Cumulative performance measures an investment's total return over a specific period, accounting for all gains and losses. It provides a comprehensive view of an investment's growth or decline over time, allowing investors to assess the success of their investment strategies. Evaluating cumulative performance is essential for investors as it helps them gauge the effectiveness of their investment decisions, compare different investment opportunities, and assess the potential risks and rewards associated with their portfolios. Various factors can impact cumulative performance, including market conditions, asset allocation, investment strategy and management, fees, and expenses. Understanding these factors is vital for making informed investment decisions and optimizing investment performance. Cumulative return is calculated by comparing the initial investment value with its current or final value, taking into account all capital gains, dividends, and interest payments. The resulting percentage indicates the total return of the investment over a given period. CAGR is a widely used measure that calculates an investment's average annual growth rate over a specified period. By considering compounding effects, CAGR provides a better understanding of an investment's growth potential and allows for easy comparisons between investments with different time horizons. Total return is a comprehensive measure of an investment's performance, taking into account both capital gains and income generated through dividends or interest payments. This approach provides a more accurate picture of an investment's overall performance, as it considers all sources of return. Equities, or stocks, are a common asset class that often exhibits significant growth potential over the long term. Cumulative performance for equities can vary widely based on factors such as company performance, industry trends, and market conditions. Fixed income investments, such as bonds, typically offer more stable returns and lower risk compared to equities. Cumulative performance in fixed income depends on factors like interest rate fluctuations, credit quality, and the bond's maturity. Real estate investments can provide both income and capital appreciation, contributing to their cumulative performance. Factors influencing real estate performance include location, property type, market conditions, and management quality. Commodities, such as gold, oil, and agricultural products, can offer diversification benefits and may perform differently from traditional asset classes. Cumulative performance in commodities is influenced by factors such as supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and currency fluctuations. Benchmarking involves comparing an investment's cumulative performance to a relevant market index or industry standard. This approach helps investors evaluate their investments relative to the broader market and identify areas for improvement. Relative performance evaluation compares an investment's cumulative performance to that of similar investments or peer groups. This analysis can help investors identify top-performing investments within a particular category and make more informed investment decisions. Risk-adjusted performance measures, such as the Sharpe ratio and Sortino ratio, take both cumulative performance and investment risk into account. These metrics allow investors to compare investments with different risk profiles on a level playing field, facilitating more informed decision-making. Market conditions, including economic growth, interest rates, and geopolitical events, can significantly impact the cumulative performance of investments. By understanding these factors, investors can better assess their investments' potential risks and rewards and make more informed decisions. Asset allocation, or the distribution of investments across different asset classes, plays a crucial role in determining cumulative performance. A well-diversified portfolio can help reduce risk and improve overall performance by spreading investments across various asset classes with different risk-return characteristics. The investment strategy and management approach employed can significantly influence cumulative performance. Active management, which involves making tactical decisions to capitalize on market opportunities, may yield higher returns. In contrast, passive management, which aims to replicate the performance of a specific index, generally offers lower costs and more predictable performance. Fees and expenses associated with investments, such as management fees, trading costs, and taxes, can erode cumulative performance over time. Investors should carefully consider these costs when evaluating investment opportunities and choose cost-effective strategies to maximize returns. Analyzing cumulative performance can help investors assess the effectiveness of their current asset allocation and determine if any adjustments are needed. Regular portfolio rebalancing can help maintain the desired risk-return profile and optimize overall performance. Performance attribution involves identifying the factors that contributed to an investment's cumulative performance, such as asset allocation, security selection, and market timing. This analysis can help investors refine their investment strategies and make more informed decisions. Assessing cumulative performance can help investors identify top-performing investments and underperforming assets that may warrant further investigation. By understanding the drivers of performance, investors can uncover new investment opportunities and make more informed decisions. While cumulative performance provides valuable insights into an investment's historical performance, past results do not guarantee future outcomes. Investors should consider other factors, such as current market conditions and future growth prospects when making investment decisions. Cumulative performance figures may not accurately reflect the true performance of an investment when fees and taxes are not considered. Investors should account for these costs when assessing investment performance to ensure they are making informed decisions. Focusing solely on cumulative performance may overlook the level of risk associated with an investment. Investors should also consider risk-adjusted performance measures, such as the Sharpe ratio, to better understand investment performance. Diversification, or spreading investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, can help reduce risk and improve cumulative performance by mitigating the impact of poor-performing investments on the overall portfolio. Choosing between active and passive management strategies can influence cumulative performance. While active management may offer the potential for higher returns, passive management typically involves lower costs and more predictable performance, which may be more suitable for certain investors. Adopting a long-term investment approach can help improve cumulative performance by allowing investments to grow and compound over time. Long-term investors are also less likely to be swayed by short-term market fluctuations, which can lead to more informed decision-making. Cumulative performance is an essential metric for evaluating the success of investment strategies, comparing different investment opportunities, and assessing potential risks and rewards. Investors can make more informed decisions and optimize their portfolios by understanding the factors that influence cumulative performance and incorporating risk-adjusted performance measures. Although past performance does not guarantee future results, analyzing cumulative performance can provide valuable insights and inform investment decisions, ultimately contributing to a more successful investment experience. Understanding the limitations of cumulative performance, such as the impact of fees and taxes and the importance of considering risk, is crucial when evaluating investments. By employing strategies like diversification, selecting the appropriate management approach, and adopting a long-term investment mindset, investors can work towards improving their cumulative performance and achieving their financial goals. Cumulative performance plays a vital role in investment analysis and decision-making. By comprehending the factors that affect cumulative performance and taking a comprehensive approach to evaluate investments, investors can make more informed decisions and enhance their overall investment performance in various market conditions.What Is Cumulative Performance?
Measuring Cumulative Performance
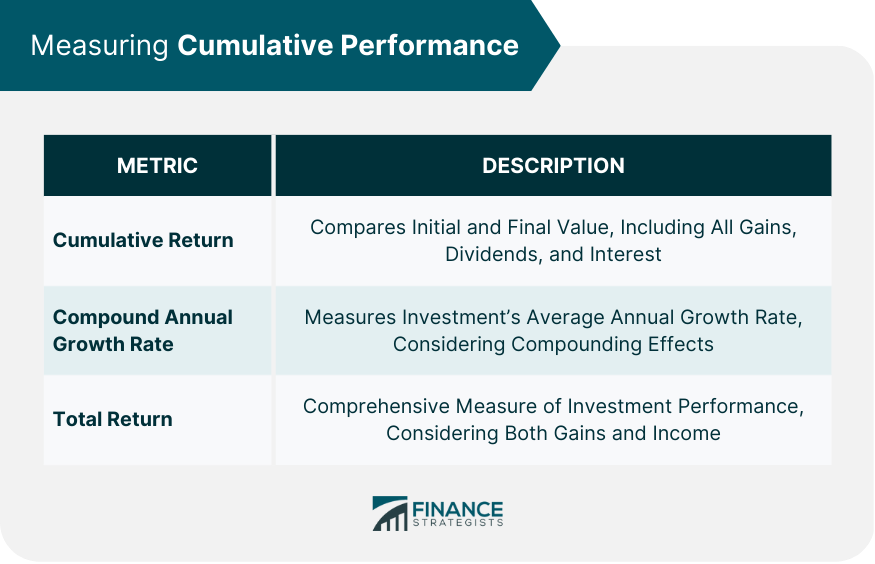
Cumulative Return Calculation
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)
Total Return, Including Dividends and Capital Gains
Cumulative Performance in Different Asset Classes
Equities
Fixed Income
Real Estate
Commodities
Comparing Cumulative Performance
Benchmarking Against Indices
Relative Performance Evaluation
Risk-Adjusted Performance Measures
Factors Influencing Cumulative Performance
Market Conditions
Asset Allocation
Investment Strategy and Management
Fees and Expenses

Using Cumulative Performance for Investment Decisions
Portfolio Analysis and Rebalancing
Performance Attribution
Identifying Investment Opportunities
Limitations of Cumulative Performance
Past Performance and Future Results
Impact of Fees and Taxes
Risk Consideration
Improving Cumulative Performance
Diversification
Active vs Passive Management
Long-Term Investment Approach
Final Thoughts
Cumulative Performance FAQs
Cumulative performance measures an investment's total return over a specific period, accounting for all gains and losses. It is important for investors because it provides a comprehensive view of an investment's growth or decline over time, allowing them to assess the success of their investment strategies and compare different investment opportunities.
Cumulative return is calculated by comparing the initial investment value with its current or final value, taking into account all capital gains, dividends, and interest payments. The resulting percentage indicates the total return of the investment over a given period.
Various factors can impact cumulative performance, including market conditions, asset allocation, investment strategy, and management, fees, and expenses. Understanding these factors is vital for making informed investment decisions and optimizing investment performance.
Investors can use cumulative performance to analyze their current portfolios, identify areas for improvement, and make more informed investment decisions. They can also use performance attribution to refine their investment strategies and uncover new investment opportunities.
Limitations of cumulative performance include past performance not guarantee future results, the impact of fees and taxes, and the importance of considering risk. Investors should also use risk-adjusted performance measures, such as the Sharpe ratio, to better understand investment performance.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











