Sustainable investing, also known as responsible investing, is an investment approach that considers environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors alongside traditional financial analysis. By considering ESG factors, investors can better assess the risks and opportunities associated with a company and make more informed investment decisions. The objective is to support businesses that demonstrate a commitment to positive social and environmental impacts, ethical practices, and long-term value creation. SRI involves avoiding investments in companies that engage in activities deemed harmful or unethical, such as tobacco or weapons manufacturing, while impact investing focuses on investing in companies or projects that have a measurable social or environmental impact. Overall, sustainable investing seeks to align investors' financial goals with their values and promote a more sustainable and equitable future. At the core of sustainable investing lies the ESG criteria, which evaluate companies' performance in environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and governance practices. Environmental factors include a company's carbon footprint, resource management, and waste reduction efforts. Social factors encompass labor practices, community engagement, and diversity and inclusion. Governance factors involve corporate ethics, board structure, and executive compensation. The United Nations' 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a global call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all by 2030. Sustainable investors often use the SDGs as a framework to guide their investment decisions, selecting companies that contribute to these goals through their business practices and initiatives. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) refers to the commitment of companies to act ethically, responsibly, and sustainably in their business operations. CSR has become a critical component of sustainable investing. Investors increasingly expect companies to take responsibility for their social and environmental impacts and prioritize long-term value creation over short-term gains. Sustainable investing aims to promote long-term value creation by focusing on companies with strong ESG performance. Research has shown that businesses prioritizing ESG factors often outperform their peers in the long run, suggesting that sustainable investing can lead to better financial returns and reduced risk exposure. Positive screening involves selecting companies demonstrating strong ESG performance, while negative screening excludes companies involved in harmful industries or practices. These strategies allow investors to align their portfolios with their values and minimize exposure to ESG risks. ESG integration is the systematic incorporation of ESG factors into traditional financial analysis. This approach aims to identify companies with strong ESG performance and long-term growth potential, resulting in better-informed investment decisions. Impact investing is a strategy that seeks to generate measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns. Investors who adopt this approach typically target companies, funds, or projects that address specific social or environmental challenges, such as clean energy or affordable housing. Thematic investing focuses on investments that align with specific ESG themes, such as climate change, gender equality, or sustainable agriculture. This strategy allows investors to concentrate their portfolios on sectors or industries contributing to a more sustainable future. Shareholder engagement involves investors using their ownership rights to influence corporate behavior and promote responsible business practices. This can include voting on shareholder resolutions, engaging in dialogue with management, or participating in collaborative initiatives with other investors. ESG ratings and analysis are essential tools for evaluating the sustainability performance of companies. Numerous providers, such as MSCI, Sustainalytics, and Bloomberg, offer ESG ratings, research, and analytical tools to help investors make informed decisions. Third-party assessment providers play a critical role in sustainable investing by offering independent evaluations of companies' ESG performance. These providers use various methodologies and data sources to assess companies, helping investors identify leaders and laggards in sustainability. Despite the growing availability of ESG data, several challenges and limitations persist. These include data inconsistencies, the need for standardized reporting frameworks, and varying methodologies among assessment providers. Investors should be aware of these limitations and use a combination of ESG ratings, research, and other sources to make well-informed investment decisions. Companies that demonstrate strong ESG performance or are involved in sustainable projects issue sustainable stocks and bonds. These investment options allow investors to directly support businesses that prioritize sustainability while potentially benefiting from financial returns. Green bonds finance environmentally friendly projects, while social bonds fund projects with positive social outcomes. Sustainability bonds combine the objectives of green and social bonds, financing projects that meet both environmental and social criteria. These bonds have become increasingly popular as investors seek to align their portfolios with sustainable goals. Sustainable Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and index funds offer diversified exposure to a basket of sustainable investments. These funds track indices composed of companies with strong ESG performance or focus on specific sustainability themes, providing investors with a cost-effective and accessible way to invest in sustainable assets. Socially responsible mutual funds are actively managed funds that invest in companies with strong ESG performance or those that align with specific sustainability objectives. These funds employ various strategies to build portfolios that generate financial returns while promoting sustainability, including positive screening, negative screening, and thematic investing. Pension funds and insurance companies significantly influence the sustainable investing landscape due to their large asset pools and long-term investment horizons. These institutions increasingly recognize the importance of ESG factors in managing risks and generating long-term returns, leading to a growing allocation of their assets to sustainable investments. Banks and asset managers play a crucial role in promoting sustainable investing by offering investment products and services that incorporate ESG factors. As demand for sustainable investments grows, these institutions are developing new products, such as ESG-themed funds and green loans, to meet investor needs. Regulatory frameworks and policies are essential drivers of sustainable investing. Governments and regulatory bodies around the world are implementing measures to promote transparency, standardization, and integration of ESG factors into investment practices, helping to accelerate the adoption of sustainable investing. Governments, businesses, and individual investors all have a critical role to play in the future of sustainable investing. These stakeholders can drive significant progress toward a more sustainable global economy by aligning their policies, practices, and investment decisions with sustainable objectives. Greenwashing, or the practice of making misleading sustainability claims, remains a concern in the sustainable investing landscape. Addressing this issue requires greater transparency, standardization, and regulation to ensure that sustainable investments truly align with their stated objectives. Sustainable investing is an investment approach that considers environmental, social, and governance factors alongside traditional financial analysis. The principles of sustainable investing involve evaluating companies based on their ESG criteria, using the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals as a framework, promoting corporate social responsibility, and aiming for long-term value creation. Investors can adopt various strategies for sustainable investing, such as positive and negative screening, ESG integration, impact investing, thematic investing, and shareholder engagement. They can also use tools such as ESG ratings, research, and analytical tools to assess companies' sustainability performance. Sustainable investing instruments include sustainable stocks and bonds, green, social, and sustainability bonds, exchange-traded funds, and socially responsible mutual funds. To effectively integrate sustainable investing strategies into their financial plan and achieve their sustainable investment goals, readers are encouraged to seek guidance from a wealth management professional. What Is Sustainable Investing?
The Principles of Sustainable Investing
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Criteria
The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The Importance of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Long-Term Value Creation
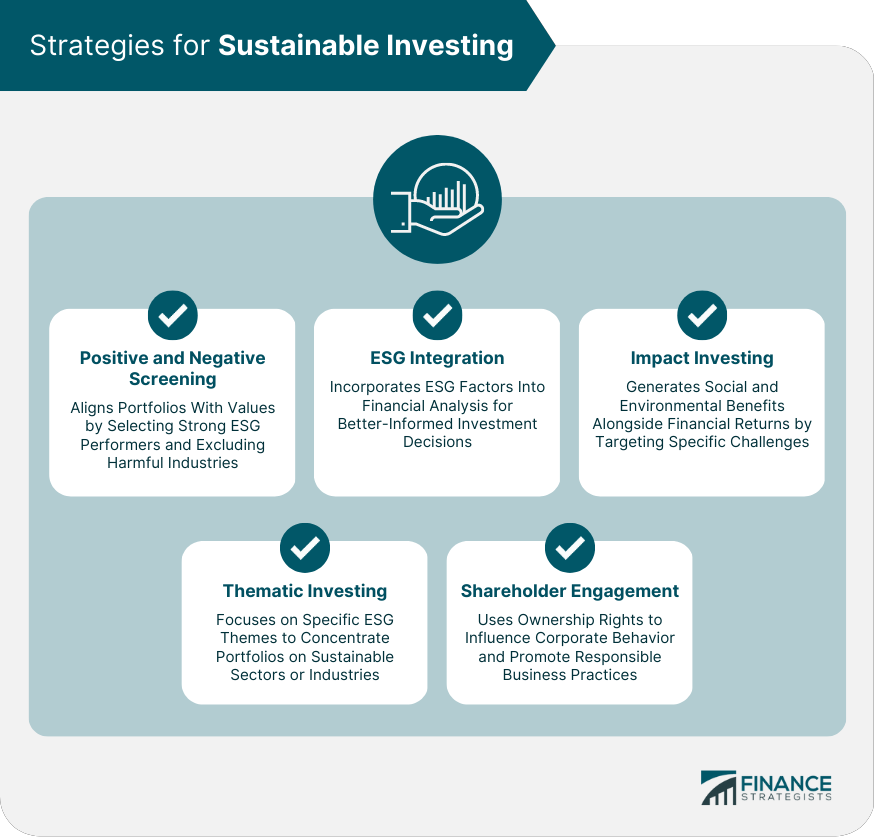
Strategies for Sustainable Investing
Positive and Negative Screening
ESG Integration
Impact Investing
Thematic Investing
Shareholder Engagement
Assessing Sustainable Investments
ESG Ratings and Analysis
The Role of Third-Party Assessment Providers
Challenges and Limitations of ESG Data
Sustainable Investing Instruments
Sustainable Stocks and Bonds
Green, Social, and Sustainability Bonds
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and Index Funds
Socially Responsible Mutual Funds
The Role of Institutional Investors and Financial Institutions
Pension Funds and Insurance Companies
Banks and Asset Managers
Regulatory Frameworks and Policies
The Future of Sustainable Investing
The Role of Governments, Businesses, and Individual Investors
Addressing Greenwashing and Transparency Concerns
Conclusion
It seeks to align investors' financial goals with their values by supporting businesses that demonstrate a commitment to positive social and environmental impacts, ethical practices, and long-term value creation.
Sustainable Investing FAQs
Sustainable investing is an investment approach that considers environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors and traditional financial analysis. It is important because it promotes responsible business practices, addresses global challenges, and fosters long-term value creation while potentially generating financial returns for investors.
ESG criteria evaluate companies' performance in environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and governance practices. They play a crucial role in sustainable investing by helping investors identify companies with strong sustainability performance, which may lead to better long-term growth potential and reduced risk exposure.
Common strategies in sustainable investing include positive and negative screening, ESG integration, impact investing, thematic investing, and shareholder engagement. These strategies enable investors to align their portfolios with their values and support companies prioritizing sustainability and long-term value creation.
Various investment instruments are available for sustainable investing, such as sustainable stocks and bonds, green, social, and sustainability bonds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and index funds focused on ESG criteria and socially responsible mutual funds. These instruments offer investors diversified exposure to sustainable assets and enable them to support businesses committed to responsible practices.
To assess the sustainability performance of companies for sustainable investing, you can rely on ESG ratings and analysis provided by third-party assessment providers like MSCI, Sustainalytics, and Bloomberg. However, be aware of challenges and limitations in ESG data, such as inconsistencies and varying methodologies. It is essential to use a combination of ESG ratings, research, and other sources to make well-informed investment decisions.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











