Dead Cat Bounce is a financial term used to describe a temporary recovery in asset prices after a significant decline, followed by a subsequent fall. The metaphor implies that even a dead cat will bounce if it falls from a high enough point, signifying that any asset, even those considered worthless, can show a temporary surge in price. The phrase is believed to have originated from the Singaporean and Malaysian stock markets in the 1980s, highlighting a bearish market scenario. It is a cynical and somewhat macabre reference, reflecting the volatile nature of markets and investor psychology. A Dead Cat Bounce is characterized by a short-term reversal in the downtrend of an asset's price. It's often triggered by buyers stepping in to capitalize on the perceived value after a sharp decline. Before a Dead Cat Bounce occurs, there's typically a rapid, often drastic, decline in the asset's price. This plunge is usually due to widespread selling, sometimes instigated by negative news or poor financial results. After the brief recovery, a continuation of the downtrend follows. This downturn is the defining factor that differentiates a Dead Cat Bounce from a genuine recovery, underscoring the transitory nature of the bounce. A Dead Cat Bounce is characterized by a short-lived and relatively weak uptrend in asset prices. It occurs after a significant decline and is often followed by a continuation of the downtrend. Conversely, a Genuine Recovery is marked by a more sustained and robust uptrend, backed by improved fundamentals, positive market sentiment, or other favorable factors. During a Dead Cat Bounce, the volume and momentum behind the price increase are typically lower compared to a Genuine Recovery. The temporary recovery in a Dead Cat Bounce lacks the necessary strength and support to sustain a prolonged upward trend. In contrast, a Genuine Recovery tends to exhibit higher trading volumes and stronger momentum, indicating greater market participation and confidence. A Dead Cat Bounce typically occurs without significant improvements in the underlying fundamentals of the asset or the broader market. It is often driven by short-term speculative buying or opportunistic trading. On the other hand, a Genuine Recovery is accompanied by positive developments in the fundamental factors such as strong earnings growth, favorable economic conditions, or positive regulatory changes. Dead Cat Bounces often occur in bearish market conditions, where investor sentiment is negative and fear dominates. The temporary price increase may create a sense of optimism, but it is short-lived. Genuine Recoveries occur in more positive market environments with optimistic sentiment. They reflect a genuine improvement in market conditions and investor confidence. A Dead Cat Bounce is typically a temporary market phenomenon that does not change the overall downtrend. It does not alter the long-term bearish outlook for the asset. In contrast, a Genuine Recovery suggests a shift in the market trend and holds the potential for a sustained upward trajectory. It indicates a positive long-term outlook for the asset. Traders use various technical analysis tools to identify a potential Dead Cat Bounce. These might include moving averages, price and volume patterns, and momentum indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). Some traders use short-selling strategies during a Dead Cat Bounce to profit from the anticipated decline that follows the temporary recovery. However, timing these trades can be challenging, requiring considerable skill and experience. Trading a Dead Cat Bounce carries substantial risk, as the precise timing of the bounce and subsequent price decline can be challenging to predict. However, if executed correctly, it can also provide lucrative rewards due to the heightened market volatility. In technical analysis, various indicators and patterns signal a potential Dead Cat Bounce. For instance, candlestick patterns like the 'Bearish Engulfing' or 'Three Black Crows' could suggest an impending bounce. While technical analysis can be valuable in identifying potential Dead Cat Bounces, it has limitations. Predictions are based on historical data and do not guarantee future outcomes. Furthermore, technical analysis often fails to account for sudden market changes caused by unexpected news or events. Market psychology plays a significant role in the occurrence of a Dead Cat Bounce. Fear and greed often drive market participants to make irrational decisions, such as buying into a temporary recovery. Certain behavioral biases, like the recency bias and herd mentality, can lead investors to fall for the Dead Cat Bounce trap. These biases can cloud judgment and lead to risky financial decisions. The concept of a Dead Cat Bounce is not limited to the stock market. It's also observed in the Forex market, where currency pairs can exhibit similar patterns following significant price declines. In the commodity markets, prices can experience a Dead Cat Bounce due to factors like supply-demand imbalances or geopolitical events. For instance, oil prices often exhibit this phenomenon following supply disruptions or significant demand shifts. The rapidly evolving cryptocurrency market has also seen instances of Dead Cat Bounces. Volatility and speculative trading in this market often amplify these occurrences, leading to drastic price swings. Some financial experts criticize the concept of the Dead Cat Bounce, arguing that it oversimplifies complex market dynamics. They contend that multiple factors influence asset prices, and focusing solely on price movements can lead to misleading conclusions. The occurrence of Dead Cat Bounces challenges the Efficient Market Hypothesis, suggesting that markets can be overreactive and driven by irrational behavior. This inefficiency presents both opportunities and challenges for traders and investors. One of the most notable instances of a Dead Cat Bounce occurred during the Global Financial Crisis of 2008. Many stocks rebounded momentarily before continuing their downward spiral. A more recent example can be seen in the cryptocurrency market where Bitcoin experienced a Dead Cat Bounce in 2018 after its price fell drastically from its peak in December 2017. When a Dead Cat Bounce occurs, it can significantly impact market participants. Uninformed investors may suffer heavy losses if they buy into the temporary recovery, while savvy traders may use this opportunity to profit from volatility. A Dead Cat Bounce is a temporary recovery in asset prices following a significant decline. It is characterized by a brief uptrend that is preceded by a rapid decline and followed by a continuation of the downtrend. While a Dead Cat Bounce may initially appear as a potential market turnaround, it is crucial to distinguish it from a genuine recovery, as mistaking it can lead to financial losses. Traders and investors can use technical analysis tools to identify potential Dead Cat Bounces, but it carries inherent risks due to the challenges in timing the bounce and subsequent price decline. Despite criticism from some financial experts, the occurrence of Dead Cat Bounces challenges the Efficient Market Hypothesis, highlighting the impact of market psychology and irrational behavior. This phenomenon is not limited to the stock market but can also be observed in other financial markets such as foreign exchange, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Overall, understanding and being aware of the concept of a Dead Cat Bounce can help market participants make informed decisions and navigate volatile market conditions more effectively. However, it is crucial to approach such situations with caution, conduct thorough analysis, and consider multiple factors before making investment or trading decisions. Market participants should always be mindful of the risks involved and seek professional advice when needed to mitigate potential losses.What Is a Dead Cat Bounce?
Characteristics of a Dead Cat Bounce
Brief Uptrend
Rapid Decline Preceding the Bounce
Subsequent Continuation of the Downtrend
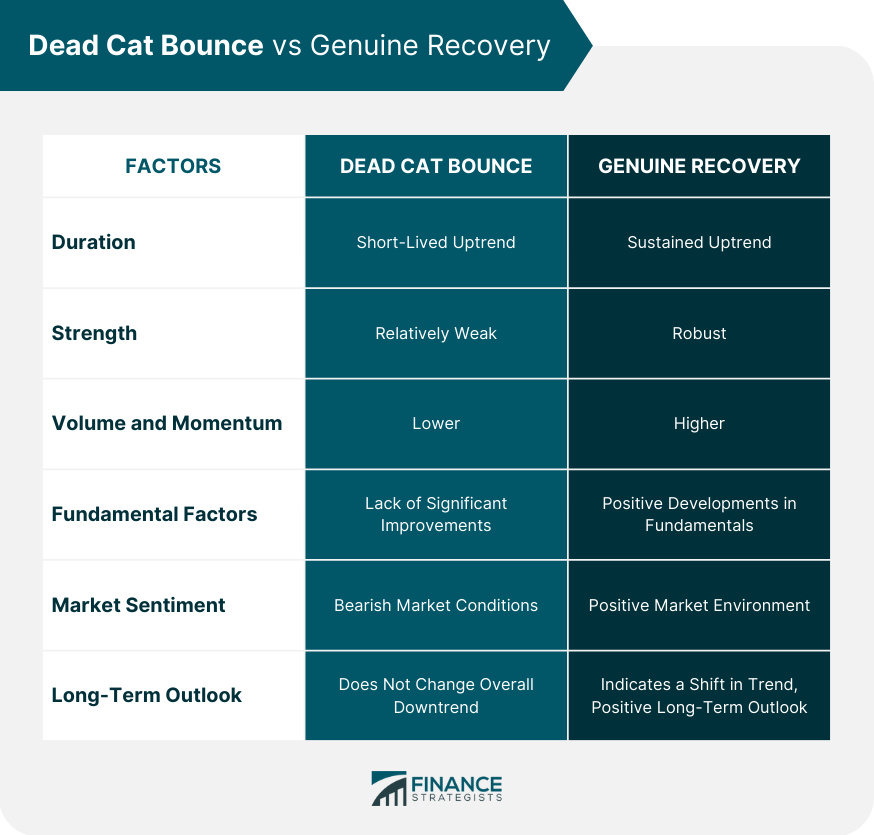
Dead Cat Bounce vs Genuine Recovery
Duration and Strength
Volume and Momentum
Fundamental Factors
Market Sentiment
Long-Term Outlook
Dead Cat Bounce in Stock Trading
How Traders Identify a Dead Cat Bounce
Strategies for Trading During a Dead Cat Bounce
Risks and Potential Rewards
Dead Cat Bounce in Technical Analysis
Relevant Indicators and Patterns
Limitations of Technical Analysis
Dead Cat Bounce in Market Psychology
Influence of Emotions on Trading Decisions
Behavioral Biases Related to Dead Cat Bounce
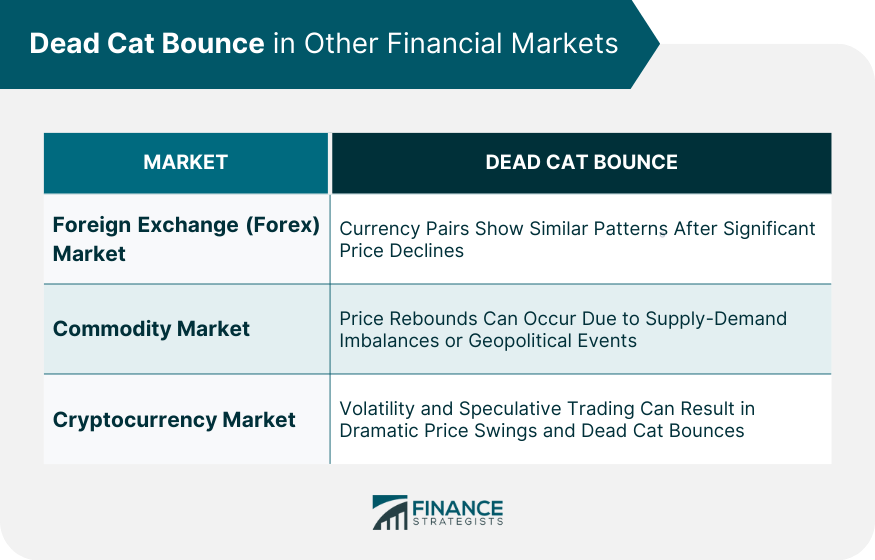
Dead Cat Bounce in Other Financial Markets
Foreign Exchange Market (Forex)
Commodity Market
Cryptocurrency Market
Criticism and Controversies Surrounding the Dead Cat Bounce
Criticism From Financial Experts
Impact on Market Efficiency
Occurrences of a Dead Cat Bounce in Financial History
Case Studies
The Impact on Market Participants
Final Thoughts
Dead Cat Bounce FAQs
Distinguishing between a Dead Cat Bounce and a genuine recovery can be challenging. One key factor to consider is the duration and strength of the uptrend. A Dead Cat Bounce is typically short-lived and lacks the volume or momentum to sustain a prolonged recovery. Additionally, analyzing the underlying fundamentals and market sentiment can help differentiate between a temporary bounce and a more sustainable market turnaround.
Yes, several technical indicators can aid in identifying a potential Dead Cat Bounce. Moving averages, price and volume patterns, and momentum indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) can provide valuable insights. Additionally, certain candlestick patterns like the 'Bearish Engulfing' or 'Three Black Crows' may suggest an impending Dead Cat Bounce.
Trading a Dead Cat Bounce can be profitable if executed correctly. However, it comes with substantial risk. Timing the bounce and subsequent price decline accurately can be challenging. Experienced traders often use short-selling strategies during a Dead Cat Bounce to profit from the anticipated decline. It is important to note that trading strategies should be based on thorough analysis and risk management practices.
No, Dead Cat Bounces can be observed in various financial markets. While the term originated in the stock market, similar patterns can be seen in the Forex market, commodity markets, and even the cryptocurrency market. The occurrence of a Dead Cat Bounce is not limited to a specific market but rather reflects the behavioral and psychological dynamics of market participants.
Market psychology plays a significant role in the occurrence of a Dead Cat Bounce. Emotions such as fear and greed can drive market participants to make irrational decisions, leading to buying into a temporary recovery. Behavioral biases like the recency bias and herd mentality can also contribute to falling for the Dead Cat Bounce trap. Understanding and managing these psychological factors is crucial for making informed investment decisions and avoiding potential pitfalls.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











