Investing can be a daunting task, especially when there are countless options to choose from. However, age-based investment options provide a way for investors to tailor their investments to their specific age and financial goals. These options are designed to change as investors age, providing different investment strategies for different life stages. Age-based investment options refer to investment strategies that change based on an investor's age. These options are designed to be more aggressive when investors are young and become more conservative as they age. This is because younger investors have more time to ride out the ups and downs of the market, while older investors have less time and a greater need to preserve their savings. Age-based investment options are essential because they help investors align their investments with their financial goals. By investing in options that are tailored to their age, investors can maximize their returns while minimizing their risks. This is particularly important because different age groups have different financial goals and risk tolerances. There are two main types of age-based investment options: retirement accounts and college savings plans. Retirement accounts are investment vehicles designed to help individuals save for retirement. There are several types of retirement accounts, including traditional Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs), Roth IRAs, 401(k)s, and 403(b)s. A traditional IRA is a tax-deferred retirement account. This means that investors can deduct their contributions from their taxable income, reducing their tax bill. However, investors will need to pay taxes on their contributions and earnings when they withdraw them during retirement. A Roth IRA is a retirement account that allows investors to contribute after-tax dollars. The money in a Roth IRA grows tax-free, and investors can withdraw their contributions and earnings tax-free during retirement. A 401(k) is a retirement account offered by employers. These accounts allow employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income to their retirement savings. Employers often match a portion of their employees' contributions. A 403(b) is a retirement account offered to employees of public schools, universities, and certain tax-exempt organizations. Like a 401(k), a 403(b) allows employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income to their retirement savings. College savings plans are investment vehicles designed to help families save for their children's education. There are two main types of college savings plans: 529 plans and Coverdell education savings accounts. A 529 plan is a tax-advantaged savings plan designed to help families save for college. The money in a 529 plan grows tax-free, and withdrawals are tax-free as long as they are used for qualified education expenses. A Coverdell education savings account is a tax-advantaged savings plan designed to help families save for education expenses, including K-12 and college. Like a 529 plan, the money in a Coverdell account grows tax-free, and withdrawals are tax-free as long as they are used for qualified education expenses. Age-based investment options offer several benefits to investors. Many age-based investment options offer tax benefits. For example, traditional IRAs and 401(k)s allow investors to deduct their contributions from their taxable income, reducing their tax bill. Roth IRAs and 529 plans offer tax-free growth and withdrawals for qualified expenses. These tax benefits can help investors maximize their returns and keep more of their hard-earned money. Age-based investment options typically offer a diversified portfolio, which can help investors manage risk. Diversification means investing in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. By diversifying their portfolio, investors can spread their risk across different investments and reduce the impact of market volatility on their overall portfolio. Age-based investment options are designed to manage risk based on an investor's age. Younger investors can afford to take on more risk because they have more time to recover from market downturns. As investors approach retirement age, age-based investment options become more conservative, reducing the risk of losing money in the market. Investing can be overwhelming, especially for those who are new to it. Age-based investment options simplify the investment decision-making process by providing a pre-designed investment strategy based on an investor's age. Investors can choose the option that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance, without needing to understand the complexities of individual investments. While age-based investment options offer several benefits, they also have some drawbacks. Age-based investment options typically offer a limited selection of investments, which may not be suitable for all investors. For example, some age-based investment options may not offer exposure to alternative investments, such as real estate or commodities. Age-based investment options, such as traditional IRAs and 401(k)s, have penalties for early withdrawals. These penalties can be significant and can erode an investor's returns. Investors who may need to access their funds before retirement age may want to consider other investment options that offer more flexibility. Age-based investment options are designed to change as an investor ages. While this is a benefit for some, it can be a drawback for others who may want to customize their investment strategy. Investors who have specific investment goals or risk tolerances may not find age-based investment options suitable for their needs. Age-based investment options offer a way for investors to align their investments with their financial goals and risk tolerance. Retirement accounts, such as traditional IRAs and 401(k)s, and college savings plans, such as 529 plans and Coverdell education savings accounts, are two types of age-based investment options. These options offer several benefits, including tax benefits, diversification, risk management, and simplified investment decision-making. However, they also have some drawbacks, including limited investment options, potential penalties for early withdrawals, and a lack of flexibility. Investors should carefully consider their financial goals and risk tolerance before choosing an age-based investment option that is right for them.What Are Age-Based Investment Options
Types of Age-Based Investment Options
Retirement Accounts
Traditional IRA
Roth IRA
401(k)
403(b)
College Savings Plans
529 Plan
Coverdell Education Savings Account
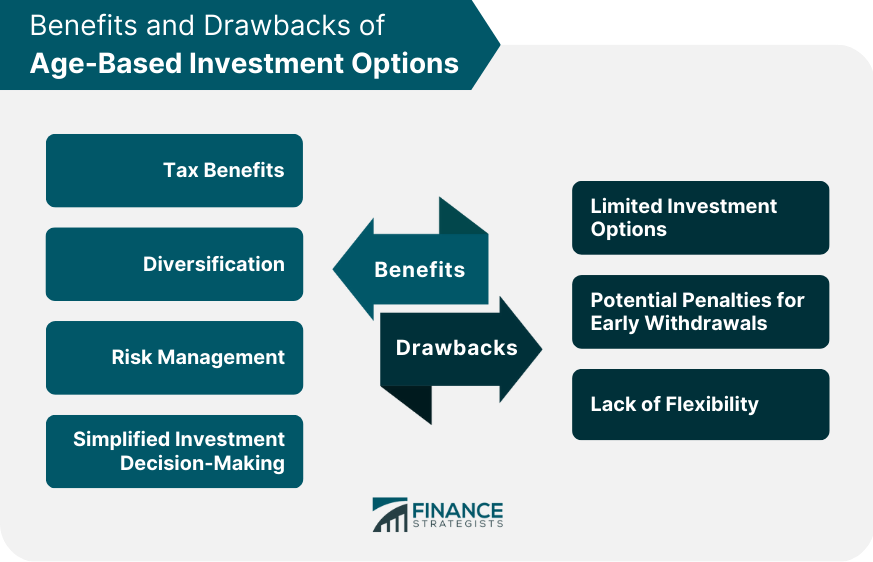
Benefits of Age-Based Investment Options
Tax Benefits
Diversification
Risk Management
Simplified Investment Decision-Making
Drawbacks of Age-Based Investment Options
Limited Investment Options
Potential Penalties for Early Withdrawals
Lack of Flexibility
Conclusion
Age-Based Investment Options FAQs
Age-based investment options are investment strategies that change based on an investor's age. These options are designed to be more aggressive when investors are young and become more conservative as they age.
There are two main types of age-based investment options: retirement accounts and college savings plans. Retirement accounts include traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs, 401(k)s, and 403(b)s. College savings plans include 529 plans and Coverdell education savings accounts.
Age-based investment options offer several benefits, including tax benefits, diversification, risk management, and simplified investment decision-making. These options help investors align their investments with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Age-based investment options have some drawbacks, including limited investment options, potential penalties for early withdrawals, and a lack of flexibility. These options may not be suitable for all investors, particularly those with specific investment goals or risk tolerances.
To choose the right age-based investment option, you should consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. You should also evaluate the investment options available within each option and compare them to your investment goals. It's important to consult with a financial advisor to ensure that you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial objectives.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











