"Weak hands" is a term in finance referring to traders and investors lacking either conviction in their strategies or the means to implement them effectively. These individuals frequently react impulsively to market volatility, often selling their investments prematurely out of fear or greed, thus missing out on long-term trends. On the other hand, "strong hands" or "diamond hands" signify investors who maintain their positions despite market turbulence. They demonstrate remarkable patience and commitment to their investment strategies, typically leading to considerable gains over time. The psychological underpinnings of weak hands are rooted in fear and greed. These traders may hastily sell during market downturns out of fear, only to regret their decisions upon market recovery. Conversely, greed may lead them to pursue rapid profits, causing them to buy high and sell low, which contradicts successful trading strategies. A predominant characteristic of weak hands traders is their lack of conviction in their trading strategies. Their decisions are typically influenced by short-term market events, and they frequently second-guess their choices. They often lack a clear investment plan, and they may flip-flop between strategies, contributing to erratic trading behavior and often unfavorable outcomes. Weak hands traders often lack the necessary resources, both financial and emotional, to withstand market downturns. They may not have sufficient capital to hold on to their investments during market corrections or bear markets. On an emotional level, they often struggle with the stress and anxiety that can accompany market volatility, leading them to make rash decisions. Weak hands can have a significant impact on market volatility. Their tendency to react impulsively to market news and events can lead to sharp price swings as they collectively buy or sell in response to market stimuli. This can result in heightened market volatility, creating a more challenging environment for all traders and investors. Weak hands often play a role in precipitating price drops. When they panic and sell their holdings en masse during periods of market stress, they can exacerbate price declines. This can create a self-fulfilling prophecy, as their selling can spur further selling by other weak hands traders, leading to even larger price drops. The behavior of weak hands traders can be exploited by savvy market participants for their own gain. For example, "pump and dump" schemes involve artificially inflating the price of a security to attract weak hands, who are lured by the prospect of quick gains, and then selling off the security, causing its price to plummet and leaving the weak hands with substantial losses. In the stock market, weak hands can contribute to sudden price drops and increased volatility. Their tendency to sell at the first sign of trouble can exacerbate declines during market corrections, and their herd-like behavior can amplify market movements, both up and down. In the futures market, weak hands are often those traders who have no intention of taking delivery of the underlying commodity or index. They engage in speculative trading and may exit their positions prematurely, contributing to price volatility. The cryptocurrency market, with its infamous volatility, is particularly prone to the influence of weak hands. As these markets are relatively new and often poorly understood by many participants, they can be a hotbed for fear-driven trading behavior, with weak hands contributing to drastic price swings. Weak hands can influence market swings through their reactionary trading behavior. They often sell in response to negative news or market downturns and buy in response to positive news or market upswings. This can amplify price swings, contributing to market volatility. The aftermath of weak hands' actions can be a market that is more volatile and potentially more challenging to navigate. Their actions can exacerbate market downturns, leading to larger losses for those who sell during these periods. On the other hand, their actions can also create buying opportunities for those with the patience and foresight to take advantage of price dips caused by weak hands selling. In the long run, markets tend to recover from these short-term movements, but not before weak hands may incur significant losses. The primary difference between weak hands and strong hands lies in their trading strategies. Weak hands tend to be short-term oriented, reactionary, and influenced by fear and greed. They often lack a solid trading plan and frequently make impulsive decisions in response to market fluctuations. On the other hand, strong hands maintain a long-term perspective, sticking to their investment strategies even during times of market stress. They are typically well-researched and patient and show remarkable resilience in the face of volatility. Market sentiment has a significant influence on both weak and strong hands. Weak hands are highly sensitive to market sentiment, often buying during periods of extreme optimism and selling during periods of extreme pessimism. Their behavior is typically reactionary, driven by the fear of missing out (FOMO) or the fear of losing money. In contrast, strong hands are less swayed by market sentiment. They typically rely on careful analysis and a well-thought-out investment strategy, allowing them to weather periods of negative sentiment and take advantage of market dips. The long-term impacts on the portfolios of weak hands versus strong hands can be substantial. Weak hands, with their propensity for buying high and selling low, often erode their investment capital over time. They may miss out on significant market recoveries following downturns because they sold out of fear. Strong hands, conversely, are more likely to reap the benefits of compound growth over the long term. By sticking to their strategies and riding out market volatility, they stand a better chance of achieving substantial gains over time. Emotional resilience is crucial for overcoming the weak hands mentality. This involves developing the ability to remain calm and rational during periods of market stress, resisting the urge to make impulsive decisions based on fear or greed. Emotional resilience can be fostered through various techniques, such as mindfulness, stress management practices, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support overall wellbeing. Financial education plays a vital role in strengthening weak hands. By gaining a solid understanding of market dynamics, risk management, and sound investment strategies, weak hands can build the knowledge base required to make more informed decisions. This can help reduce impulsive behavior driven by fear or greed and encourage a more disciplined approach to trading. Financial education can come from various sources, including books, online courses, seminars, and mentorship from experienced traders. Risk management is another crucial coping strategy for weak hands. This can involve setting clear trading goals, using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, diversifying investments to spread risk, and only investing money one can afford to lose. Risk management also entails regularly reviewing and adjusting one's investment strategy in response to changing market conditions or personal circumstances. By adopting these strategies, weak hands can transform themselves into strong hands, better-navigating market volatility and working towards successful long-term investment outcomes. It's important to remember that all investors, even those with the steadiest of hands, can benefit from continually learning, practicing emotional resilience, and implementing sound risk management practices. Weak hands" refers to traders and investors who are quick to make rash decisions due to market volatility, often selling their positions prematurely during downturns. This behavior, driven by fear or greed, contrasts sharply with "strong" or "diamond hands" who maintain their investments amidst turbulence, showing conviction and patience that often yield long-term benefits. Weak hands can significantly affect market dynamics, potentially escalating volatility and price drops. However, successful investing typically requires a mix of financial education, emotional resilience, and robust risk management, irrespective of one's investing style. For those grappling with market pressures, professional wealth management services can offer resources and strategies to navigate financial market complexities.What Are Weak Hands?
Characteristics of Weak Hands Traders
Lack of Conviction in Strategies
Insufficient Resources

Role of Weak Hands in the Financial Market
Impact on Market Volatility
Role in Price Drops
Potential for Market Manipulation
Influence of Weak Hands on Market Dynamics
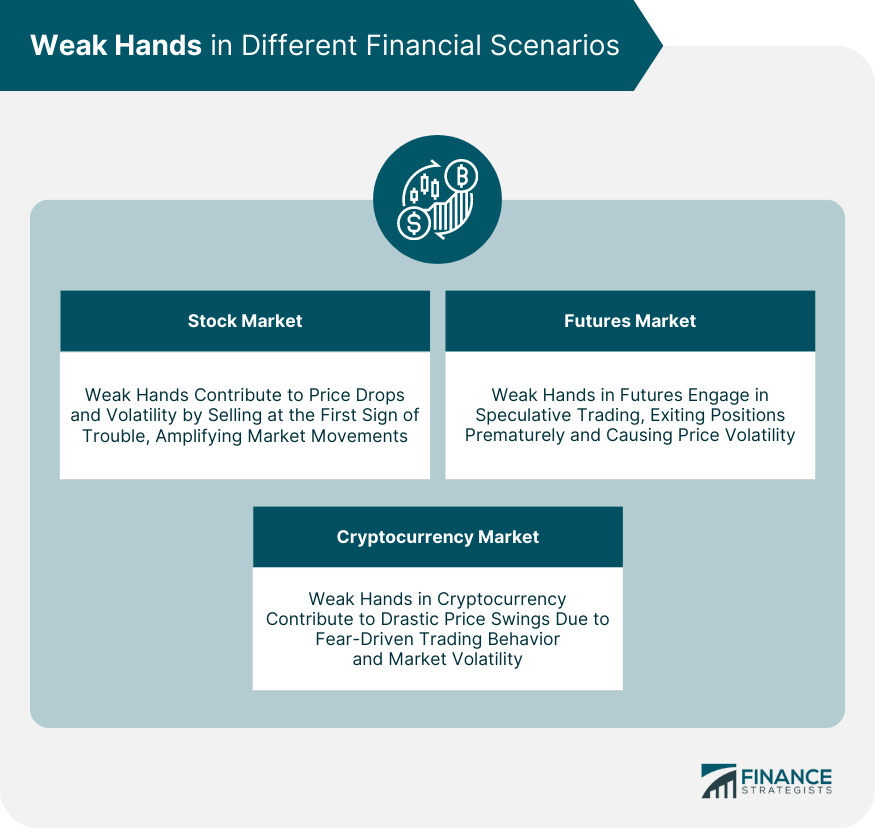
Weak Hands in Different Financial Scenarios
Stock Market
Futures Market
Cryptocurrency Market
How Weak Hands Can Influence Market Swings
Aftermath of Weak Hands' Actions
Weak Hands vs Strong Hands (Diamond Hands)
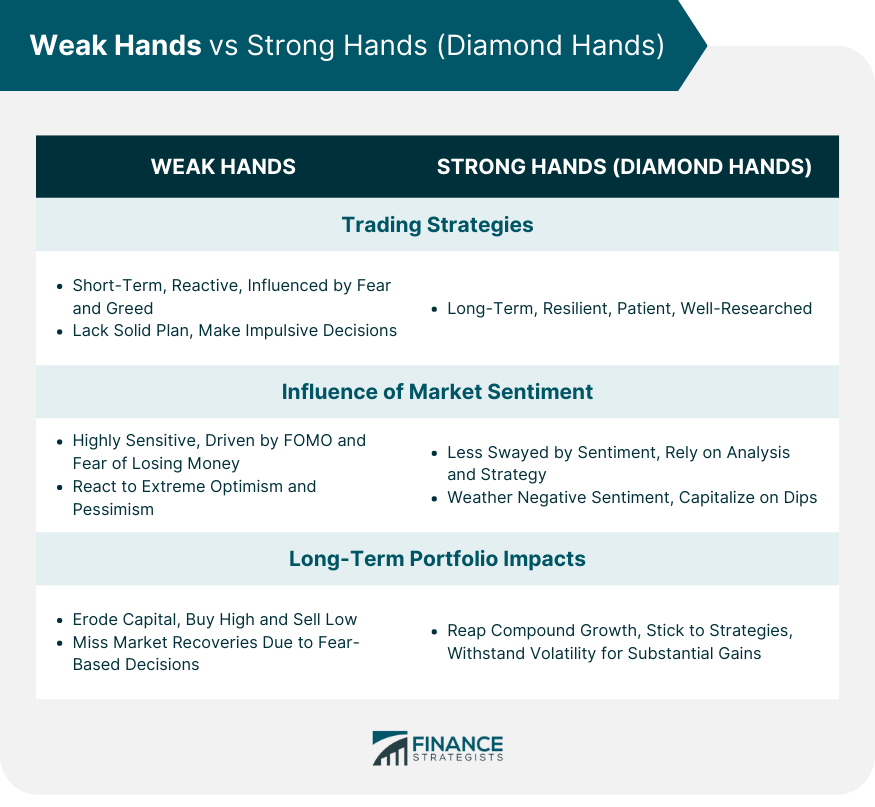
Comparison of Trading Strategies
Influence of Market Sentiment on Both Categories
Long-Term Portfolio Impacts
Coping Strategies for Weak Hands
Developing Emotional Resilience in Trading
Role of Financial Education in Strengthening Weak Hands
Risk Management Strategies to Handle Weak Hands
Final Thoughts
Weak Hands FAQs
Weak hands refer to traders or investors who lack conviction in their strategies or lack the resources to carry them out, often selling their positions at the first sign of market trouble.
Weak hands can influence market dynamics significantly. Their impulsive reactions to market events can lead to heightened volatility, exacerbate price drops, and potentially create opportunities for market manipulation.
Building emotional resilience, pursuing financial education, and implementing sound risk management strategies can help you avoid becoming weak hands and improve your trading outcomes.
The primary difference lies in their reaction to market volatility. Weak hands tend to panic and sell during market downturns, while strong hands maintain their positions, demonstrating patience and faith in their long-term investment strategies.
Absolutely. With the right education, mindset, and risk management practices, weak hands can strengthen their resolve, become less reactive to market volatility, and transform into strong hands.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











