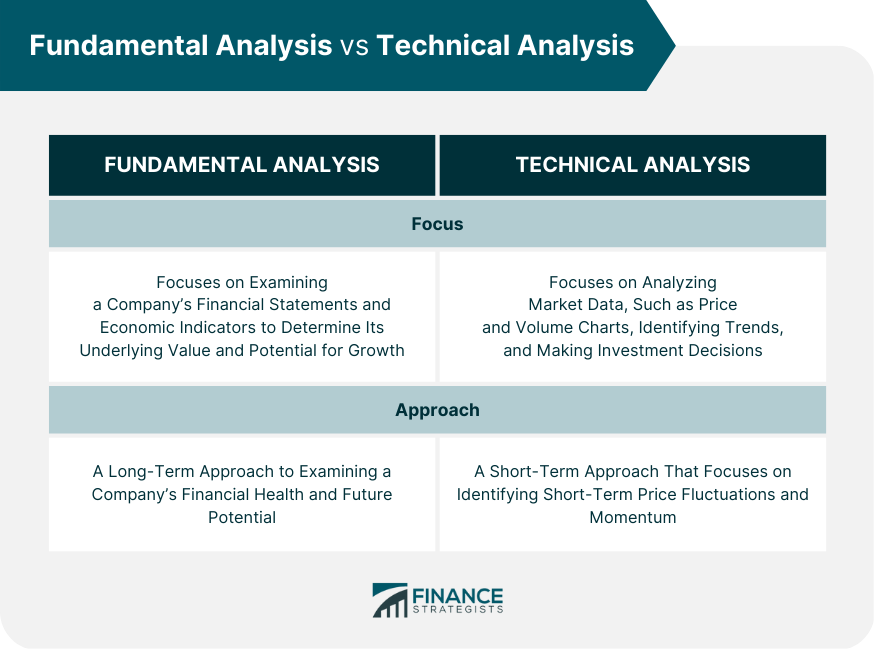
Fundamental and technical analyses are two popular approaches investors use to evaluate financial instruments. Fundamental analysis involves examining a company's financial statements and economic indicators to determine its underlying value and potential for growth. On the other hand, the technical analysis consists in analyzing market data, such as price and volume charts, in identifying trends and making investment decisions. While both approaches have strengths and weaknesses, investors can use them together to achieve better investment results. Investors can choose the approach that best suits their needs by considering their investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Fundamental analysis is an investment approach that examines a company's financial statements and economic indicators to determine its underlying value and potential for growth. Fundamental analysis aims to determine the intrinsic value of a stock or other financial instrument and compare it with its current market price. A good investment opportunity presents itself when a stock is undervalued, which occurs when the intrinsic value of the stock is higher than its market price. Fundamental analysis is essential in investment decision-making because it provides investors with a complete picture of a company's financial health and future potential. By analyzing a company's financial statements, investors can determine its profitability, revenue growth, and cash flow. They can also assess the company's management, competitive advantages, and market position. One advantage of fundamental analysis is that it provides a long-term view of a company's financial health and future potential. It is also helpful for identifying undervalued stocks that represent good investment opportunities. However, fundamental analysis can be time-consuming and requires significant expertise to perform effectively. Additionally, the fundamental analysis does not always account for short-term market fluctuations or changes in investor sentiment. An example of fundamental analysis is using the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio to evaluate a company's stock. The P/E ratio is calculated by dividing a company's stock price by its earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio may indicate that a stock is undervalued, while a high P/E ratio may indicate that a stock is overvalued. Technical analysis is an investment approach that analyzes market data, such as price and volume charts, to identify trends and make investment decisions. Technical analysis aims to identify patterns and trends that can be used to predict future price movements. Technical analysis is essential in investment decision-making because it provides investors with insights into market trends and momentum. By analyzing price and volume charts, investors can identify patterns and trends that can be used to predict future price movements. Technical analysis is instrumental in identifying short-term price fluctuations and momentum. One advantage of technical analysis is that it helps identify short-term price fluctuations and momentum. It is also relatively easy to perform, and many tools and indicators are available to assist investors. However, technical analysis has its limitations. It does not provide insights into a company's financial health or future potential. Additionally, technical analysis is susceptible to false signals, resulting in poor investment decisions. An example of technical analysis in practice is using trend lines to identify support and resistance levels. Trend lines connect two or more price points and can be used to identify trends in a stock's price movement. Support levels are areas where buyers are likely to enter the market, while resistance levels are areas where sellers are likely to enter the market. While fundamental and technical analysis has some similarities, they significantly differ in approach and methodology. Fundamental analysis focuses on examining a company's financial statements and economic indicators to determine its underlying value and potential for growth. In contrast, technical analysis focuses on analyzing market data, such as price and volume charts, identifying trends, and making investment decisions. Fundamental analysis is a long-term approach to examining a company's financial health and future potential. On the other hand, technical analysis is a short-term approach that focuses on identifying short-term price fluctuations and momentum. When choosing between fundamental and technical analysis, investors should consider several factors, including their investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Fundamental analysis may be the better approach if an investor is looking for long-term growth. Technical analysis may be more appropriate if an investor seeks short-term gains. While fundamental and technical analysis have their strengths and weaknesses, they can be used together to provide a more complete picture of a company's financial health and future potential. By integrating both approaches, investors can identify undervalued stocks that also have short-term momentum. Value investing is an example of a successful investment strategy that combines fundamental and technical analysis. Value investing involves identifying undervalued stocks using fundamental analysis and then using technical analysis to time the entry and exit points. By combining both approaches, investors can achieve long-term growth while also taking advantage of short-term price fluctuations. Understanding the differences between fundamental and technical analysis is essential for making informed investment decisions. Fundamental analysis provides a long-term view of a company's financial health and future potential, while technical analysis is useful for identifying short-term price fluctuations and momentum. By integrating both approaches, investors can achieve better investment results. However, analyzing financial markets and making investment decisions can be challenging, especially for those who are new to it. To navigate the complexities of the market and make the best investment decisions, it is advisable to seek the services of a qualified wealth management specialist. Overview of Fundamental vs Technical Analysis
Fundamental Analysis
Importance of Fundamental Analysis in Investment Decision-Making
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fundamental Analysis
Examples of Fundamental Analysis in Practice
Technical Analysis
Importance of Technical Analysis in Investment Decision-Making
Advantages and Disadvantages of Technical Analysis
Examples of Technical Analysis in Practice
Differences Between Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Choosing Between Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Integrating Both Approaches for Better Investment Decision-Making
Combining Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Conclusion
Fundamental vs Technical Analysis FAQs
Fundamental analysis focuses on examining a company's financial statements and economic indicators to determine its underlying value and potential for growth. In contrast, technical analysis focuses on analyzing market data, such as price and volume charts, identifying trends, and making investment decisions.
Your approach will depend on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Fundamental analysis may be the better approach if you are looking for long-term growth. Technical analysis may be more appropriate if you are looking for short-term gains.
Yes, fundamental and technical analysis can be used together to provide a complete picture of a company's financial health and future potential. By integrating both approaches, investors can identify undervalued stocks with short-term momentum.
One advantage of fundamental analysis is that it provides a long-term view of a company's financial health and future potential. However, it can be time-consuming and requires significant expertise to perform effectively.
One advantage of technical analysis is that it is helpful in identifying short-term price fluctuations and momentum. However, it does not provide insights into a company's financial health or future potential and is susceptible to false signals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











