Callable bonds are debt securities issued by corporations or governments that grant the issuer the right to redeem the bonds before maturity. This redemption feature allows the issuer to manage their debt obligations based on changing interest rates and financial conditions. Issuers opt for callable bonds to benefit from decreasing interest rates or to refinance their debt at a lower cost. Callable bonds typically have higher coupon rates compared to non-callable bonds, making them attractive for investors seeking higher yields. Unlike callable bonds, non-callable ones cannot be redeemed before maturity. Callable bonds tend to offer higher coupon rates to compensate for the call risk, whereas non-callable bonds usually have lower coupon rates. European callable bonds can only be called by the issuer on a specific call date. This feature provides investors with a certain degree of predictability, as they can expect the bond to remain outstanding until the specified call date. American callable bonds allow issuers to call the bonds at any time after the call protection period has expired. The issuer has multiple opportunities to redeem the bonds, depending on the interest rate environment and their financial needs. Bermuda callable bonds combine features of both European and American callable bonds. They can be called on specific dates after the call protection period, offering a balance between predictability for investors and flexibility for issuers. Multi-callable bonds can be called on multiple specified dates, giving issuers even more flexibility in managing their debt obligations. Investors may receive higher coupon rates as compensation for the increased call risk. The call price is the amount that the issuer must pay to redeem the bond before its maturity date. It is typically expressed as a percentage of the bond's face value and may include a call premium to compensate investors for the early redemption. The call date is the first date on which the issuer has the right to redeem the bond. Callable bonds may have one or multiple call dates, depending on the bond's structure and type. The call protection period is the timeframe during which the issuer is not allowed to call the bond. This period protects investors from early redemption and provides some certainty regarding the bond's cash flow. Yield to call (YTC) is the rate of return an investor can expect to receive if the bond is called on a specific date. It takes into account the bond's current price, call price, coupon payments, and time to the call date. Interest rates play a crucial role in determining the attractiveness of callable bonds. When interest rates fall, issuers are more likely to call their bonds to refinance at lower borrowing costs. Conversely, callable bonds are less likely to be called when interest rates rise, as issuers would face higher borrowing costs. The issuer's credit rating impacts the callable bond's risk and return profile. Higher-rated issuers are less likely to default, resulting in lower perceived risk and a lower coupon rate. Lower-rated issuers may offer higher coupon rates to attract investors, but these bonds carry a higher risk of default. The time to maturity affects the bond's sensitivity to interest rate changes and call risk. Callable bonds with longer maturity have a higher duration, making them more sensitive to interest rate changes. Additionally, longer maturity bonds may have higher call risk, as the issuer has more opportunities to call the bond during its lifetime. Economic conditions can influence the likelihood of callable bonds being redeemed. In a strong economy, issuers may have improved credit ratings and access to lower borrowing costs, making it more attractive to call their bonds. In weaker economic conditions, issuers may face higher borrowing costs and be less likely to call their bonds. Including callable bonds in a diversified fixed-income portfolio can help investors manage risk and generate higher income. The higher coupon rates offered by callable bonds help offset lower returns from other fixed-income securities. Investors can use callable bonds to hedge against interest rate risk by buying bonds with different call features and maturities. This strategy can help protect the portfolio's value in various interest rate environments. Callable bonds can be used to manage a portfolio's duration and reduce its sensitivity to interest rate changes. Investors can create a portfolio with a more stable duration profile by including callable bonds with different call dates and call protection periods. Investors can use bond valuation models to estimate the fair value of callable bonds, taking into account factors such as interest rates, credit rating, and call features. Common models include the Black-Scholes-Merton model and the binomial interest rate tree model. Analyzing the yield curve can help investors understand the relationship between callable bond yields and interest rates, providing insights into the bond's sensitivity to interest rate changes and potential call risk. Investors should perform credit analysis to assess the issuer's creditworthiness and the likelihood of default. This can include evaluating the issuer's financial statements, industry trends, and economic conditions. Including callable bonds in a diversified fixed-income portfolio can help investors manage risk and generate higher income. The higher coupon rates offered by callable bonds help offset lower returns from other fixed-income securities. Investors can use callable bonds to hedge against interest rate risk by buying bonds with different call features and maturities. This strategy can help protect the portfolio's value in various interest rate environments. Callable bonds can be used to manage a portfolio's duration and reduce its sensitivity to interest rate changes. Investors can create a portfolio with a more stable duration profile by including callable bonds with different call dates and call protection periods. Investors can use bond valuation models to estimate the fair value of callable bonds, taking into account factors such as interest rates, credit rating, and call features. Common models include the Black-Scholes-Merton model and the binomial interest rate tree model. Analyzing the yield curve can help investors understand the relationship between callable bond yields and interest rates, providing insights into the bond's sensitivity to interest rate changes and potential call risk. Investors should perform credit analysis to assess the issuer's creditworthiness and the likelihood of default. This can include evaluating the issuer's financial statements, industry trends, and economic conditions. Callable bonds offer issuers flexibility in managing their debt obligations, allowing them to take advantage of favorable market conditions and lower borrowing costs by redeeming their bonds early. Callable bonds typically provide higher coupon rates than non-callable bonds, making them attractive to income-seeking investors willing to accept the call risk. If interest rates decline and the issuer calls the bond, investors may benefit from capital gains, as the bond's market value will have increased due to the lower interest rate environment. When a bond is called, investors face reinvestment risk, as they must find new investment opportunities in a lower interest rate environment. This can result in lower returns and reduced income streams. Callable bonds introduce an element of uncertainty for investors, as the bond's cash flow and duration may change if the issuer decides to call the bond early. Callable bonds tend to have lower market values compared to non-callable bonds with similar credit ratings and maturities. This is due to the call risk and reinvestment risk associated with callable bonds. Callable bonds offer both advantages and disadvantages to both investors and issuers. Callable bonds allow issuers to manage their debt obligations based on changing market conditions while offering investors the potential for higher coupon rates and capital gains. However, callable bonds also introduce an element of uncertainty and reinvestment risk for investors, which may impact their returns. Investors should carefully consider the call features, credit rating, and time to maturity when evaluating callable bonds for investment. Additionally, incorporating callable bonds into a diversified fixed-income portfolio can help investors manage risk and generate higher income. Callable bonds can be analyzed using various valuation models and techniques, including bond valuation models, yield curve analysis, and credit analysis. Overall, callable bonds can provide investors with attractive returns, but investors should be aware of the call risk and reinvestment risk associated with these securities. As with any investment, investors should conduct thorough research and analysis before making investment decisions. Callable bonds can be a valuable addition to an investor's portfolio, but it's important to carefully evaluate the call features, credit rating, and time to maturity. If you need assistance with wealth management, consider seeking help from a financial advisor. Incorporating callable bonds into a diversified fixed-income portfolio can help manage risk and generate higher income. With the right approach, callable bonds can provide investors with attractive returns.What Are Callable Bonds?
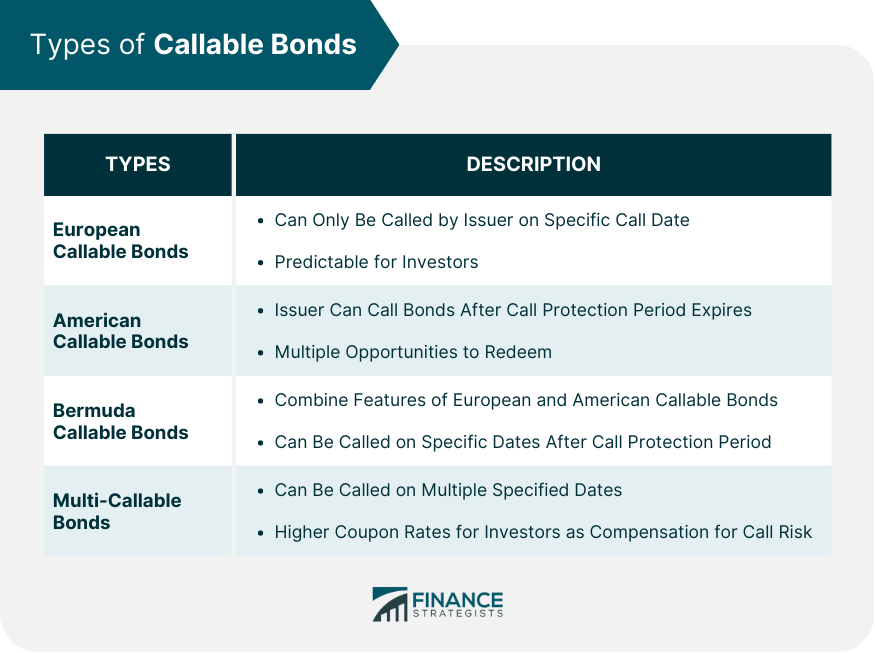
Types of Callable Bonds
European Callable Bonds
American Callable Bonds
Bermuda Callable Bonds
Multi-Callable Bonds
Key Components of Callable Bonds
Call Price
Call Date
Call Protection Period
Yield to Call

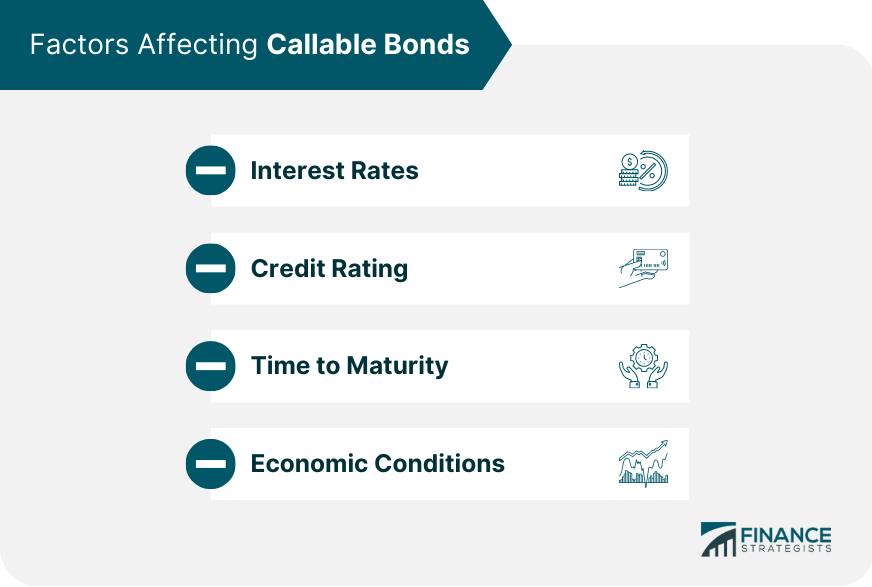
Factors Affecting Callable Bonds
Interest Rates
Credit Rating
Time to Maturity
Economic Conditions
Callable Bonds and Investment Strategies
Portfolio Diversification
Hedging Against Interest Rate Risk
Duration Management
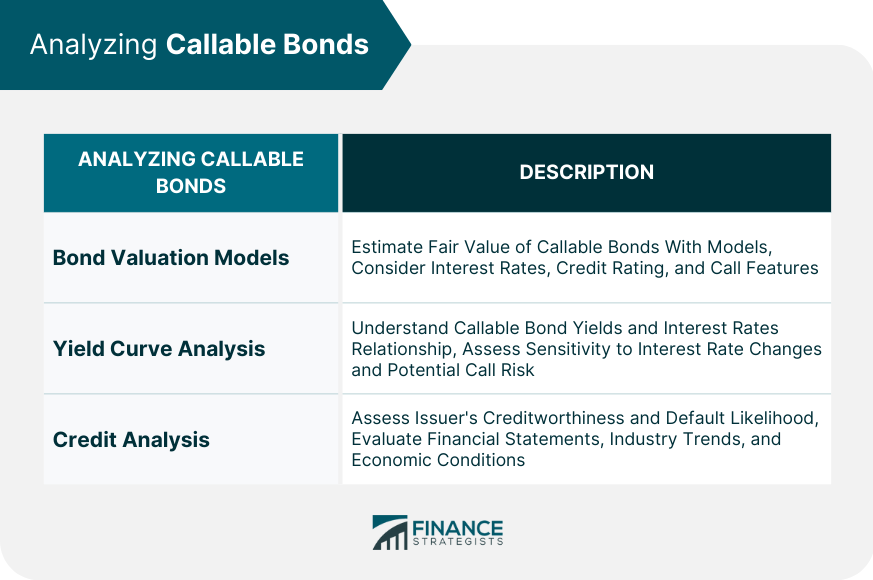
Analyzing Callable Bonds
Bond Valuation Models
Yield Curve Analysis
Credit Analysis
Callable Bonds and Investment Strategies
Portfolio Diversification
Hedging Against Interest Rate Risk
Duration Management
Analyzing Callable Bonds
Bond Valuation Models
Yield Curve Analysis
Credit Analysis

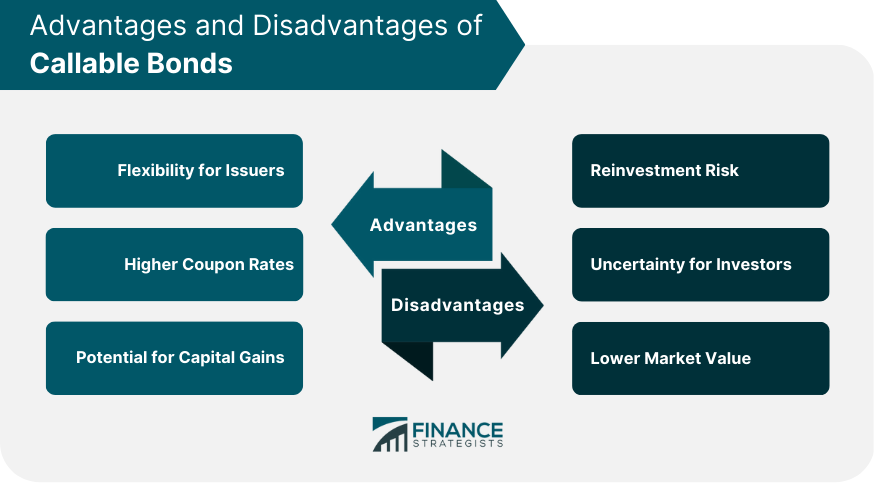
Advantages of Callable Bonds
Flexibility for Issuers
Higher Coupon Rates
Potential for Capital Gains
Disadvantages of Callable Bonds
Reinvestment Risk
Uncertainty for Investors
Lower Market Value
Conclusion
Callable Bonds FAQs
Callable bonds are bonds that can be redeemed by the issuer before the maturity date.
European callable bonds can only be called by the issuer on a specific call date, while American callable bonds allow issuers to call the bonds at any time after the call protection period has expired.
Investors can analyze callable bonds using bond valuation models, yield curve analysis, and credit analysis.
The call protection period is the timeframe during which the issuer is not allowed to call the bond.
Investors should consider the call features, credit rating, and time to maturity when evaluating callable bonds for investment.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











