An international bond is a debt security issued by a government, corporation, or other entity in a foreign country. These bonds are typically denominated in a currency different from the issuer's domestic currency and can be traded on the international bond market. International bonds allow investors to diversify their portfolio by investing in different countries and currencies, while issuers can access a broader pool of investors and potentially lower borrowing costs. They can be issued in various forms, such as Eurobonds, foreign bonds, or global bonds. While each type of bond has unique characteristics, they all share the common feature of allowing investors to participate in the global bond market and gain exposure to foreign issuers and currencies. International bonds play an essential role in wealth management by providing investors with opportunities to diversify their investment portfolios and reduce overall risk. By investing in international bonds, investors can gain exposure to different economies, interest rates, and currencies, which can help to mitigate the impact of domestic market fluctuations and economic downturns. In addition to diversification benefits, international bonds can also offer higher yields compared to domestic bonds, particularly for investors in developed markets with low-interest rates. This can enhance the overall return potential of an investment portfolio and help to achieve long-term financial goals. Sovereign bonds are debt securities issued by a country's government. These bonds are typically denominated in the issuing country's currency or a major global currency, such as the US dollar or euro. Sovereign bonds are considered relatively low-risk investments, as they are backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government. Investors in sovereign bonds can benefit from relatively stable returns and the potential for capital appreciation if the issuing country's creditworthiness improves or its currency strengthens. However, investing in sovereign bonds also carries certain risks, such as foreign exchange risk and political risk. Corporate bonds are financial instruments used by companies to secure funds for their activities and expansion plans. They are debt securities that can be issued in different currencies and are commonly traded on the global bond market. In comparison to sovereign bonds, corporate bonds often yield higher returns due to the elevated credit risk associated with investing in specific businesses. By investing in corporate bonds, individuals gain exposure to a wide range of industries and geographic regions, bolstering their portfolio diversification and potentially enhancing risk-adjusted returns. Nonetheless, investors must exercise caution as corporate bonds entail risks like credit risk and liquidity risk, necessitating thorough evaluation. Debt securities known as emerging market bonds are issued by governments or corporations in developing countries. Reflecting the elevated risks tied to investing in emerging markets, such as political instability, currency volatility, and lower credit quality, these bonds frequently present higher yields compared to those issued by developed nations. Through investing in emerging market bonds, investors gain exposure to high-growth economies and the potential for substantial capital appreciation. Nevertheless, the increased risks associated with these bonds, including foreign exchange risk, credit risk, and political risk, should be carefully considered. High-yield bonds, also known as junk bonds, are fixed-income securities issued by companies with lower credit ratings. These bonds offer higher interest rates than investment-grade bonds to compensate for the increased risk of default. Investors seeking greater returns may be attracted to high-yield bonds, but they carry a higher risk of potential loss. By investing in bonds from different countries and regions, investors can reduce the impact of domestic market fluctuations and economic downturns on their portfolios. This diversification can help to spread risk across various markets and currencies, potentially leading to more stable returns and a lower overall risk profile. International bonds can provide investors with access to higher-yielding bonds compared to domestic bonds, particularly for investors in developed markets with low-interest rates. Higher yields can enhance the overall return potential of an investment portfolio, helping investors achieve their long-term financial goals. Higher yields are typically associated with increased risk, such as credit risk or foreign exchange risk. However, by carefully selecting international bonds and managing these risks, investors can potentially benefit from the higher yields offered by international bonds without significantly increasing their overall risk profile. Investing in international bonds can provide investors with exposure to foreign currencies, which can offer additional diversification benefits and the potential for currency appreciation. As exchange rates fluctuate, investors may benefit from holding bonds denominated in currencies that appreciate relative to their home currency. Currency exposure can also introduce additional risks, such as foreign exchange risk, which investors must carefully consider when investing in international bonds. By managing currency risk through strategies such as currency hedging or investing in currency-hedged bond funds, investors can potentially benefit from currency exposure while mitigating the associated risks. International bonds are influenced by various factors such as interest rates, exchange rates, and economic conditions in different countries. Fluctuations in these factors can create opportunities for investors to buy bonds at lower prices and sell them at higher prices, resulting in capital gains. Additionally, diversifying a bond portfolio internationally can help mitigate risks and enhance potential returns. By tapping into global markets, investors can take advantage of potential capital gains and diversification benefits. Foreign exchange risk is the potential for changes in currency exchange rates to negatively impact the value of an investment in international bonds. As exchange rates fluctuate, the value of a bond denominated in a foreign currency may decline relative to an investor's home currency, reducing the overall return on investment. Investors can manage foreign exchange risk through strategies such as currency hedging or investing in currency-hedged bond funds. By carefully considering and managing foreign exchange risk, investors can potentially benefit from the diversification and return potential offered by international bonds without significantly increasing their overall risk profile. Credit risk exists when investing in international bonds due to the possibility of the issuer defaulting on its debt obligations. International bonds involve investing in foreign countries, which may have different economic and political conditions that increase the likelihood of default. Factors such as economic instability, currency fluctuations, government policies, and regulatory changes can impact a country's creditworthiness. This introduces a higher level of uncertainty and potential risk for investors in international bonds. Investing in international bonds carries interest rate risk due to the potential fluctuations in interest rates between countries. Changes in interest rates can impact bond prices inversely: when interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, and vice versa. When investing in international bonds, investors are exposed to the interest rate movements of multiple countries, making their investments vulnerable to shifts in global interest rate trends. These fluctuations can affect the value of the bond, resulting in potential gains or losses for investors. Managing interest rate risk is crucial in international bond investments to mitigate potential volatility and optimize returns. Political risk occurs when investing in international bonds when there are uncertainties or potential disruptions in a country's political environment that could negatively impact the investment. This can include events such as political instability, changes in government policies, civil unrest, regulatory changes, or geopolitical conflicts. These factors can affect the stability of the country's economy, currency value, and legal framework, increasing the likelihood of default or a decrease in bond values. Investors need to consider political risk alongside other factors when assessing the potential returns and risks of international bond investments. Country risk refers to the potential for economic, political, or social factors in a foreign country to negatively impact the value of an investment in international bonds. Investors should carefully consider the country risk associated with the bonds they are considering, as it can significantly influence the overall risk profile of their investment. Factors that can contribute to country risk include political stability, economic growth, fiscal and monetary policy, and regulatory environments. By assessing these factors and selecting bonds from countries with lower levels of country risk, investors can potentially improve the risk-adjusted returns of their international bond investments. Credit ratings are an important tool for assessing the creditworthiness of bond issuers, including governments and corporations. These ratings are assigned by credit rating agencies, such as Standard & Poor's, Moody's, and Fitch Ratings, and provide an indication of the issuer's ability and willingness to meet their debt obligations. Investors should consider the credit ratings of the international bonds they are considering, as they can help to gauge the level of credit risk associated with the investment. Higher-rated bonds generally offer lower yields but carry a lower risk of default, while lower-rated bonds offer higher yields but carry a higher risk of default. Investors should consider currency risk when investing in international bonds because fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly impact investment returns. When investing in bonds denominated in foreign currencies, changes in the exchange rate between the investor's currency and the bond's currency can lead to gains or losses. For instance, if an investor purchases a bond denominated in euros and the euro depreciates against their home currency, the investor's returns will be reduced when converting back to their currency. This risk can be substantial and needs careful consideration to mitigate potential losses and optimize investment outcomes. Liquidity risk refers to the possibility of not being able to buy or sell an investment quickly at a fair price. In the context of international bonds, it is crucial to consider liquidity risk before investing because international bonds may have lower liquidity compared to domestic bonds. Factors such as limited trading volume, exchange rate fluctuations, and time zone differences can affect liquidity. Insufficient liquidity can hinder an investor's ability to exit a position or obtain competitive pricing. Therefore, understanding and managing liquidity risk is essential to ensure the feasibility and efficiency of international bond investments. Investing in international bonds can be a valuable addition to your investment portfolio, allowing you to diversify your holdings across different countries and currencies. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to invest in international bonds: Research and Understand International Bond Markets: Start by researching and understanding the various international bond markets available. Each country may have its own bond market, and it's important to familiarize yourself with the specific characteristics, risks, and regulations of each market. Determine Your Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance: Clarify your investment goals and assess your risk tolerance. Consider factors such as desired returns, investment duration, and your ability to handle fluctuations in exchange rates and interest rates. Select a Brokerage Account: Choose a reputable brokerage firm that offers access to international bond markets. Ensure the brokerage provides the necessary tools, research resources, and support to invest in international bonds. Examples of popular online brokerage platforms include Interactive Brokers, TD Ameritrade, and Charles Schwab. Open a Brokerage Account: Follow the account opening process with your chosen brokerage firm. This usually involves providing personal identification documents and completing the required forms. Some brokerage firms may require additional information for international investments. Fund Your Account: Deposit funds into your brokerage account to have the necessary capital for investing in international bonds. Ensure you have enough funds to cover transaction fees and potential currency exchange costs. Conduct Fundamental Analysis: Before selecting specific international bonds, conduct thorough fundamental analysis. Consider factors such as the issuing country's economic stability, political climate, debt levels, and interest rate outlook. Evaluate the creditworthiness and ratings of the bond issuer. Assess Currency Risk: Investing in international bonds exposes you to currency risk. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the value of your investment. Assess the currency risk associated with the bonds you are considering and evaluate your risk tolerance for potential currency fluctuations. Select Bonds: Once you have conducted your analysis, select the international bonds that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance. Consider factors such as yield, maturity, credit quality, and currency exposure. Consult with your broker or financial advisor if you need assistance in selecting suitable bonds. Place Your Order: With the selected bonds in mind, place your buy order through your brokerage account. Specify the quantity, price, and any other relevant parameters. Be aware that international bond trades may have specific settlement periods and transaction costs, so familiarize yourself with these details. Monitor Your Investments: After purchasing international bonds, regularly monitor your investments to stay informed about any developments that may impact their value. Stay updated on changes in the issuing country's economic or political landscape, as well as any shifts in interest rates or credit ratings. International bonds can offer investors a range of benefits, including portfolio diversification, access to higher-yielding bonds, exposure to foreign currencies, and the potential for capital gains. However, investing in international bonds also involves risks, such as foreign exchange risk, credit risk, interest rate risk, and political risk. To successfully invest in international bonds, investors should carefully consider factors such as country risk, credit rating, currency risk, and liquidity risk when selecting bonds for their portfolio. Additionally, investors can choose from various investment vehicles, such as exchange-traded funds, mutual funds, direct purchases of bonds, and global bond index funds, to access the international bond market and create a diversified, risk-adjusted investment portfolio.What Is an International Bond?
Importance of International Bond in Wealth Management
Types of International Bonds
Sovereign Bonds
Corporate Bonds
Emerging Market Bonds
High-Yield Bonds
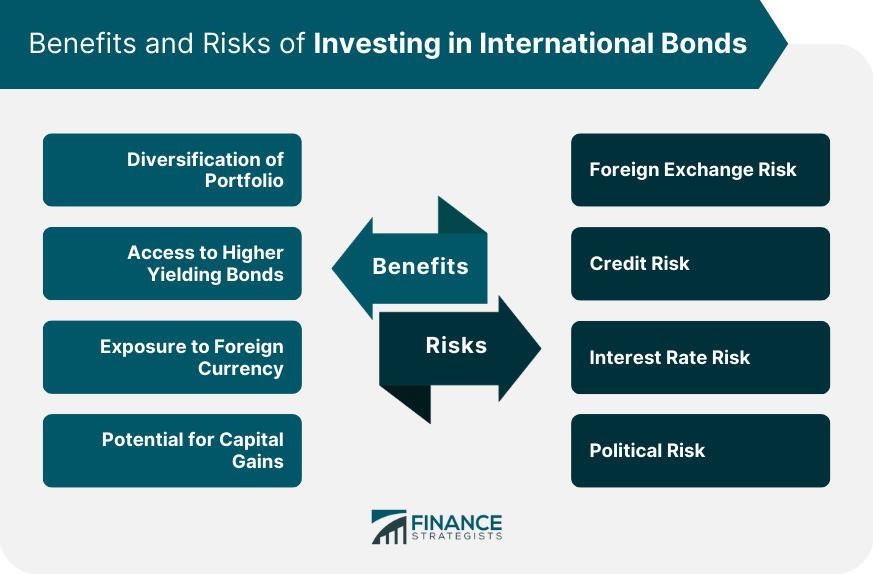
Benefits of Investing in International Bonds
Diversification of Portfolio
Access to Higher Yielding Bonds
Exposure to Foreign Currency
Potential for Capital Gains
Risks of Investing in International Bonds
Foreign Exchange Risk
Credit Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Political Risk
Factors to Consider When Investing in International Bonds
Country Risk
Credit Rating
Currency Risk
Liquidity Risk
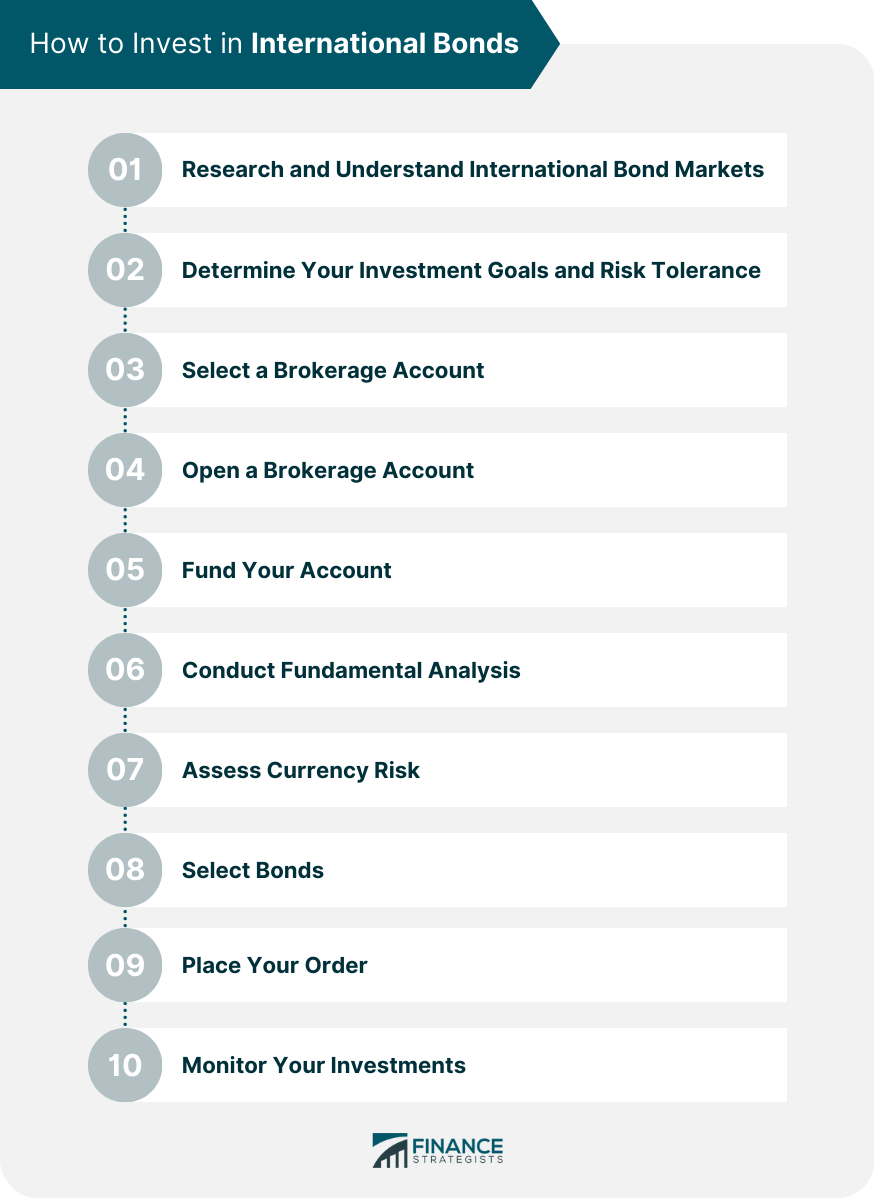
How to Invest in International Bonds
Final Thoughts
International Bond FAQs
An international bond is a debt security issued by a foreign entity, such as a foreign government or corporation, in a currency other than the domestic currency.
Investing in international bonds can provide diversification, access to higher yields, exposure to foreign currency, and potential for capital gains.
Some of the risks include foreign exchange risk, credit risk, interest rate risk, and political risk.
Investors can invest in international bonds through exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, direct purchase of bonds, or global bond index funds.
Investors should consider country risk, credit rating, currency risk, and liquidity risk before investing in international bonds. It is important to seek professional advice before making investment decisions.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











