What Is the Low Volume Pullback?
In financial trading, the low volume pullback is a technical scenario that occurs when the price of an asset temporarily moves in the opposite direction of a prevailing trend, and the trading volume is lower than average.
This is often seen as a period of consolidation before the asset resumes its initial trend.
Volume plays a pivotal role in technical analysis as it provides extra information that can aid in making informed decisions. Trading volume can provide insights into the strength of a particular price move, reflecting the overall activity and liquidity in a market.
A high volume often indicates strong investor interest and can point to the start of a new trend. In contrast, low trading volume can suggest a lack of confidence or interest, often occurring during market indecision periods.
Understanding the Concept of the Low Volume Pullback
Impact of Volume on Price Movements
The volume of trading directly influences price movements. For instance, if a price increases on a high volume, it suggests that the uptrend is robust and has a higher probability of continuing.
On the other hand, if the price falls during low volume, it is usually a sign that the downward trend is weak and may soon reverse. This is the fundamental principle behind the low volume pullback strategy.
How Low Volume Pullbacks Indicate Trading Opportunities
Low volume pullbacks often signal a temporary pause in a trend rather than a reversal, providing trading opportunities. When the volume is low during a price pullback, it suggests that there is little selling pressure, and the main trend is likely to resume soon.
Traders can use these pullbacks as a chance to enter the market or add to their existing positions at a better price point.
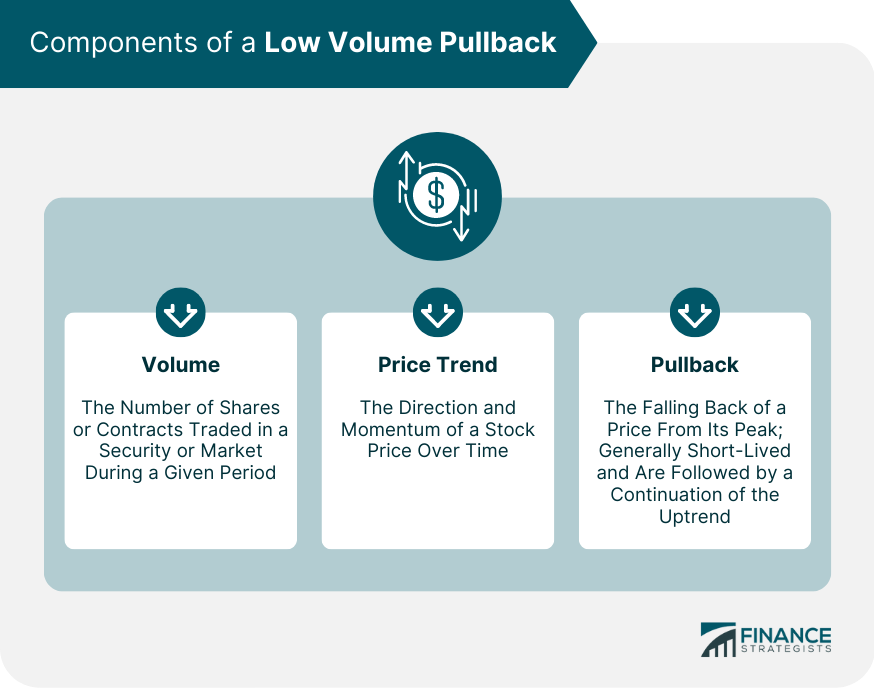
Components of a Low Volume Pullback
Volume
Volume is the number of shares or contracts traded in a security or market during a given period. It is one of the simplest but essential measures of market activity.
In the context of low volume pullbacks, traders look for a decrease in volume during a pullback, suggesting the trend's potential resumption.
Price Trend
A price trend refers to the direction and momentum of a stock price over time. In the case of a low volume pullback, the underlying trend is an uptrend, meaning prices have generally been rising.
Pullback
A pullback refers to the falling back of a price from its peak. Pullbacks are generally short-lived and are followed by a continuation of the uptrend. During these pullbacks, traders can potentially capitalize on the opportunity to buy at lower prices.
How to Identify Low Volume Pullbacks in the Stock Market
Tools for Volume Analysis
Numerous tools can help traders analyze volume. The Volume Indicator in trading platforms like MetaTrader shows the number of shares traded during a given period.
The On-Balance Volume (OBV) and Money Flow Index (MFI) are other commonly used tools for volume analysis, helping assess the flow of capital into and out of a security.
Identifying Decreased Volume During a Pullback
Identifying a decrease in volume during a pullback is crucial in the low volume pullback strategy. Traders can use the aforementioned volume indicators to notice this.
If the volume decreases during the pullback phase, it could signify that the selling pressure is weakening and that the original trend might continue soon.
Observing Market Trends and Patterns
Along with volume analysis, monitoring overall market trends and patterns is essential. Understanding the broader market sentiment can offer additional confirmation for potential trades. This involves identifying significant support and resistance levels, trend lines, and price patterns.
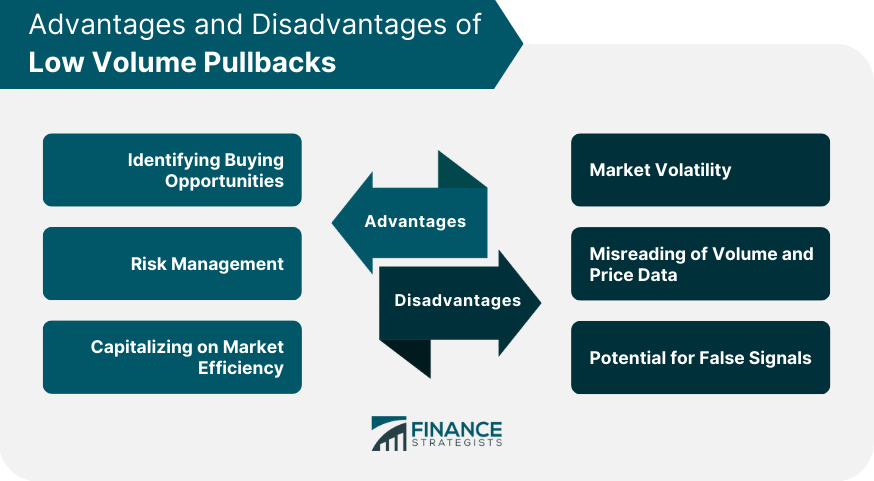
Advantages of a Low Volume Pullback Strategy
Identifying Buying Opportunities
One of the main advantages of the low volume pullback strategy is its ability to identify potential buying opportunities. As the price pulls back on low volume, it suggests that the selling pressure is weak and that the original upward trend may resume.
This can provide an advantageous entry point for traders looking to join the uptrend.
Risk Management
Using this strategy, traders can also manage risk effectively. Entering the market during a low volume pullback means that traders buy when the price is low and not at its peak, thereby reducing potential downside risk.
Capitalizing on Market Efficiency
The low volume pullback strategy allows traders to capitalize on market efficiency. The theory of market efficiency suggests that prices reflect all available information.
During periods of low volume pullbacks, the decrease in trading volume could imply that fewer market participants are selling, potentially leading to an upward price move once the selling pressure dissipates.
Drawbacks of a Low Volume Pullback Strategy
Market Volatility
While low volume pullbacks can provide trading opportunities, they may also pose challenges during periods of high market volatility.
During such periods, price movements can become unpredictable, and a low volume pullback might not always indicate a trend resumption.
Misreading of Volume and Price Data
Another potential pitfall is the misreading or misinterpretation of volume and price data. The absence of high trading volumes during a pullback sometimes means that the price will resume its upward trend. It could be a pause before further decline.
Potential for False Signals
Like any trading strategy, the low volume pullback approach is not immune to false signals. Sometimes, a low volume pullback may appear to be setting up, only for the price to move in the opposite direction.
Traders should use other forms of technical analysis to confirm signals and manage risk.
Implementing the Low Volume Pullback Strategy
Steps to Implementing the Strategy
Implementing the low volume pullback strategy involves a few critical steps. First, traders need to identify an uptrend. Next, they need to observe a pullback within this uptrend, accompanied by a decrease in volume.
Once these conditions are met, traders can consider entering a long position, anticipating that the price will resume its upward trajectory.
Role of Patience and Discipline
Patience and discipline are essential when implementing this strategy. Traders must wait for the right conditions to align before entering a trade. Similarly, they must stick to their trading plan and not let emotions dictate their decisions.
Adjusting the Strategy based on Market Conditions
Traders should always be prepared to adjust their strategy based on current market conditions. If the market is particularly volatile, it may be prudent to use additional indicators or tools to confirm the low volume pullback signal.
Conclusion
The low volume pullback strategy is essential in a trader's toolkit. It identifies potential buying opportunities in an uptrend, capitalizes on market efficiency, and manages risk effectively.
However, like any strategy, it is not foolproof and must be used in conjunction with other technical analysis tools to confirm signals and avoid potential pitfalls.
The continued digitalization and democratization of trading mean that technical analysis and strategies like the low volume pullback will remain relevant.
Traders now have access to an abundance of real-time data and advanced analysis tools that can assist in identifying and capitalizing on low volume pullbacks.
Furthermore, the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in trading could lead to more sophisticated volume analysis tools, potentially enhancing the accuracy of the low volume pullback strategy.
Low Volume Pullback FAQs
A low volume pullback occurs when the price of an asset temporarily moves against the prevailing trend, and the trading volume is lower than average. It is often seen as a period of consolidation before the asset resumes its initial trend.
Low volume pullbacks often signal a temporary pause in a trend rather than a reversal, providing trading opportunities. If the volume is low during a pullback, it suggests that there is little selling pressure and the main trend is likely to resume soon.
Several tools like the Volume Indicator, On-Balance Volume (OBV), and Money Flow Index (MFI) can help traders analyze volume and identify low volume pullbacks.
The advantages include identifying buying opportunities, managing risk, and capitalizing on market efficiency. The disadvantages include potential challenges during periods of high market volatility, the possibility of misreading volume and price data, and the potential for false signals.
Yes, the low volume pullback strategy remains relevant in today's trading environment. The increasing availability of real-time data and advanced analysis tools can assist traders in identifying and capitalizing on low volume pullbacks.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











