectibles
Risks and Returns of Alternative Investments
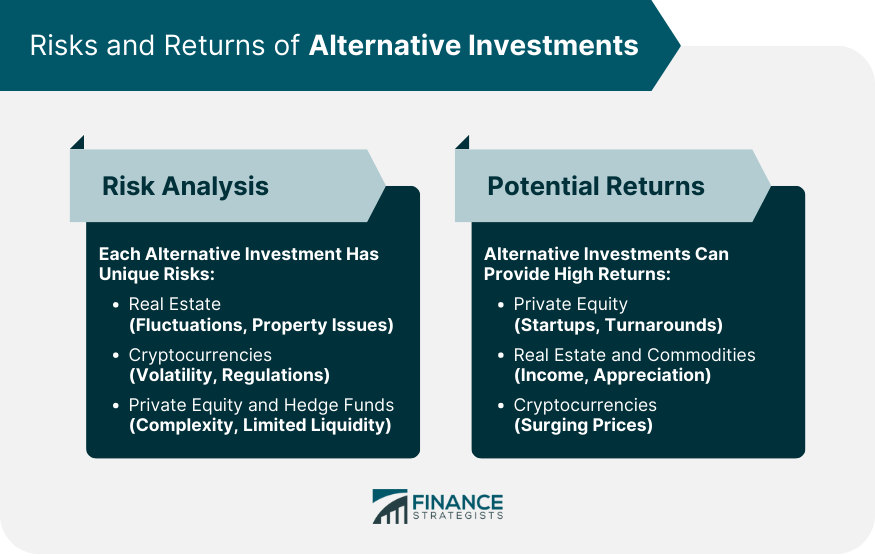
Risk Analysis of Each Type of Alternative Investment
Potential Returns From Alternative Investments
Comparisons With Risks and Returns From Stocks and Bonds
Role of Alternative Investments in Portfolio Diversification
Potential Benefits of Portfolio Diversification
How Alternative Investments Can Enhance Diversification
Regulation and Transparency in Alternative Investments
Regulatory Environment for Alternative Investments
Issues Regarding Transparency in Alternative Investments
How These Factors Differ From Stocks and Bonds
Conclusion
Alternative Investments to Stocks and Bonds FAQs
Alternative investments include a wide range of asset classes outside of stocks and bonds. Some examples include real estate, private equity, hedge funds, commodities, cryptocurrencies, and collectibles.
Investors may consider adding alternative investments to their portfolios for diversification purposes. Alternative investments often have a low correlation with traditional investments like stocks and bonds, which can help reduce portfolio volatility and potentially enhance returns.
While alternative investments can offer potential diversification benefits and potentially higher returns, they also come with their unique risks. These risks can include increased volatility, less regulation, and lower transparency compared to traditional investments like stocks and bonds.
Alternative investments generally face less regulation than traditional investments like stocks and bonds, which can result in increased risks. In terms of transparency, stocks, and bonds are typically traded on exchanges with price information readily available, while alternative investments often lack this level of transparency.
As technology continues to evolve, new types of alternative investments are likely to emerge. Cryptocurrencies are a recent example of this. While future trends are difficult to predict with certainty, the evolving landscape of investing suggests that the realm of alternative investments will continue to expand and diversify, providing more options for investors to consider.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











