Positive screening is a process of selecting stocks or securities that meet certain predefined criteria, such as financial performance, ethical considerations, or social responsibility. In investing, positive screening works by identifying companies that meet specific values or investment goals, rather than simply avoiding companies that do not. Positive screening criteria may vary depending on the investor's individual values and investment goals, and can include financial metrics such as earnings growth, revenue growth, and dividend yield, sustainable business practices, diversity and inclusion, and community engagement. By using positive screening, investors can potentially identify companies that align with their values and investment goals, leading to better investment returns over the long term. Positive screening actively seeks out companies that meet specific ESG criteria, focusing on firms with strong sustainability practices and responsible corporate behavior. This approach emphasizes investment in businesses that are contributing positively to society and the environment. Negative screening, on the other hand, involves excluding companies that do not align with an investor's values or have poor ESG performance. This approach typically excludes industries such as tobacco, gambling, and fossil fuels, which are considered harmful or controversial. Compared to negative screening, positive screening offers a more proactive and targeted approach to responsible investing. It enables investors to actively support companies that are making a positive impact on society and the environment, thus driving change and encouraging responsible business practices. Companies with strong environmental performance demonstrate sustainable practices, such as efficient use of resources, waste reduction, and pollution prevention. Firms that actively work to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and support clean energy initiatives contribute to climate change mitigation efforts. Investing in companies that prioritize biodiversity and habitat conservation, as well as those that promote responsible land and water use, can help protect the environment for future generations. Positive screening may include companies that uphold high standards of human rights and labor practices, such as fair wages, safe working conditions, and anti-discrimination policies. Companies committed to fostering diverse, inclusive, and equitable work environments demonstrate strong social performance and are attractive to responsible investors. Firms that actively engage with and contribute to their local communities through philanthropy and volunteer initiatives are considered socially responsible. Investing in companies with diverse and independent boards can lead to better decision-making and overall corporate governance. Executive compensation structures that are transparent, fair, and linked to long-term company performance can minimize potential conflicts of interest and align the interests of management with those of shareholders. Companies that prioritize shareholder rights and engagement, such as providing avenues for shareholder input and maintaining transparent communication, are considered to have strong governance practices. The best-in-class approach involves selecting companies that outperform their peers in terms of ESG performance within a given industry or sector. Thematic investing focuses on specific ESG-related themes, such as clean energy, water scarcity, or gender equality, and targets companies that contribute to solving these challenges. Impact investing emphasizes investments in companies that generate measurable positive social and environmental impact, alongside financial returns. ESG integration involves incorporating ESG criteria into traditional financial analysis and decision-making processes to enhance risk assessment and identify potential opportunities. Companies with strong ESG performance often exhibit lower risk profiles and are better positioned for long-term success, which may result in higher financial returns for investors. Investing in companies with robust ESG practices can help mitigate risks associated with poor governance environmental concerns, and social issues, thus protecting the investor's portfolio. Positive screening allows investors to align their investments with their personal values and ethical beliefs, supporting companies that contribute positively to society and the environment. By investing in companies with strong ESG performance, investors can encourage responsible business practices, driving positive change and promoting sustainable development. One of the main challenges of positive screening is the lack of standardized criteria for measuring ESG performance, which can make it difficult to compare and evaluate companies. Some companies may engage in greenwashing, or the practice of making misleading claims about their environmental and social performance, which can hinder investors' ability to make informed decisions. Positive screening may result in a more limited pool of investment options, as companies that meet specific ESG criteria might be fewer in number compared to the broader market. The growing importance of positive screening in the world of investing reflects a shift in investor priorities and a heightened focus on sustainability and corporate responsibility. By actively seeking out companies with strong ESG performance, investors can play a pivotal role in driving change and promoting sustainable development. As the field of positive screening continues to evolve, investors will be better equipped to make informed decisions that align with their values and contribute to a better future for all.What Is Positive Screening?
Positive Screening vs Negative Screening
Positive Screening: A Proactive Approach
Negative Screening: An Exclusionary Approach
Advantages of Positive Screening
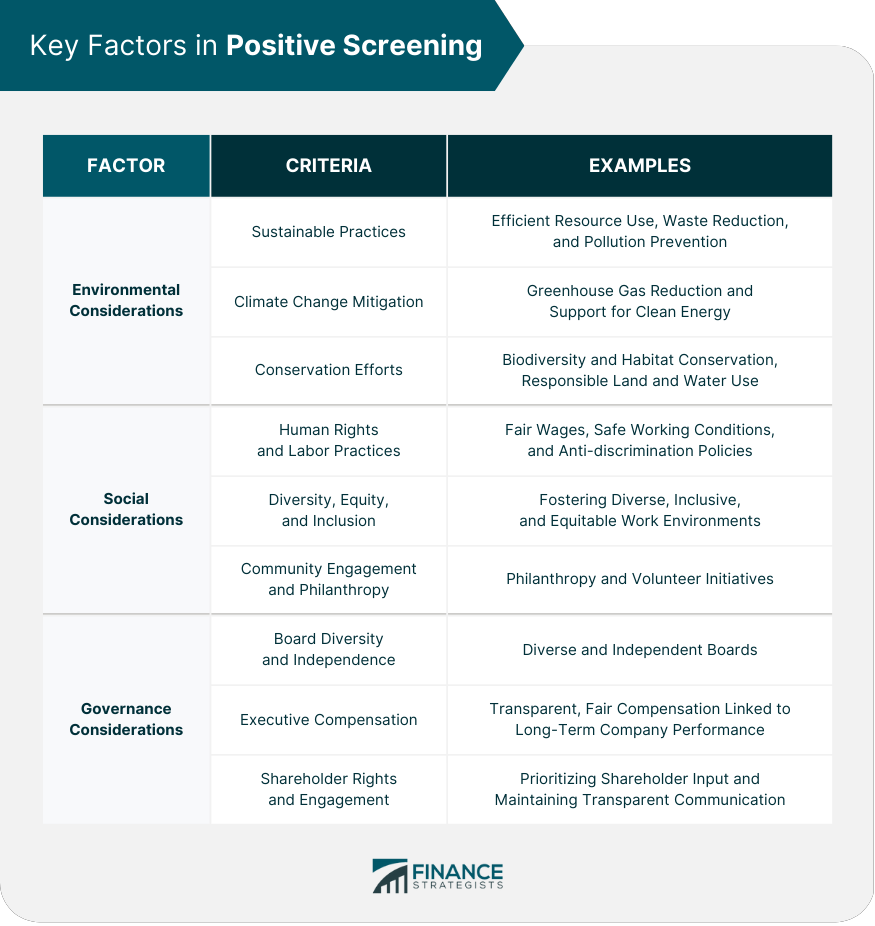
Key Factors in Positive Screening
Environmental Considerations
Sustainable Practices
Climate Change Mitigation
Conservation Efforts
Social Considerations
Human Rights and Labor Practices
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Community Engagement and Philanthropy
Governance Considerations
Board Diversity and Independence
Executive Compensation
Shareholder Rights and Engagement
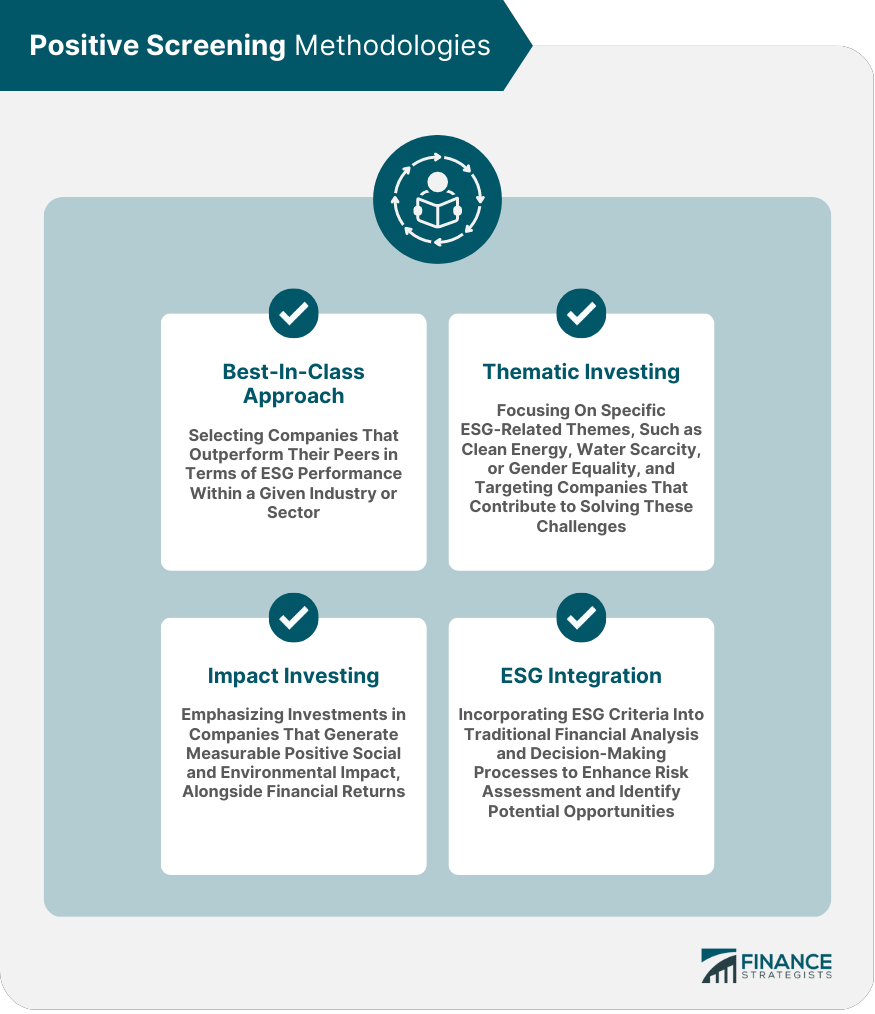
Positive Screening Methodologies
Best-In-Class Approach
Thematic Investing
Impact Investing
ESG Integration
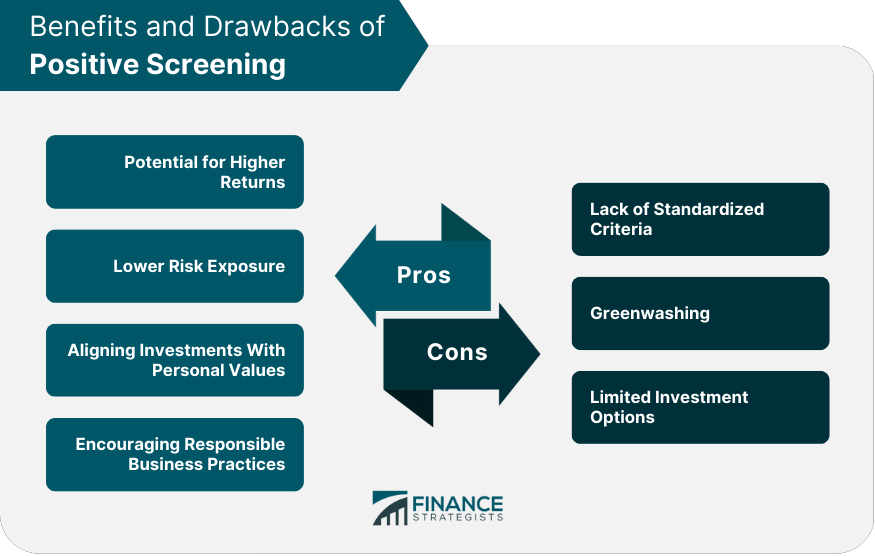
Benefits of Positive Screening
Potential for Higher Returns
Lower Risk Exposure
Aligning Investments With Personal Values
Encouraging Responsible Business Practices
Challenges of Positive Screening
Lack of Standardized Criteria
Greenwashing
Limited Investment Options
Conclusion
Positive Screening FAQs
Positive screening is a process of selecting stocks or securities that meet certain predefined criteria, such as financial performance, ethical considerations, or social responsibility. The goal of positive screening is to identify companies that meet specific values or investment goals, rather than simply avoiding companies that do not.
Positive screening and negative screening are both methods of selecting securities for investment, but they differ in their approach. Negative screening involves eliminating securities that do not meet certain criteria, such as those related to social responsibility or ethical considerations. Positive screening, on the other hand, focuses on selecting securities that meet specific criteria, often related to financial performance or investment goals.
Some common criteria used in positive screening include financial metrics such as earnings growth, revenue growth, and dividend yield, as well as environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors such as sustainable business practices, diversity and inclusion, and community engagement. Positive screening criteria may also vary depending on the investor's individual values and investment goals.
Positive screening can help investors identify companies that align with their values and investment goals, potentially leading to better investment returns over the long term. Additionally, investing in companies with strong financial and ESG performance may help mitigate risks and improve portfolio diversification.
One potential drawback of positive screening is that it may limit investment opportunities by excluding companies that do not meet certain criteria. Additionally, the criteria used in positive screening may be subjective and vary between investors, potentially leading to different investment outcomes. It's important for investors to carefully consider their individual values and investment goals when implementing a positive screening strategy.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











