Before diving into the steps to read an annual report, it is essential to understand the key components of an annual report. The following are the major components of an annual report: The financial statements are the heart of an annual report. These statements provide information on a company's financial position, operating results, and cash flows. The three primary financial statements are the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. The balance sheet provides a momentary overview of a company's financial position, revealing its assets, liabilities, and equity. The company owns the assets, and the liabilities are what it owes. The difference between assets and liabilities is the company's equity, also known as shareholder's equity. The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, shows a company's revenue, expenses, and net income or loss over a specific period, usually a year. The revenue is the company's money from selling goods or services; the expenses are the costs associated with generating that revenue. The net income is the difference between revenue and expenses. The cash flow statement shows how a company's position changed over the year. It reflects the inflows and outflows of cash from operating, investing, and financing activities. The MD&A is a section of the annual report that provides management's analysis of the company's financial performance and future outlook. It discusses the company's results of operations, liquidity, capital resources, and significant trends and uncertainties. The auditor's report is a statement by an independent auditor that provides an opinion on whether the company's financial statements are free from material misstatements and are presented relative to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). The notes to financial statements provide additional information on the items presented in the financial statements. It includes details on accounting policies, significant accounting estimates, and other disclosures. Now that we have covered the key components of an annual report let us dive into the steps to read an annual report. The following steps can help you understand a company's financial position, performance, and future outlook. The cover page of an annual report usually includes the company's name, logo, and the year of the word. It may also include a message from the CEO or Chairman of the Board. While the cover page may not provide any financial information, it can give you an idea of the company's branding and marketing strategy. The letter to shareholders is usually written by the CEO or Chairman of the Board and provides a high-level overview of the company's performance over the year. It may also discuss the company's strategy, achievements, challenges, and future outlook. The letter to shareholders can give you a sense of the company's management style and priorities. The financial statements, which include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, provide a comprehensive overview of a company's financial health and performance over a specific period, usually a year. By analyzing the financial statements, investors and business owners can gain insights into a company's profitability, liquidity, solvency, and cash flow management. The balance sheet shows the company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific time. In contrast, the income statement shows the company's revenue, expenses, and net income or loss over a particular period. The cash flow statement shows how a company's position changed over the year. Analyzing the financial statements can help investors and business owners understand a company's financial situation and potential risks and opportunities. The MD&A section provides management's analysis of the company's financial performance and future outlook. The MD&A can give you an idea of the company's business strategy, competitive environment, and potential risks and opportunities. The auditor's report provides an independent opinion on whether the company's financial statements are free from material misstatements and are presented fairly in accordance with GAAP. The auditor's report can give you an idea of the reliability and accuracy of the financial statements. The notes to financial statements provide additional information on the items presented in the financial statements. The notes can help you understand the accounting policies and estimates used by the company and other significant disclosures. Reading an annual report can be overwhelming, especially if you must familiarize yourself with financial statements and accounting terminology. The following tips can help you analyze the information presented in the annual report: Annual reports use a lot of accounting terminologies, such as EBITDA, P/E ratio, and ROE. It is essential to understand these terms to correctly interpret financial statements. You can find a glossary of accounting terms in the notes to financial accounts or online resources. When analyzing the financial statements, look for trends and changes over time. For example, has the company's revenue increased or decreased over the past few years? Is the company's debt increasing or decreasing? Trends and changes can give you an idea of the company's financial performance and potential risks. Comparing the company's financial ratios with industry averages can help you understand the company's competitiveness and financial health. You can find industry averages in online resources or financial databases. The footnotes and disclosures provide additional information on the items presented in the financial statements. For example, the footnotes can provide details on accounting policies and estimates, significant risks, and contingencies. Reading the footnotes and disclosures can help you understand the assumptions and judgments made by the company's management. Annual reports also provide non-financial information, such as the company's business strategy, competitive environment, and social responsibility initiatives. Analyzing non-financial information can help you understand the company's performance and potential risks and opportunities. Annual reports also include a section on risk factors, describing potential risks that may affect the company's business and financial performance. Paying attention to risk factors can help you understand the potential downside of investing in the company. Annual reports can be a valuable tool for investors and business owners. For investors, annual reports can provide insights into a company's financial performance, growth potential, and risks. Investors can use the information in the annual report to make informed investment decisions and monitor their investments. For business owners, annual reports can provide insights into their company's financial health and performance. Business owners can use the information in the annual report to evaluate their business strategy, identify areas of improvement, and make informed decisions on future investments and expansions. Reading an annual report is essential for investors and business owners to evaluate a company's financial health and performance. By understanding the key components of an annual report, following the steps to read it, and analyzing the information presented, one can gain valuable insights into a company's profitability, liquidity, solvency, and potential risks and opportunities. Annual reports comprehensively overview a company's business strategy, competitive environment, and potential risks and opportunities. However, analyzing financial statements and understanding accounting terminology can be challenging, especially for those unfamiliar with finance. Therefore, seeking a wealth management advisor’s assistance is highly recommended to guide you through analyzing annual reports and making informed investment decisions.Key Components of Annual Report
Financial Statements
Balance Sheet
Income Statement
Cash Flow Statement
Management Discussion and Analysis (MD&A)
Auditor's Report
Notes to Financial Statements
Steps to Read the Annual Report

Step 1: Review the Cover Page
Step 2: Read the Letter to Shareholders
Step 3: Review Financial Statements
Step 4: Analyze Management Discussion and Analysis (MD&A)
Step 5: Review Auditor's Report
Step 6: Read the Notes to Financial Statements
Tips for Reading Annual Report
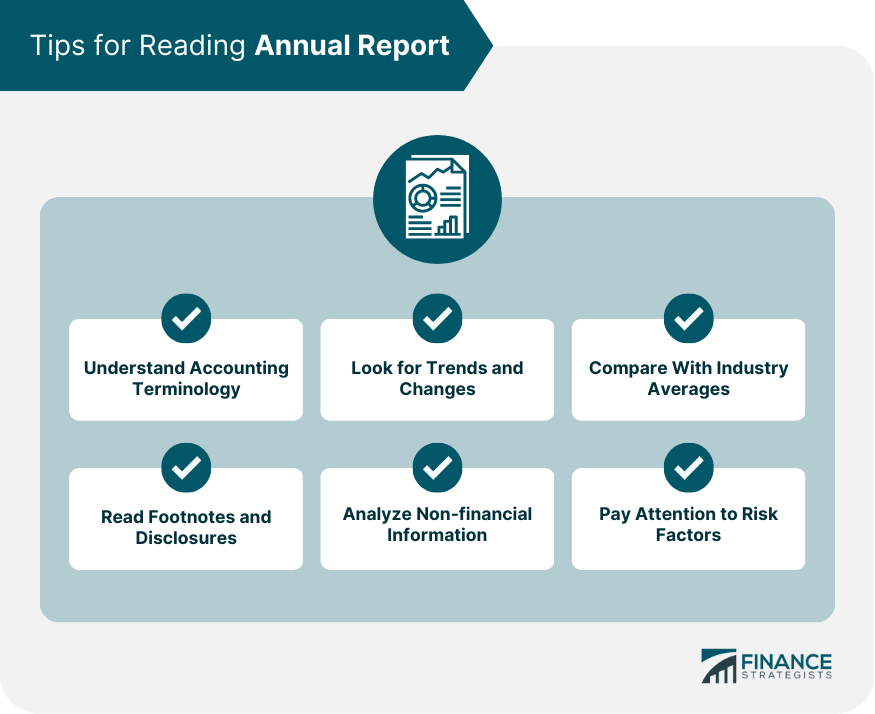
Understand Accounting Terminology
Look for Trends and Changes
Compare With Industry Averages
Read Footnotes and Disclosures
Analyze Non-financial Information
Pay Attention to Risk Factors
Importance of Annual Reports for Investors and Business Owners
The Bottom Line
How to Read an Annual Report FAQs
An annual report is a document publicly traded companies must submit to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) annually. It overviews a company's financial performance, business strategy, competitive environment, and potential risks and opportunities. Learning how to read annual reports is essential for investors and business owners to evaluate a company's financial health and performance.
The key components of an annual report include financial statements, management discussion and analysis (MD&A), auditor's report, and notes to financial statements. Financial statements include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, providing a comprehensive overview of a company's financial position and performance.
The steps to read an annual report include reviewing the cover page, reading the letter to shareholders, analyzing the financial statements, reviewing the MD&A, reviewing the auditor's report, and reading the notes to financial statements. Following these steps can help investors and business owners gain valuable insights into a company's financial health and performance.
Some tips for analyzing an annual report include understanding accounting terminology, looking for trends and changes, comparing with industry averages, reading footnotes and disclosures, analyzing non-financial information, and paying attention to risk factors. Analyzing annual reports can help investors and business owners make informed investment decisions and achieve their financial goals.
Analyzing financial statements and understanding accounting terminology can be challenging, especially for those unfamiliar with finance. Therefore, it is highly recommended to seek the services of a wealth management advisor's services to guide you through analyzing annual reports and making informed investment decisions. A wealth management advisor can help you navigate the complexities of the financial world and achieve your financial goals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











