A guaranteed bond is a type of fixed-income security where the repayment of the principal and interest is guaranteed by a third party, typically a government or a financial institution, ensuring a lower risk for investors. Guaranteed bonds provide a secure investment option for investors seeking steady income and low risk, while also offering issuers a means to raise capital at lower borrowing costs due to the reduced risk associated with the guarantee. Entities that issue guaranteed bonds can include governments, financial institutions, corporations, and other organizations seeking to raise capital through debt issuance, with the backing of a credible guarantor. One of the key features of guaranteed bonds is principal protection, meaning that the initial investment is secured, and investors can expect to receive their principal amount back upon the bond's maturity. Guaranteed bonds provide periodic interest payments, also known as coupon payments, to investors as a source of income throughout the bond's term, offering a predictable income stream. The maturity period of a guaranteed bond refers to the length of time until the bond's principal is repaid, with maturities ranging from short-term to long-term, depending on the specific bond and issuer. Credit rating agencies assign ratings to guaranteed bonds based on the creditworthiness of the issuer and the guarantor, with higher-rated bonds generally considered lower risk and more attractive to investors. The guarantor backing a guaranteed bond is a crucial aspect, as it ensures the repayment of the bond's principal and interest in case the issuer is unable to fulfill its obligations. Government-guaranteed bonds are issued by governments or government agencies and are backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government, making them one of the safest investment options in the bond market. Bank-guaranteed bonds are issued by financial institutions with the backing of a bank or a consortium of banks, providing additional security for investors and allowing the issuer to obtain more favorable borrowing terms. Corporate-guaranteed bonds are issued by corporations and backed by another corporation or financial institution, offering investors a higher level of security than traditional corporate bonds while still providing competitive yields. Asset-backed bonds are guaranteed by specific assets, such as mortgages or other loans, and provide investors with a claim on the cash flows generated by these assets, offering an additional layer of security compared to traditional bonds. Guaranteed bonds offer a lower risk profile compared to other fixed-income securities, as the principal and interest payments are backed by a third-party guarantor, providing a higher level of security for investors. Investing in guaranteed bonds provides a predictable and steady stream of income through regular interest payments, making them an attractive option for investors seeking stability and a reliable source of income. Including guaranteed bonds in an investment portfolio can help diversify risk, as they typically have a low correlation with other asset classes, such as stocks, and can provide a buffer against market volatility. Certain types of guaranteed bonds, particularly those issued by governments, may offer tax benefits, such as exemption from federal, state, or local taxes on the interest income earned, making them more attractive to investors in higher tax brackets. Due to their lower risk profile, guaranteed bonds typically offer lower potential returns compared to other fixed-income securities or equities, which may not be suitable for investors seeking higher returns or capital appreciation. Guaranteed bonds are subject to interest rate risk, as rising interest rates can negatively impact the market value of bonds, resulting in potential capital losses for investors who need to sell their bonds before maturity. Inflation risk is a concern for guaranteed bond investors, as the fixed interest payments may not keep pace with rising inflation, eroding the real purchasing power of the income received over time. While guaranteed bonds are generally considered low risk, they are still subject to credit risk, as the issuer or guarantor could experience financial difficulties or default, potentially impacting the bond's value and the ability to receive principal and interest payments. Investors can purchase guaranteed bonds in the primary market, where new bonds are issued and sold directly to investors, often through financial institutions or broker-dealers. Guaranteed bonds can also be bought and sold in the secondary market, where investors trade previously issued bonds among themselves, providing liquidity and the opportunity to invest in a broader range of bonds. Bond funds, such as mutual funds or closed-end funds, offer investors exposure to a diversified portfolio of guaranteed bonds, allowing for professional management and simplified access to the bond market. Investing in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that focus on guaranteed bonds can provide investors with a diversified and liquid investment option, as ETFs trade on stock exchanges and can be bought and sold throughout the trading day. When considering guaranteed bonds, it is essential to evaluate how they align with an investor's overall investment goals, such as income generation, capital preservation, or portfolio diversification. Understanding one's risk tolerance is crucial when investing in guaranteed bonds, as they offer a lower risk profile compared to other investments, making them suitable for conservative investors or those nearing retirement. Investors should consider their investment time horizon when selecting guaranteed bonds, as longer maturity periods may offer higher yields but also expose investors to greater interest rate risk. Evaluating the credit quality of the issuer and guarantor is important when selecting guaranteed bonds, as higher credit ratings typically indicate a lower risk of default and a more secure investment. In conclusion, guaranteed bonds provide a lower-risk investment option with steady income and diversification benefits, making them an attractive choice for conservative investors or those seeking a stable source of income in their portfolios. Key features of guaranteed bonds include principal protection, interest payments, maturity periods, credit ratings, and guarantor backing. Investors should carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of investing in guaranteed bonds, considering factors such as lower potential returns, interest rate risk, inflation risk, and credit risk before making a decision. It is essential for investors to assess their personal financial goals and risk tolerance when considering guaranteed bonds, ensuring that their investment strategy aligns with their overall objectives and risk appetite.What Is a Guaranteed Bond?
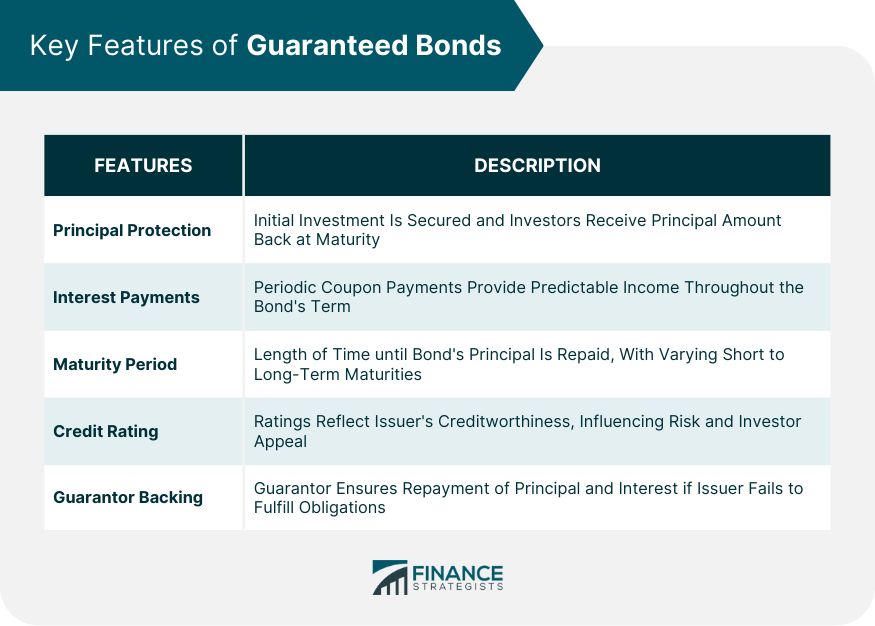
Key Features of Guaranteed Bonds
Principal Protection
Interest Payments
Maturity Period
Credit Rating
Guarantor Backing
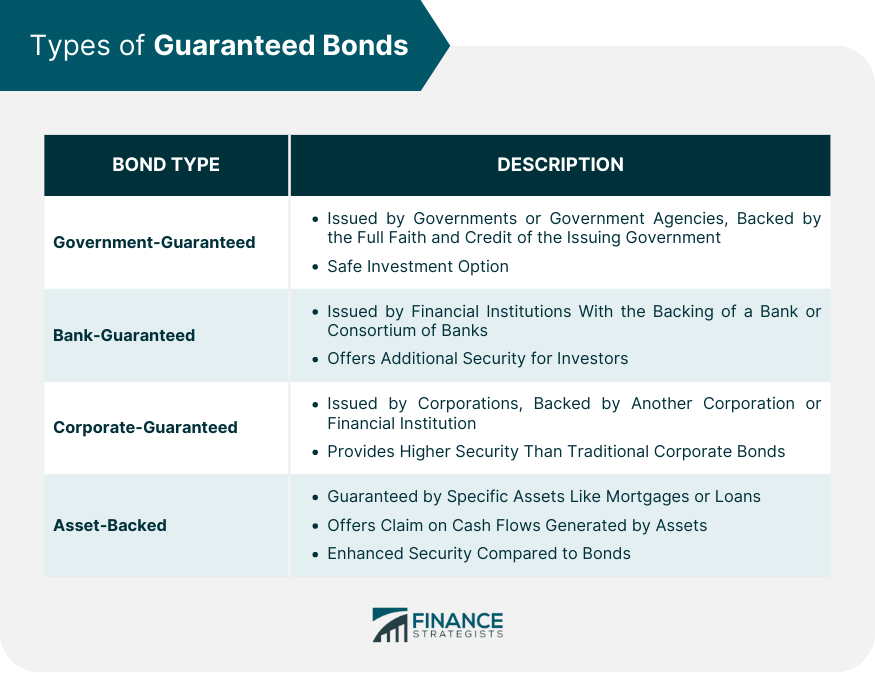
Types of Guaranteed Bonds
Government-Guaranteed Bonds
Bank-Guaranteed Bonds
Corporate-Guaranteed Bonds
Asset-Backed Bonds
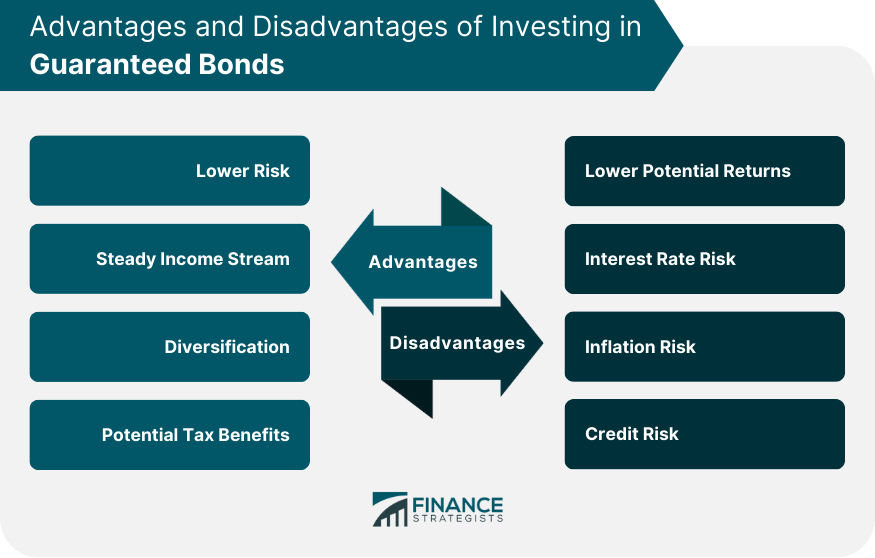
Advantages of Investing in Guaranteed Bonds
Lower Risk
Steady Income Stream
Diversification
Potential Tax Benefits
Disadvantages of Investing in Guaranteed Bonds
Lower Potential Returns
Interest Rate Risk
Inflation Risk
Credit Risk
How to Invest in Guaranteed Bonds
Primary Market
Secondary Market
Bond Funds
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Considerations for Investing in Guaranteed Bonds
Investment Goals
Risk Tolerance
Time Horizon
Credit Quality
Final Thoughts
Guaranteed Bond FAQs
A guaranteed bond is a fixed-income security where a third party, such as a government or financial institution, guarantees the repayment of the principal and interest. This added security reduces the risk for investors compared to other types of bonds that do not have a guarantor backing.
Key features of a guaranteed bond include principal protection, periodic interest payments, a defined maturity period, credit ratings, and the backing of a credible guarantor to ensure repayment of principal and interest.
Investing in guaranteed bonds offers several advantages, such as lower risk, a steady income stream through regular interest payments, diversification of investment portfolios, and potential tax benefits on certain government-issued bonds.
Despite their lower risk profile, guaranteed bonds have some disadvantages, including lower potential returns compared to other investments, interest rate risk, inflation risk, and credit risk related to the issuer or guarantor.
You can invest in guaranteed bonds through the primary market, secondary market, bond funds, or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Before investing, consider factors such as your investment goals, risk tolerance, time horizon, and the credit quality of the issuer and guarantor to ensure the guaranteed bond aligns with your financial objectives.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











