What Is the Falling Knife?
"Falling Knife" is a term in finance denoting a rapid, sharp drop in a security's price, whether it's a stock, bond, or commodity.
The phrase conveys the high risk involved in attempting to purchase the security during this drastic fall, similar to the danger of trying to catch a literal falling knife.
It is essential in investing as it represents a potentially perilous situation often mistaken for a buying opportunity, especially by new investors.
However, without thorough analysis and understanding of the factors causing the plunge, it's akin to catching a falling knife – extremely risky.
Thus, a sound understanding of this concept can assist investors in making informed decisions, thereby avoiding significant financial pitfalls.
Understanding the Falling Knife
History and Origin of the Term
The term "Falling Knife" has been part of stock market jargon for decades. It originated from the age-old wisdom of "never try to catch a falling knife." It paints a vivid picture of the potential danger of buying assets when their price is plummeting rapidly.
Just as one would be cautious not to catch a literal falling knife for fear of injury, investors are warned against buying falling securities due to the risk of significant financial loss.
Falling Knife in the Financial Market
A typical scenario of a Falling Knife could be a company whose stock price starts to drop sharply due to a poor earnings report, unfavorable market conditions, or other negative news.
As the price falls, investors may rush to sell their holdings, further accelerating the price decline. Some investors, spotting the rapid price drop, may consider it a good time to buy, thinking the price will eventually rebound.
However, without careful analysis, these investors may find themselves incurring heavy losses if the stock price continues to fall.
Characteristics of a Falling Knife
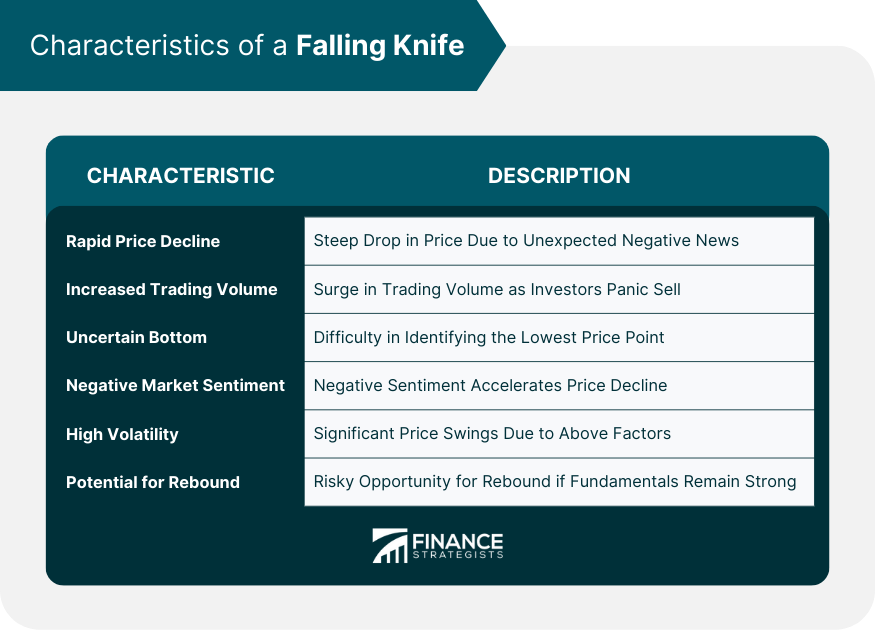
Rapid Price Decline
Rapid price decline can often be triggered by unexpected negative news, such as a disappointing earnings report, a shift in industry dynamics, regulatory changes, or broader market turbulence.
This feature makes a falling knife easy to spot but difficult to predict and manage, as the asset's value can erode dramatically in a short period of time.
Increased Trading Volume
Increased trading volume often due to panic selling by investors who fear that the asset's price will continue to fall.
As investors scramble to exit their positions, the asset's trading volume rises significantly, which can further amplify the rapid decline in price.
This elevated trading volume can also cause increased market volatility, which can create additional uncertainty and risk for investors.
Uncertain Bottom
Due to the rapid and often unpredictable nature of the price decline, it's not easy to ascertain the point at which the asset's price will stabilize and start to rebound.
This uncertainty is particularly risky for investors who might be tempted to "catch" the falling knife, or buy the asset in the hopes that its price will soon recover. However, if the bottom hasn't truly been reached, these investors could potentially face even more significant losses.
Negative Market Sentiment
A falling knife situation is usually characterized by negative market sentiment towards the asset. This could be due to poor financial performance, adverse industry trends, unfavorable economic conditions, or a loss of investor confidence in the company's management.
Negative sentiment can further accelerate the price decline, as more investors decide to sell their holdings.
High Volatility
Falling knives are typically accompanied by high levels of price volatility. The drastic swings in price, driven by the factors mentioned above, can create a stressful and uncertain investment environment.
The high volatility can further exacerbate the panic selling, leading to even more significant price declines.
Potential for Rebound
Despite the negative connotations of a falling knife, it can sometimes present a buying opportunity for risk-tolerant investors.
If the underlying fundamentals of the asset remain strong despite the negative news or market sentiment, the asset could potentially rebound once the situation stabilizes. However, this requires careful analysis and timing, as the risk of further price decline remains high.
Potential Risks of Catching a Falling Knife
Risk of Predicting the Bottom of a Price Drop
One of the main risks in a Falling Knife situation is the challenge of accurately predicting when the price will hit bottom.
Despite technical indicators and analysis, no tool can predict with absolute certainty when the price drop will cease.
Investors who prematurely believe they've identified the bottom may find themselves in deeper financial peril if the price continues to fall after they've bought the asset.
Financial Losses Associated With a Falling Knife
In a Falling Knife scenario, financial losses can be significant. Investors who buy the asset during its steep decline risk seeing their investment value shrink as prices continue to drop.
If the price does not rebound, or if the company goes bankrupt, investors may lose the entirety of their invested capital.
Danger of a "Value Trap"
One particular risk in a Falling Knife situation is the so-called "value trap." A value trap occurs when investors mistake a company's falling share price for a sign that the stock is undervalued.
Attracted by the seemingly low price, they buy the stock, hoping for a price rebound.
However, if the price drop was due to fundamental problems within the company, such as declining profits or increasing debt, the stock may not recover, and investors may be left holding shares that are worth significantly less than what they paid for them.

Strategies to Avoid Catching a Falling Knife
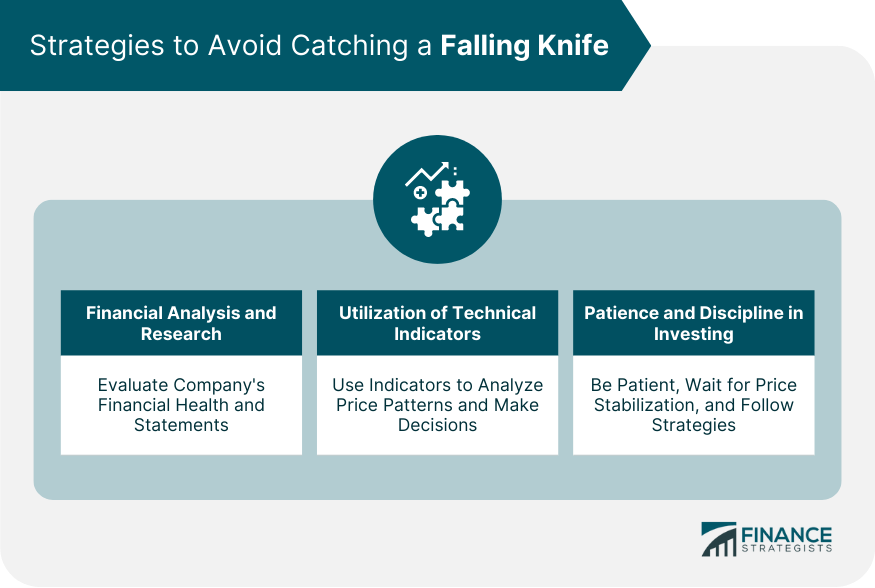
Importance of Financial Analysis and Research
Conducting comprehensive financial analysis and research is critical to avoid catching a falling knife. This approach includes evaluating a company's financial health, scrutinizing its income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
By doing so, investors can ascertain whether the price drop is due to temporary market sentiment or a fundamental issue within the company.
Furthermore, staying updated with the latest news concerning the company and the industry it operates in can also provide valuable insights into the cause of the price drop.
Utilization of Technical Indicators
Investors can also use technical indicators to avoid catching a falling knife. These tools help identify patterns in price movements and trading volume, allowing investors to make educated guesses about future price directions.
Common indicators include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands. While they cannot predict future price movements with absolute certainty, they can provide additional information to inform investment decisions.
Importance of Patience and Discipline in Investing
In investing, it's crucial to remain patient and disciplined, particularly in a falling knife scenario. Instead of succumbing to the fear or greed that often drives hasty buying decisions, successful investors wait for clear signs of price stabilization before considering a purchase.
They also stick to their predetermined investment strategy and risk tolerance, even during volatile market situations.
Investment Strategies in the Context of a Falling Knife
Defensive Strategies: Hedging, Diversification
Defensive strategies, such as hedging and diversification, can help mitigate the potential losses from a falling knife.
Hedging involves taking an investment position intended to offset potential losses that may be incurred by another investment.
Diversification, on the other hand, involves spreading investments across various assets or asset classes to reduce exposure to any single asset or risk.
Contrarian Investing Approach
Some investors employ a contrarian investing approach in the context of a falling knife.
This strategy involves going against the prevailing market trends, with the belief that the market overreacts to good and bad news, causing stock price movements that do not correspond with a company's long-term fundamentals.
A contrarian investor would see a falling knife situation as a potential opportunity, but this strategy carries significant risk and requires thorough research and analysis.
Short Selling and Its Relation to a Falling Knife
Short selling is another strategy related to falling knives. It involves selling a security that the investor does not own, in the hope of buying it back later at a lower price.
This strategy can be profitable during a falling knife scenario, but it also carries significant risks, as losses can be substantial if the price of the security rises.
Falling Knife and Financial Market Dynamics
Impact of a Falling Knife Scenario on the Broader Market
A falling knife scenario can have a significant impact on the broader market. It can trigger panic selling, leading to increased market volatility and potentially a market-wide downward trend.
Role of Market Sentiment in a Falling Knife Situation
Market sentiment plays a crucial role in a falling knife situation. Negative news or poor earnings reports can lead to fear-driven sell-offs. Conversely, positive sentiment can also cause a sharp rebound in prices, turning the falling knife into a potential buying opportunity.
Correlation Between Economic Cycles and Falling Knife Scenarios
Economic cycles significantly influence falling knife scenarios. During economic downturns or recessions, falling knife scenarios are more common as businesses face reduced revenues and profits.
Understanding these cycles can help investors anticipate potential falling knives and prepare accordingly.
Final Thoughts
A "falling knife" in investing refers to a sudden, sharp decline in a security's price, with increased trading volume and unpredictable bottoming-out. It carries the risk of significant financial losses if the bottom is misjudged.
To mitigate these risks, thorough financial analysis and research, including the use of technical indicators, help determine if the drop is temporary or fundamental.
It is crucial to exercise patience, discipline, and wait for clear signs of price stabilization before considering a purchase.
Defensive strategies like hedging and diversification, along with contrarian investing and short selling, can be beneficial.
Seeking professional advice from wealth management services can provide further assistance in managing investment decisions during market volatility.
Falling Knife FAQs
A Falling Knife refers to a sharp and rapid decline in the price of a security. It's a term used in the financial markets to denote a high-risk situation where an asset's price is plummeting significantly and rapidly.
The risks involve substantial potential financial losses if an investor buys the asset during its steep price decline and the price does not rebound. Difficulty in predicting the bottom of a price drop, the danger of a value trap, and the possibility of total loss of the invested capital are among the associated risks.
Technical indicators can provide additional insights into price trends and potential reversals. While they cannot predict with absolute certainty when a price drop will cease, they can help identify patterns in price movements and trading volumes, aiding in informed investment decisions.
Strategies to mitigate these risks include comprehensive financial analysis and research, utilization of technical indicators, and maintaining patience and discipline in investing. Defensive strategies like hedging and diversification can also help reduce risk, as can contrarian investing and short selling approaches.
Market sentiment plays a crucial role in a Falling Knife scenario. Negative news or poor earnings reports can lead to fear-driven sell-offs, accelerating the price drop. Conversely, positive sentiment can trigger a sharp rebound in prices, potentially turning a falling knife into a buying opportunity.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











