A buy limit order is an order placed with a broker to purchase a specific number of shares at a specified price or lower. It is a strategy employed by traders who are looking to acquire securities at a price that they consider attractive. The basic principle behind a buy limit order is the idea of buying low. Investors set the price at which they wish to purchase a stock, and the broker executes the order once the stock's price falls to that level. If the price does not reach the specified limit, the order remains unfulfilled. Hence, buy limit orders offer a way to automate the trading process, ensuring investors do not miss out on opportunities to buy shares at their desired price. Buy limit orders are crucial in trading as they provide investors with greater control over the purchase price. They are especially beneficial in volatile markets where stock prices can fluctuate rapidly, providing a mechanism to buy stocks at a lower price without constant market monitoring. Furthermore, buy limit orders help investors manage their risk effectively by allowing them to predetermine their potential investment cost. A market order is a request made by an investor to buy or sell a security at the best available price in the current market. It is the quickest and easiest way to execute a trade, though there is no price guarantee as the final execution price may differ from the market price when the order was placed, especially in fast-moving and volatile markets. A limit order is a type of order to buy or sell a stock at a specific price or better. There are two types of limit orders: As previously defined, a buy limit order is an order to purchase a stock at a specific price or lower. Conversely, a sell limit order is an order to sell a security at a specific price or higher. This allows investors to ensure they get their desired profit if the stock's price rises to their specified limit. A stop order, also known as a stop-loss order, is a type of order that becomes executable once a security reaches a particular price, and is then filled at the current market price. There are two types: A buy stop order is set above the current market price. It turns into a market order once the security reaches the specified stop price. A sell stop order is set below the current market price and becomes a market order once the security falls to the specified stop price. Buy limit orders differ from other types of orders primarily based on the control they offer to investors. Unlike market orders, which execute at the best available price, buy limit orders only execute at the limit price or lower, ensuring investors do not overpay. Compared to stop orders, which become market orders once a specific price is reached, buy limit orders give investors more price certainty, although they carry the risk of the order not being filled if the stock price doesn't reach the limit price. To place a buy limit order, an investor needs to specify the quantity of the security they wish to purchase, the limit price at which they want to buy, and the duration the order should stay open. A buy limit order is executed when the price of the security falls to the limit price or lower. The broker is responsible for monitoring the market and executing the order at the specified price. It's important to note that while a buy limit order guarantees the price at which a stock will be bought, it does not guarantee the order's full execution, especially in fast-moving markets. When an investor places a buy limit order, three potential outcomes can occur. First, the stock price falls to the limit price, and the order is fully executed. Second, the stock price falls to the limit price, but due to insufficient stock available at that price, the order is partially filled. Third, the stock price never reaches the limit price, and the order remains unfulfilled. The primary advantage of a buy limit order is the level of price control it offers. Investors predetermine the price they're willing to pay for a stock, ensuring they don't pay more than their specified limit. Buy limit orders also serve as a valuable risk management tool. By specifying the maximum price they're willing to pay, investors limit potential losses should the stock price fall after purchase. Finally, buy limit orders provide investors with flexibility and control. They can be placed at any time, even outside of market hours, and will be executed when the market conditions meet the set price. This allows investors to manage their trades effectively without constant market monitoring. One of the most significant risks associated with buy limit orders is the potential for non-execution. If the stock price does not reach the predetermined limit price, the order will not be executed, and the investor might miss out on potential profit opportunities. Buy limit orders can also lead to partial fills. This situation arises when only a part of the order can be executed due to limited availability of shares at the desired price. While the investor gets some shares at the preferred price, the remaining shares may have to be purchased at a higher price. Despite offering a level of protection against overpaying for a stock, buy limit orders do not protect investors from market fluctuations. If the price of a stock rapidly decreases after purchase, an investor could incur significant losses. Investors must consider the stock's volatility when setting a limit price. Highly volatile stocks are more likely to reach the limit price but can also lead to significant losses if the price falls after purchase. The timing of the market is another crucial factor. During periods of high market volatility, limit orders are more likely to be filled. Finally, the investor's financial goals and risk tolerance must be taken into account. Those with a lower risk tolerance might set a lower limit price to minimize potential losses. While a buy limit order instructs the broker to purchase a security at a specific price or lower, a buy stop order is placed above the market price and triggers once the market price reaches or surpasses the stop price. Buy limit orders are generally used when investors believe a stock's price will decrease before it rises, while buy stop orders are used when they anticipate the stock price will continue to rise after reaching a specific level. Buy limit orders guarantee a purchase price but risk non-execution, while buy stop orders ensure execution but not the final purchase price, which can lead to buying a stock at a higher-than-expected price. Pairing a buy limit order with a stop-loss order can help manage risk effectively. While the buy limit order sets the maximum price to purchase a stock, the stop-loss order sets the minimum price to sell it, thereby limiting potential losses. Buy limit orders can be particularly effective in volatile markets, where stock prices fluctuate rapidly. They allow investors to buy a stock at a lower price without the need for constant market monitoring. It's important to set realistic limit prices. If the limit price is set too low, the order might never get filled, causing the investor to miss out on potential profits. In bull markets, where prices are rising, buy limit orders might be less likely to get filled because the stock price may not fall to the limit price. In contrast, in bear markets, where prices are falling, buy limit orders have a higher chance of being executed. However, the risk is that the price may continue to fall after purchase. In sideways or flat markets, buy limit orders can be an effective tool to purchase stocks at the lower end of the price range. Buy limit orders, by definition, are an important investing tool that allow traders to purchase a stock at a specific price or lower. They come into play in various types of stock orders, including limit orders and stop orders. These investment vehicles have their unique characteristics and situational usage, and understanding the difference between them, such as between a buy limit order and a buy stop order, can help traders navigate the financial markets more efficiently. The advantages of using buy limit orders, including price control, risk management, and flexibility, can make them an appealing choice for investors. However, they also come with potential disadvantages such as the risk of non-execution, partial fills, and exposure to market fluctuation risk. When setting a buy limit order, several factors should be considered including the volatility of the stock price, timing the market, and personal financial goals and risk tolerance. Traders can also employ certain strategies to maximize the benefits of buy limit orders, such as pairing them with stop-loss orders, utilizing them in volatile markets, and setting realistic price limits. While buy limit orders can be a powerful tool for investors, it's important to use them wisely and in alignment with individual financial goals and risk appetite. It is recommended to consult with a professional wealth management service to help you incorporate buy limit orders into a broader, holistic investment strategy that meets your specific needs and goals.What Are Buy Limit Orders?
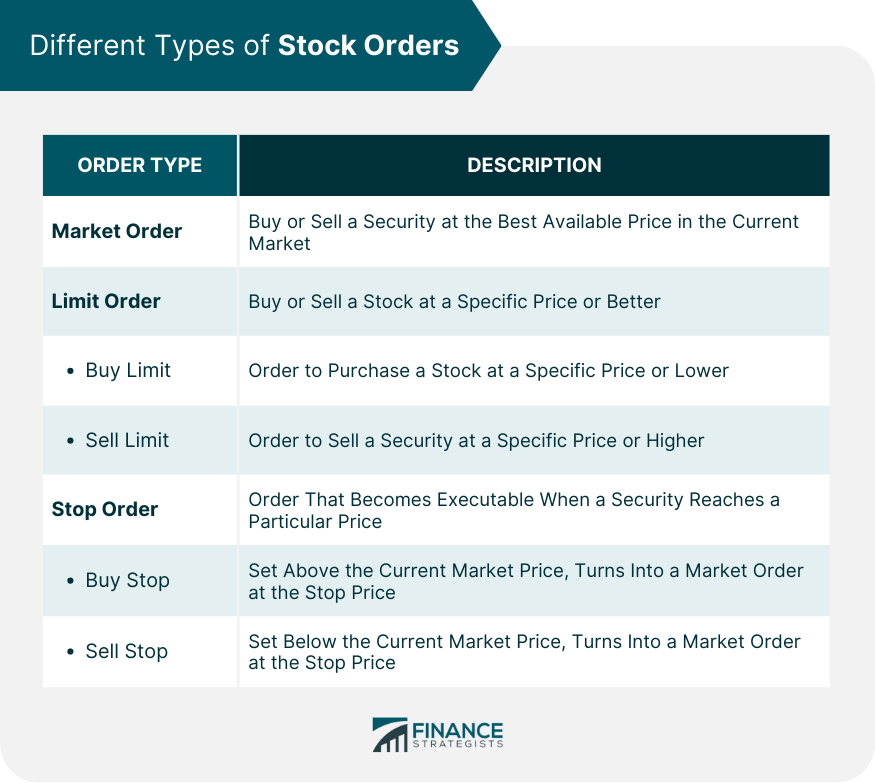
Different Types of Stock Orders
Market Order
Limit Order
Buy Limit Order
Sell Limit Order
Stop Order
Buy Stop Order
Sell Stop Order
Comparing Buy Limit Orders With Other Stock Orders
Working Mechanism of a Buy Limit Order
Placing a Buy Limit Order
Execution of a Buy Limit Order
Potential Outcomes of a Buy Limit Order
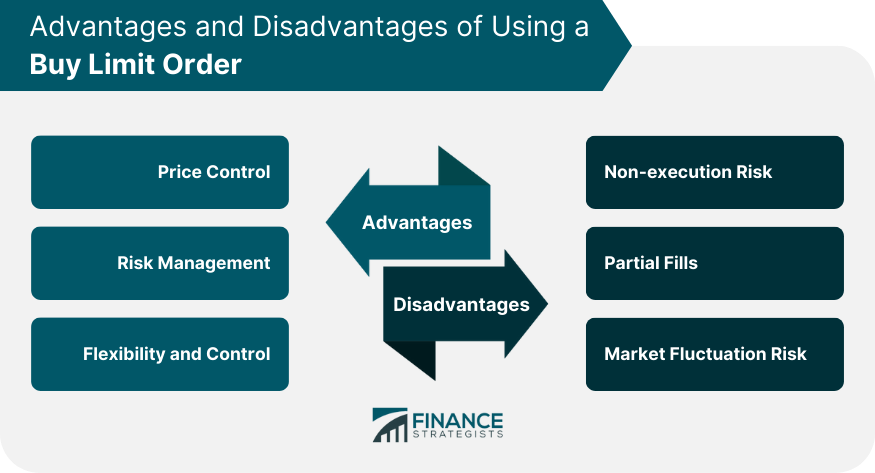
Advantages of Using a Buy Limit Order
Price Control
Risk Management
Flexibility and Control
Disadvantages and Risks of a Buy Limit Order
Non-execution Risk
Partial Fills
Market Fluctuation Risk
Factors to Consider When Placing a Buy Limit Order
Stock Price Volatility
Market Timing
Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance

Buy Limit Order vs Buy Stop Order
Definitions and Differences
Situational Usage
Advantages and Disadvantages
Strategies for Using Buy Limit Orders Effectively
Pairing With Stop-Loss Orders
Using in a Volatile Market
Setting Realistic Price Limits
Buy Limit Orders in Different Market Conditions
Bull Markets
Bear Markets
Sideways Markets

Final Thoughts
Buy Limit Orders FAQs
A buy limit order is an order placed with a broker to purchase a specific number of shares at a predetermined price or lower.
A buy limit order is executed when the stock's price falls to the specified limit price or lower. If the stock price doesn't reach the limit price, the order remains unfulfilled.
Buy limit orders offer price control, risk management, and flexibility. They allow investors to specify the maximum price they're willing to pay for a stock, limiting potential losses.
The disadvantages of buy limit orders include the risk of non-execution if the stock price doesn't reach the limit price, partial fills due to limited stock availability, and potential losses from market fluctuations.
A buy limit order is placed when an investor wishes to buy a stock at a specified price or lower, whereas a buy stop order is placed above the market price and turns into a market order once the stop price is reached or surpassed.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











