Premium Bonds aren't a separate category of bonds, but rather bonds that are sold at a price above their face value or par. If the prevailing interest rates in the economy fall after issuance, these bonds become more attractive because they offer a higher return relative to newer bonds issued at lower rates. As a result, these bonds can command a premium price in the bond market. Purchasers pay more upfront but earn more interest over the bond's lifespan. At maturity, however, only the face value of the bond is returned, not the premium paid. These bonds can be a sound investment for income-seeking investors and those wanting to diversify their portfolio. Nonetheless, they may not be the best choice for all investors, particularly those seeking capital growth or those who may need to sell the bond before maturity, as they could lose some or all of the premium they paid. Certificates of Deposit (CDs) are time-deposit accounts offered by banks with a fixed term. They offer a fixed interest rate and return the principal at maturity. Unlike premium bonds, which may lose value if sold before maturity, CDs ensure return of the principal at maturity. However, their interest rates are generally lower than those of premium bonds. Savings accounts provide a safe place to store cash while earning a modest amount of interest. Unlike premium bonds, they are highly liquid, meaning you can withdraw your money at any time. But the yield is generally much lower than what premium bonds can provide. Money market funds invest in short-term, high-quality debt from governments, banks, or corporations. They aim to maintain a stable value while paying dividends to shareholders. They offer more liquidity than premium bonds and a slightly higher yield than savings accounts, but typically less yield than premium bonds. Annuities are contracts with an insurance company where the investor provides a lump sum in exchange for regular income payments over a specified period or for life. Unlike premium bonds that pay periodic interest, annuities can provide a steady income stream in retirement, making them suitable for different investment needs. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and mutual funds offer a way to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets. They may include stocks, bonds, commodities, or a mix of asset types. These funds provide diversification that single premium bonds cannot offer, spreading risk across different sectors and companies. Investing directly in stocks offers potentially high returns but also comes with high risk. Unlike premium bonds that provide regular interest payments, stocks can provide capital gains and dividends, but the risk of loss is much higher. Real estate can be a profitable investment, either through property appreciation, rental income, or both. Unlike premium bonds, real estate can provide a hedge against inflation. However, it requires significant capital and can be illiquid. Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security. The most well-known cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, but there are now thousands of different cryptocurrencies with various features and functions. Cryptocurrencies can offer high returns, with some investors making substantial profits. However, they are highly volatile and speculative, making them much riskier than premium bonds. There's also the risk of digital theft if your cryptocurrency is not stored securely. Commodities, such as gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products, present a compelling alternative to premium bonds. Unlike premium bonds, commodities can provide a hedge against inflation and volatility in other markets. Investing in commodities can be done directly through physical purchases or indirectly through futures contracts, ETFs, or shares in commodity companies. If your aim is to accumulate wealth over the long term, you might lean towards assets that typically appreciate over time, like stocks or real estate. On the other hand, if your goal is to generate a steady income, conventional bonds or dividend-yielding stocks may be more suitable. Different investments come with different levels of risk. High-risk investments like stocks and cryptocurrencies can offer high potential returns but can also lead to substantial losses. Lower-risk options like bonds or savings accounts provide modest but more stable returns. Understanding your ability and willingness to withstand potential losses is essential in determining the type of investments that are suitable for you. If you have a long-term horizon, you can afford to take on more risk for potentially higher returns, as you have more time to recover from any short-term losses. If your horizon is short, safer investments are generally more advisable. For instance, stocks tend to perform well during economic upswings, while bonds and gold are typically more resilient during downturns. Keeping a pulse on economic conditions can help you make informed investment decisions. Liquidity refers to how quickly an investment can be converted into cash without significantly impacting its price. If you anticipate needing to access your investment on short notice, you may want to stick to more liquid investments like stocks and cryptocurrency. For instance, certain types of conventional bonds offer tax-free interest payments, while dividends from stocks may be subject to taxes. Understanding the tax implications of different investments can help you maximize your after-tax returns. Diversification is a fundamental concept in investing, and its importance cannot be overstated when considering alternatives to premium bonds. It involves spreading your investments across various asset types to reduce risk and potentially enhance returns. The logic behind diversification is rooted in the idea that not all investments will perform well at the same time. When one asset class is declining in value, another may be increasing, thus offsetting potential losses. If you invest solely in one alternative, such as stocks, your investment performance becomes wholly tied to the performance of the stock market. If the market experiences a downturn, your portfolio could suffer significant losses. But if you diversify your investments across stocks, bonds, real estate, peer-to-peer lending, and more, you decrease the likelihood that any single negative event will significantly impact your overall portfolio. In essence, you're not putting all your eggs in one basket. Moreover, diversification isn't just about investing in different asset classes, but also within the asset classes themselves. For instance, if you choose stocks as an alternative to premium bonds, don't just invest in one or two companies or sectors. Instead, spread your investments across various industries and geographical regions to further mitigate risk. However, it's crucial to remember that while diversification can reduce risk, it does not entirely eliminate it. There are still systemic risks that can impact all types of investments, such as economic recessions or political instability. Therefore, diversification should be part of a broader investment strategy that aligns with your risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment horizon. Financial advisors can provide personalized advice based on your financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance. They can help devise a comprehensive investment strategy and guide you in selecting suitable investments. Investment brokers buy and sell securities on your behalf. While they may provide some advice, their primary role is executing transactions. CPAs provide advice on tax implications of different investments. They can help you understand how your investment decisions will affect your tax liability. Tax advisors specialize in tax planning and can provide advice on maximizing tax efficiencies in your investment portfolio. They can be particularly useful if you have complex investments or significant assets. Premium bonds can be attractive when prevailing interest rates fall after issuance, as they provide a higher return compared to newer bonds issued at lower rates. However, it's important to note that premium bonds may not be suitable for all investors, particularly those seeking capital growth or those who may need to sell the bond before maturity. It's important to consider alternative options based on factors such as financial goals, risk tolerance, investment horizon, economic conditions, liquidity needs, and tax implications. These alternatives include CDs, savings accounts, money market funds, annuities, ETFs and mutual funds, stock market investments, real estate investments, cryptocurrencies, and commodities. Each alternative offers its own benefits and limitations. Diversification is a key principle when exploring alternatives to premium bonds. By spreading investments across different asset types and within asset classes, investors can reduce risk and potentially enhance returns. Conducting thorough research and seeking advice from financial advisors or other professionals will aid in making well-informed decisions and building a resilient investment portfolio.Overview of Premium Bonds
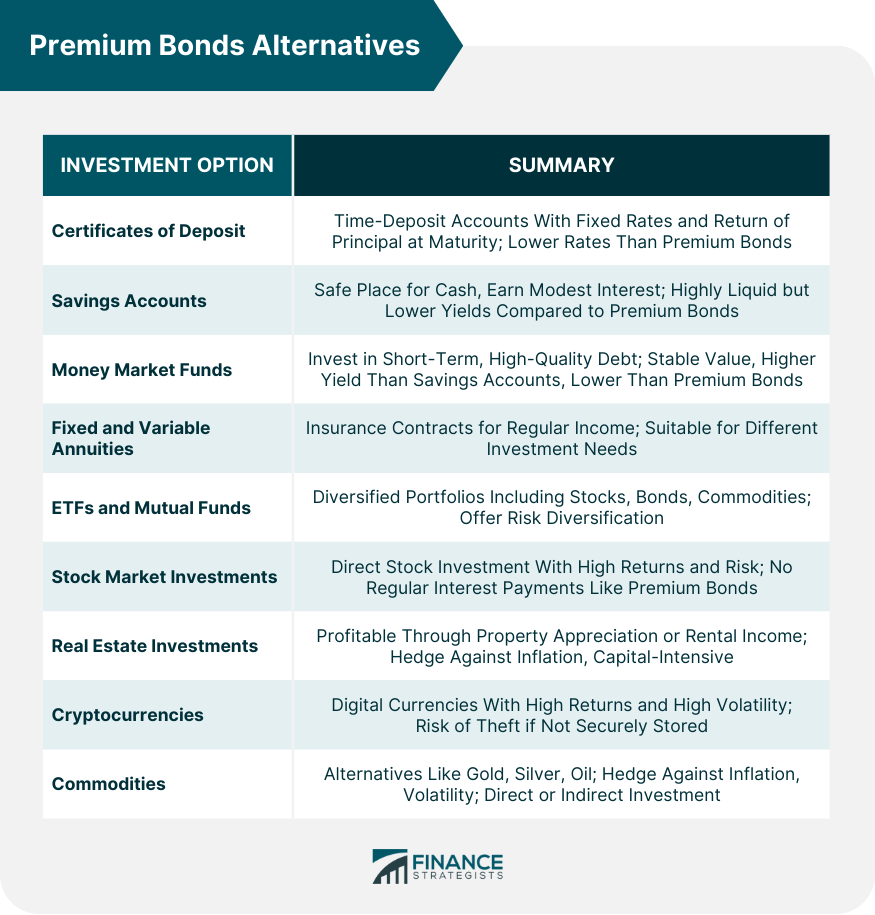
Premium Bonds Alternatives
Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
Savings Accounts
Money Market Funds
Fixed and Variable Annuities
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and Mutual Funds
Stock Market Investments
Real Estate Investments
Cryptocurrencies
Commodities
Key Considerations When Choosing Premium Bonds Alternatives
Financial Goals
Risk Tolerance
Investment Horizon
Economic Conditions
Liquidity Needs
Tax Implications

Diversification and Premium Bond Alternatives
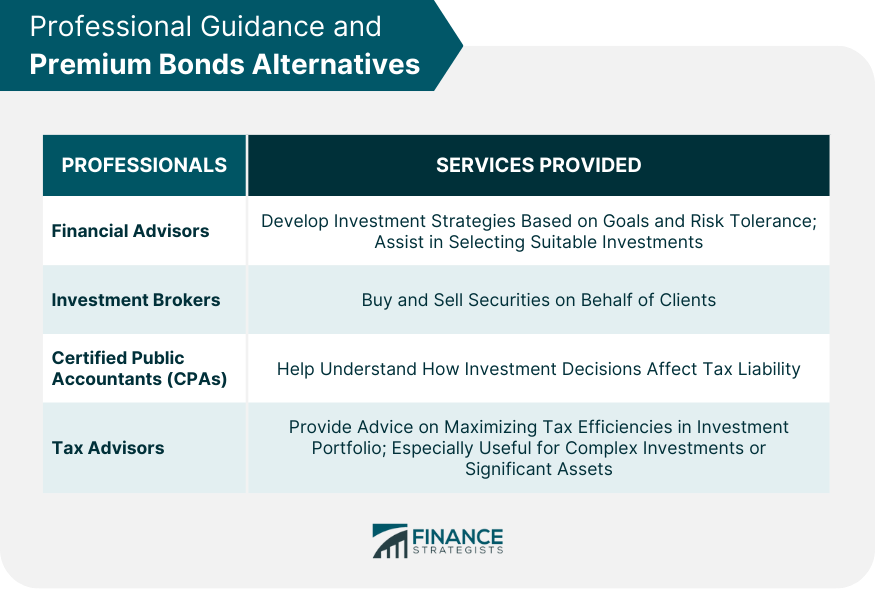
Professional Guidance and Premium Bonds Alternatives
Financial Advisors
Investment Brokers
Certified Public Accountants (CPAs)
Tax Advisors
Final Thoughts
Premium Bonds Alternatives FAQs
Premium bonds are bonds sold at a price above their face value or par. Unlike regular bonds, premium bonds offer a higher return relative to newer bonds issued at lower interest rates if prevailing interest rates fall after issuance. However, at maturity, only the face value of the bond is returned, not the premium paid.
Premium Bonds alternatives can be suitable for both short-term and long-term investments, depending on the specific choice. Some alternatives, like stocks, are often considered better for long-term investments, while others, such as cryptocurrencies, may be suitable for shorter investment horizons.
Investing in cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, carries high risk due to their volatile and speculative nature. While cryptocurrencies can offer high returns, they can also result in substantial losses. There is also a risk of digital theft if cryptocurrencies are not securely stored.
Diversification is crucial when exploring alternatives to premium bonds. By spreading investments across various asset types and within asset classes, investors can reduce risk and potentially enhance returns. Diversification helps mitigate the impact of negative events on the overall portfolio, ensuring that the performance of a single investment does not overly influence the entire portfolio.
Choosing the right alternative depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment preferences. Consider factors such as the potential return, liquidity, and the level of involvement you wish to have in managing your investments. It's often beneficial to consult with a financial advisor to determine the best alternative for your specific circumstances.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











