Impact investing refers to investing in organizations or companies with the aim of achieving a measurable social or environmental impact alongside financial returns. This dual focus on financial and social or environmental performance distinguishes impact investing from traditional investing, which primarily focuses on financial returns. Impact investments can be made in various sectors, including renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, affordable housing, healthcare, education, and more. The goal of impact investing is to support solutions to pressing social and environmental challenges while also achieving financial gains. As impact investing gains more traction, there has been a growing need to measure and manage the impact of these investments. Impact measurement and management (IMM) is the process of assessing and analyzing the social and environmental impact of an investment, as well as the ongoing management of that impact. IMM helps investors understand how their investments are impacting society and the environment, and make informed decisions on how to optimize their impact. Impact measurement is the process of assessing the social and environmental impact of an investment. It involves collecting and analyzing data to determine whether the investment is achieving its intended impact. Impact measurement helps investors understand the outcomes of their investments and identify areas for improvement. There are different types of impact measurement that investors can use, depending on their goals and objectives. The three main types of impact measurement are: Output measurement involves measuring the immediate results of an investment. This includes metrics such as the number of jobs created, the number of people trained, or the amount of greenhouse gas emissions reduced. Output measurement is important for understanding the immediate impact of an investment, but it does not capture the long-term effects. Outcome measurement involves measuring the intermediate results of an investment. This includes metrics such as the improved health outcomes of a community, increased access to education, or reduced poverty levels. Outcome measurement helps investors understand the long-term effects of an investment and its impact on society and the environment. Impact measurement involves measuring the ultimate results of an investment. This includes metrics such as the overall improvement in the quality of life, the reduction in carbon emissions, or the increase in biodiversity. Impact measurement is the most comprehensive type of measurement and provides a full picture of the impact of an investment. While impact measurement is essential for understanding the impact of an investment, it also comes with challenges and limitations. The main challenges and limitations of impact measurement are: It is often difficult to determine the extent to which an investment contributed to a particular outcome. This is because there may be other factors that also contributed to the outcome. Investors need to be aware of these external factors and understand how they may have influenced the impact of the investment. Impact measurement requires a long-term perspective. However, it can be challenging to measure the impact of an investment over a long period of time. Investors need to be patient and committed to measuring impact over the long-term. The impact of an investment may be influenced by external factors such as economic downturns, political instability, or natural disasters. Investors need to be aware of these external factors and understand how they may have impacted the investment's impact. Impact management is the ongoing process of managing and optimizing the social and environmental impact of an investment. It involves setting impact goals, collecting and analyzing impact data, and making informed decisions on how to improve impact. There are different types of impact management that investors can use, depending on their goals and objectives. The two main types of impact management are: Impact management frameworks are tools that help investors define their impact goals and measure the social and environmental impact of their investments. These frameworks provide a structured approach to managing impact and help investors identify areas for improvement. Impact management systems are software tools that help investors collect, analyze, and report impact data. These systems provide a centralized platform for managing impact data, making it easier for investors to measure impact across their portfolio and identify trends and patterns. While impact management is essential for optimizing the impact of an investment, it also comes with challenges and limitations. The main challenges and limitations of impact management are: Impact management requires making value judgments about the social and environmental impact of an investment. These value judgments may be subjective and influenced by personal biases. Investors need to be aware of their biases and strive for objectivity when making impact management decisions. Impact management can be resource-intensive, requiring time and money to collect, analyze, and report impact data. Investors need to be prepared to invest in impact management systems and processes to ensure they are able to manage impact effectively. Implementing impact management frameworks and systems can be challenging. Investors need to ensure they have the right expertise and resources to implement these systems effectively. They also need to ensure that they are collecting the right data and that the data is reliable and accurate. To ensure effective impact measurement and management, investors should follow best practices, which include: Impact measurement and management should be integrated into the investment process from the start. This ensures that impact goals and objectives are defined upfront and that impact data is collected and analyzed throughout the investment cycle. Investors should establish clear impact goals and objectives that align with their values and mission. These goals should be specific, measurable, and achievable, and should be aligned with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Investors should collect and analyze impact data on an ongoing basis. This data should be used to inform investment decisions and identify areas for improvement. Investors should also use impact data to communicate the impact of their investments to stakeholders. Investors should communicate the impact of their investments to stakeholders, including investors, clients, and the public. This helps build trust and transparency and demonstrates the investor's commitment to social and environmental impact. Impact measurement and management is an ongoing process. Investors should continually evaluate the impact of their investments and identify areas for improvement. They should also adapt their impact goals and objectives to changing social and environmental conditions. Impact measurement and management is becoming increasingly important in impact investing. As investors become more focused on achieving social and environmental impact, the demand for effective impact measurement and management is growing. The future of impact measurement and management will likely see continued investment in impact management systems and processes, as well as greater collaboration between investors and other stakeholders. There will also likely be increased standardization of impact measurement and management frameworks, making it easier for investors to compare impact across different investments. Measuring and managing impact is essential for achieving social and environmental impact in impact investing. Impact measurement and management provides investors with the tools and data they need to understand the impact of their investments and make informed decisions on how to optimize impact. By following best practices and adapting to changing social and environmental conditions, investors can ensure they are making a positive impact on society and the environment while achieving financial returns.Impact Investing: Overview
What Is Impact Measurement and Management?
Impact Measurement
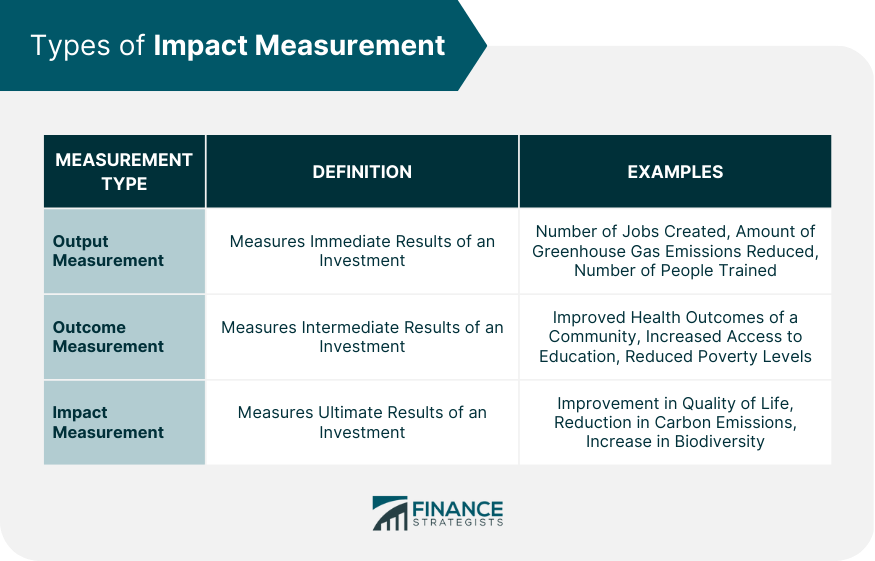
Types of Impact Measurement
Output Measurement
Outcome Measurement
Impact Measurement
Challenges and Limitations of Impact Measurement
Attribution
Timeframe
External Factors
Impact Management
Types of Impact Management
Impact Management Frameworks
Impact Management Systems
Challenges and Limitations of Impact Management
Subjectivity
Resource Constraints
Implementation Issues
Best Practices in Impact Measurement and Management
Integrating IMM Into the Investment Process
Establishing Impact Goals and Objectives
Collecting and Analyzing Impact Data
Communicating Impact to Stakeholders
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation

The Future of IMM in Impact Investing
Conclusion
Impact Measurement and Management FAQs
Impact measurement and management (IMM) is the process of assessing and analyzing the social and environmental impact of an investment, as well as the ongoing management of that impact. It helps investors understand how their investments are impacting society and the environment, and make informed decisions on how to optimize their impact.
Impact measurement is important in impact investing because it helps investors understand the outcomes of their investments and identify areas for improvement. It provides investors with a comprehensive picture of the impact of their investments and helps them make informed decisions on how to optimize impact.
There are three main types of impact measurement: output measurement, outcome measurement, and impact measurement. Output measurement involves measuring the immediate results of an investment. Outcome measurement involves measuring the intermediate results of an investment. Impact measurement involves measuring the ultimate results of an investment.
The main challenges and limitations of impact management are subjectivity, resource constraints, and implementation issues. Impact management requires making value judgments about the social and environmental impact of an investment, which may be subjective and influenced by personal biases. Impact management can also be resource-intensive, requiring time and money to collect, analyze, and report impact data. Implementing impact management frameworks and systems can also be challenging.
The best practices in impact measurement and management include integrating impact measurement and management into the investment process, establishing clear impact goals and objectives, collecting and analyzing impact data, communicating impact to stakeholders, and continually evaluating and adapting impact goals and objectives to changing social and environmental conditions.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











