Benchmarking is a systematic process of comparing an organization's performance, processes, and practices with those of the best-performing organizations in the industry. It helps businesses identify areas where improvements can be made, set realistic goals, and adopt best practices to achieve better financial performance. Benchmarking serves several purposes and provides numerous benefits, including enhancing financial performance, identifying best practices, monitoring progress over time, assessing risk and return, and supporting strategic decision-making. There are four main types of benchmarking: Internal Benchmarking: Comparing performance within the same organization, typically between different departments or branches. External Benchmarking: Comparing performance with other organizations in the same industry or sector. Functional Benchmarking: Comparing similar processes or functions across different industries. Generic Benchmarking: Comparing performance on a broader level, such as comparing customer service practices across various industries. Financial benchmarking plays a crucial role in enhancing financial performance, identifying best practices, monitoring progress over time, assessing risk and return, and supporting strategic decision-making. By comparing financial performance against industry standards or competitors, companies can identify their strengths and weaknesses and work on areas that need improvement. These are the steps involved in the financial benchmarking process. Before starting the benchmarking process, it is essential to identify the objectives of the benchmarking exercise. The objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential in the financial benchmarking process. Some common financial KPIs include: Profitability Ratios: Measures of a company's ability to generate profits, such as gross profit margin, net profit margin, and return on equity (ROE). Liquidity Ratios: Indicators of a company's ability to meet short-term financial obligations, such as the current ratio and quick ratio. Efficiency Ratios: Measures of how effectively a company utilizes its assets, such as inventory turnover and asset turnover. Debt Ratios: Indicators of a company's financial leverage, such as the debt-to-equity ratio and the debt-to-assets ratio. Selecting the right benchmarks is critical for a successful benchmarking process. Some common sources of benchmarks include industry standards, peer group comparisons, and target performance levels set by the company. Data collection and analysis are vital steps in the benchmarking process. Primary research, secondary research, and benchmarking software and tools can be employed to gather and analyze the data. After analyzing the data, companies can identify performance gaps and opportunities for improvement. Based on the findings, companies can develop action plans and implement changes to improve their financial performance. To ensure the success of the benchmarking process, it is crucial to monitor and evaluate the progress periodically. There are some benefits to financial benchmarking, including the following: By comparing financial metrics with industry standards or peer organizations, companies can determine where they are excelling and where they may be falling short. This analysis can help management make informed decisions about resource allocation, identify areas for cost-cutting, and prioritize investments to achieve long-term goals. By identifying areas of weakness and implementing best practices used by top performers, companies can make changes to their operations that will result in improved financial outcomes. For example, benchmarking can help identify inefficiencies in processes that lead to increased expenses, and the implementation of more efficient processes can lead to decreased expenses and improved profitability. By comparing financial performance with industry standards, companies can determine where they stand in relation to their peers and adjust their strategies to remain competitive. There are challenges and pitfalls involved in financial benchmarking, including the following: One of the main challenges in financial benchmarking is dealing with inaccurate or incomplete data. Only accurate data can lead to correct conclusions and undermine the entire benchmarking process. Choosing the right benchmarks can result in accurate comparisons and help the benchmarking process. With management's support, implementing changes and improvements based on benchmarking results can be manageable. Companies may lack the necessary resources and expertise to conduct a thorough and accurate benchmarking process, leading to suboptimal results. Focusing too much on the competition can sometimes lead to a narrow view of the benchmarking process, preventing companies from learning from non-competitive industries or sectors. Benchmarking is a systematic process that compares an organization's performance, processes, and practices with those of the best-performing organizations in the industry. Financial benchmarking plays a crucial role in enhancing financial performance, identifying best practices, monitoring progress over time, assessing risk and return, and supporting strategic decision-making. The financial benchmarking process involves identifying objectives, selecting relevant financial KPIs, choosing appropriate benchmarks, collecting and analyzing data, identifying gaps and opportunities, implementing changes and improvements, and monitoring and evaluating progress. The benefits of financial benchmarking include identifying strengths and weaknesses, improving financial performance, and keeping a competitive edge. However, there are also common challenges and pitfalls involved in financial benchmarking, such as dealing with inaccurate or incomplete data, inappropriate benchmark selection, lack of management buy-in, insufficient resources and expertise, and overemphasis on competition. Future trends in financial benchmarking include the integration of advanced analytics and AI, greater emphasis on ESG factors, increased importance of non-financial metrics, and evolving roles in a rapidly changing business environment.What Is Benchmarking?
Importance of Benchmarking in Finance
Financial Benchmarking Process
Identifying Benchmarking Objectives
Selecting Relevant Financial KPIs
Choosing Appropriate Benchmarks
Collecting and Analyzing Data
Identifying Gaps and Opportunities
Implementing Changes and Improvements
Monitoring and Evaluating Progress

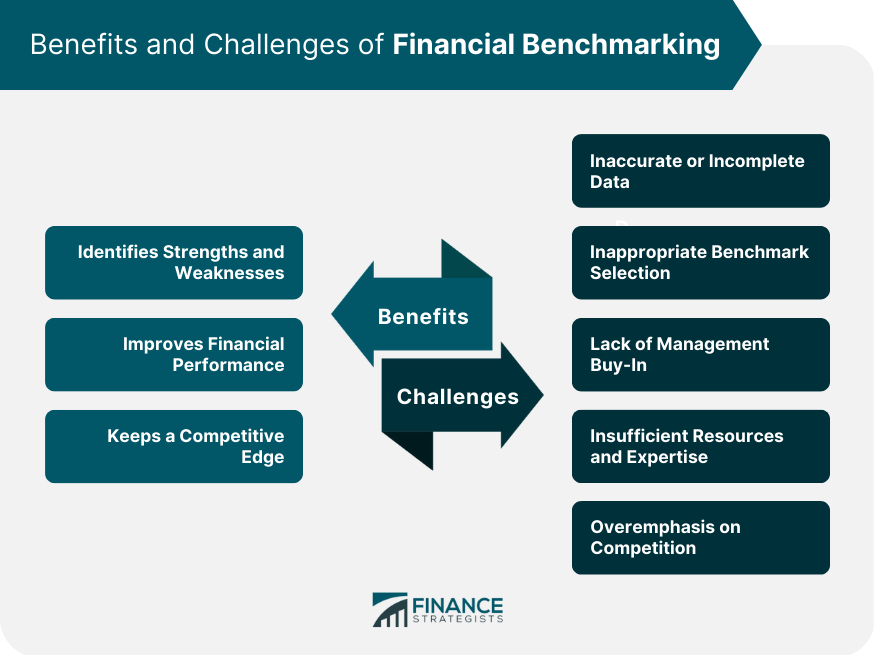
Benefits of Financial Benchmarking
Identifies Strengths and Weaknesses
Improves Financial Performance
Keeps a Competitive Edge
This analysis can help management stay ahead of trends and identify emerging opportunities or threats that may impact their financial performance.Common Challenges and Pitfalls in Financial Benchmarking
Inaccurate or Incomplete Data
Inappropriate Benchmark Selection
Lack of Management Buy-In
Insufficient Resources and Expertise
Overemphasis on Competition
Conclusion
Benchmarking FAQs
Benchmarking is the process of comparing an organization's performance metrics to industry best practices or competitors' performance metrics to identify areas for improvement.
Benchmarking is important because it helps organizations identify performance gaps, highlight improvement areas, and learn from best practices to enhance their overall performance and competitiveness.
There are several types of benchmarking, including internal benchmarking (comparing performance metrics within an organization), competitive benchmarking (comparing performance metrics against direct competitors), and functional benchmarking (comparing performance metrics with other organizations in the same industry).
The key steps in the benchmarking process include identifying the metrics to be benchmarked, selecting benchmarking partners, collecting data, analyzing the data, identifying performance gaps, developing action plans, and implementing and monitoring improvements.
The benefits of benchmarking include identifying areas for improvement, learning from best practices, enhancing organizational performance, increasing competitiveness, and improving customer satisfaction.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











