Portfolio covariance is a statistical measure that quantifies the relationship between the returns of two or more assets in a portfolio. It measures the extent to which the returns of different assets in a portfolio move in the same direction (positive covariance) or in opposite directions (negative covariance) with respect to each other. In finance, portfolio covariance is important because it helps investors to assess the risk of their portfolios. A portfolio with high covariance between its assets is considered to be riskier than a portfolio with low covariance, because the assets are more likely to move together in response to market conditions, and therefore the portfolio's overall performance is more volatile. Covariance measures the degree to which two variables move together. In portfolio management, covariance describes the relationship between the returns of two investments held in a portfolio. Covariance is calculated by multiplying the deviations of each variable from their respective means and summing these products. This calculation generates a positive or negative value that reflects the direction of the relationship between the two variables. A positive covariance value indicates that two variables move together, while a negative covariance value indicates that they move in opposite directions. The magnitude of the covariance value indicates the strength of the relationship between the two variables. Correlation measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables, while covariance measures the direction and magnitude of the relationship between the two variables. The impact of correlation on portfolio covariance depends on whether the correlation is positive, negative, or zero. The positive correlation increases portfolio covariance, while negative correlation reduces portfolio covariance. Zero correlation has no impact on portfolio covariance. Diversification involves holding a mix of investments with low or negative correlations to reduce overall portfolio risk. By diversifying, investors can reduce portfolio covariance and increase their chances of achieving optimal returns. Portfolio covariance is calculated by multiplying the weight of each investment by its covariance with every other investment in the portfolio and summing these products. Historical data can be used to calculate portfolio covariance by analyzing the past performance of investments and calculating their covariance based on this data. Several factors can impact portfolio covariance, including the number of investments in the portfolio, the weighting of each investment, and the correlation between the investments. Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) is a framework for optimizing portfolio returns by balancing risk and reward. Portfolio optimization involves selecting a mix of investments that provides the highest expected return for a given level of risk. Portfolio optimization is critical for risk management as it enables investors to construct portfolios that balance risk and reward based on their investment goals and risk tolerance. Portfolio covariance plays a critical role in portfolio optimization by helping investors construct portfolios that minimize risk and maximize returns. By diversifying their portfolios, investors can reduce portfolio covariance and increase the potential for optimal returns. Historical data has limitations in predicting future returns and correlations, making it challenging to accurately calculate portfolio covariance. Extreme events, such as market crashes, can impact portfolio covariance by increasing the correlation between investments, making it challenging to predict portfolio performance. The future correlation and covariance of investments are difficult to predict, making it challenging to optimize portfolio returns. Portfolio covariance plays a crucial role in investment decision-making by helping investors evaluate the risk and return potential of their portfolios. By understanding portfolio covariance, investors can make informed decisions about the composition of their portfolios and the level of risk they are willing to take. Asset allocation involves selecting a mix of investments across different asset classes to achieve specific investment goals while managing risk. Portfolio covariance plays a critical role in determining the optimal mix of investments for a given level of risk. Portfolio covariance is an essential component of risk assessments, enabling investors to evaluate the potential risk and return of their portfolios. By incorporating portfolio covariance in risk assessments, investors can better understand the risks associated with their investments and make informed decisions. Portfolio covariance is a crucial concept in portfolio management that measures the relationship between the returns of two or more assets in a portfolio. Understanding portfolio covariance is essential for investors to assess the risk of their portfolios and make informed decisions about their investments. Diversification is a popular risk management strategy that involves holding a mix of investments with low or negative correlations to reduce overall portfolio risk. Portfolio optimization, through the modern portfolio theory, involves selecting a mix of investments that provides the highest expected return for a given level of risk. However, portfolio covariance has limitations and challenges, including the difficulty in predicting future correlations and the impact of extreme events on portfolio performance. Despite these limitations, portfolio covariance remains a critical component in investment decision-making and risk management, enabling investors to evaluate the potential risk and return of their portfolios.What Is Portfolio Covariance?
Understanding Covariance
Definition of Covariance
Calculation of Covariance
Interpretation of Covariance
Portfolio Covariance and Diversification

Correlation vs Covariance
Impact of Correlation on Portfolio Covariance
Benefits of Diversification in Reducing Portfolio Covariance
Calculating Portfolio Covariance
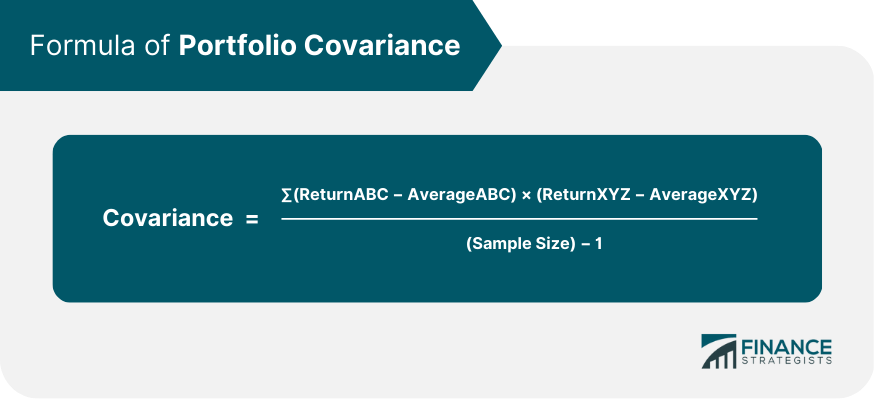
Formula for Portfolio Covariance
Calculation of Portfolio Covariance Using Historical Data
Factors that Impact Portfolio Covariance
Portfolio Optimization
Modern Portfolio Theory and Optimization
Portfolio Optimization and Risk Management
Role of Portfolio Covariance in Optimizing Portfolio Returns
Limitations and Challenges of Portfolio Covariance

Limitations of Historical Data
Impact of Extreme Events on Portfolio Covariance
Difficulty in Predicting Future Correlation and Covariance
Portfolio Covariance and Investment Decision-making
Role of Portfolio Covariance in Investment Decision Making
Portfolio Covariance and Asset Allocation
Incorporating Portfolio Covariance in Risk Assessments
The Bottom Line
Portfolio Covariance FAQs
Portfolio covariance is a measure of the relationship between the returns of two or more investments held in a portfolio. It is important in portfolio management as it helps investors evaluate the risk and return potential of their portfolios, diversify their portfolios to reduce risk, and optimize their portfolios to achieve optimal returns.
Portfolio covariance is calculated by multiplying the weight of each investment by its covariance with every other investment in the portfolio and summing these products. This calculation enables investors to evaluate the degree of correlation between investments in their portfolio.
Portfolio covariance plays a critical role in portfolio diversification by enabling investors to select investments with low or negative correlations, reducing overall portfolio risk. By diversifying their portfolios, investors can reduce portfolio covariance and increase their chances of achieving optimal returns.
Portfolio covariance plays a crucial role in portfolio optimization by helping investors construct portfolios that minimize risk and maximize returns. By diversifying their portfolios and reducing portfolio covariance, investors can optimize their portfolios to achieve optimal returns based on their investment goals and risk tolerance.
The limitations of portfolio covariance in investment decision-making include the challenge of predicting future returns and correlations based on historical data and the difficulty in predicting future correlation and covariance. Despite these limitations, portfolio covariance remains a critical tool for investment decision-making and risk management in the world of finance.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











